Concepts and functions - Pécsi Tudományegyetem
... Arteries, veins, and capillaries comprise the vascular system. Arteries and veins run parallel throughout the body with a web-like network of capillaries connecting them. Arteries use vessel size, controlled by the sympathetic nervous system, to move blood by pressure; veins use one-way valves contr ...
... Arteries, veins, and capillaries comprise the vascular system. Arteries and veins run parallel throughout the body with a web-like network of capillaries connecting them. Arteries use vessel size, controlled by the sympathetic nervous system, to move blood by pressure; veins use one-way valves contr ...
Embryonic Stem Cells: from Blastocyst to in vitro Differentiation
... Embryonic stem cells are derived from the inner cell mass (ICM) of the mammalian blastocyst. The first mammalian ES cell lines were derived from mouse blastocyst in 1981 from two independent groups (Evans and Kaufman, 1981; Martin, 1981). One distinct property of ES cells is that they remain diploid ...
... Embryonic stem cells are derived from the inner cell mass (ICM) of the mammalian blastocyst. The first mammalian ES cell lines were derived from mouse blastocyst in 1981 from two independent groups (Evans and Kaufman, 1981; Martin, 1981). One distinct property of ES cells is that they remain diploid ...
chap 22 - Teacher Pages
... 22.12 CONNECTION: The human fetus exchanges gases with the mother’s blood A human fetus does not breathe with its lungs. Instead, it exchanges gases with maternal blood in the placenta. In the placenta, capillaries of maternal blood and fetal blood run next to each other. The fetus and mother d ...
... 22.12 CONNECTION: The human fetus exchanges gases with the mother’s blood A human fetus does not breathe with its lungs. Instead, it exchanges gases with maternal blood in the placenta. In the placenta, capillaries of maternal blood and fetal blood run next to each other. The fetus and mother d ...
Certain Aspects of Cell Lineage and Morphogenesis
... R E C E N T developments in the study of the biosynthetic processes Of OOgenesis in Drosophila melanogaster (Jacob & Sirlin, 1959; King & Sang, 1959; Zalokar, 1960; Sirlin & Jacob, 1960) and a more extensive knowledge of the submicroscopic structure of the developing egg (King & Devine, 1958; Waddin ...
... R E C E N T developments in the study of the biosynthetic processes Of OOgenesis in Drosophila melanogaster (Jacob & Sirlin, 1959; King & Sang, 1959; Zalokar, 1960; Sirlin & Jacob, 1960) and a more extensive knowledge of the submicroscopic structure of the developing egg (King & Devine, 1958; Waddin ...
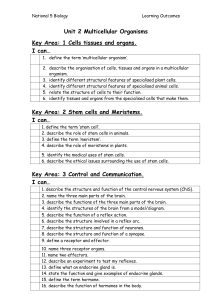
Unit 2 Key areas
... 6. describe the structure and function of xylem and phloem tissue. 7. describe the effect environmental factors have on the transpiration rate. 8. describe experiments that measure the rate of transpiration. 9. describe germination experiments. 10. define germination. 11. use microscopes to identify ...
... 6. describe the structure and function of xylem and phloem tissue. 7. describe the effect environmental factors have on the transpiration rate. 8. describe experiments that measure the rate of transpiration. 9. describe germination experiments. 10. define germination. 11. use microscopes to identify ...
Slide 1
... 22.12 CONNECTION: The human fetus exchanges gases with the mother’s blood A human fetus does not breathe with its lungs. Instead, it exchanges gases with maternal blood in the placenta. In the placenta, capillaries of maternal blood and fetal blood run next to each other. The fetus and mother d ...
... 22.12 CONNECTION: The human fetus exchanges gases with the mother’s blood A human fetus does not breathe with its lungs. Instead, it exchanges gases with maternal blood in the placenta. In the placenta, capillaries of maternal blood and fetal blood run next to each other. The fetus and mother d ...
Curriculum Map Discipline: Science Course: Anatomy & Physiology
... organic compound mean and what are four examples? What are the different types of energy? what are the four categories of chemical reactions? What is the structure and function of cells and their organelles? How do substances move through the cell membrane (passive and active)? what are general ener ...
... organic compound mean and what are four examples? What are the different types of energy? what are the four categories of chemical reactions? What is the structure and function of cells and their organelles? How do substances move through the cell membrane (passive and active)? what are general ener ...
Gas Exchange - De Anza College
... At equilibrium partial pressure of a gas in air (PO2 of 160mm Hg) = partial pressure of that gas in solution (PO2 of 160mm Hg) ...
... At equilibrium partial pressure of a gas in air (PO2 of 160mm Hg) = partial pressure of that gas in solution (PO2 of 160mm Hg) ...
The src
... What Causes Cancer? - Random mutations (mistakes at the assembly line) - Inherited mutations (pre-disposition) - Viral infections - Environmental factors (chemical; physical) Viral infection as a cause for cancer is not common in humans, but it does exist (human papillomavirus can cause carcinoma o ...
... What Causes Cancer? - Random mutations (mistakes at the assembly line) - Inherited mutations (pre-disposition) - Viral infections - Environmental factors (chemical; physical) Viral infection as a cause for cancer is not common in humans, but it does exist (human papillomavirus can cause carcinoma o ...
All-Trans Retinoic Acid Induces DU145 Cell Cycle Arrest through
... kinase members, Cdk5 needs to bind to an activator to gain kinase activity [13, 14]. One major activator for Cdk5 is p35, which was first reported in postmitotic neurons [15]. The critical role of the Cdk5-p35 complex is to support the development of the central nervous system, especially through th ...
... kinase members, Cdk5 needs to bind to an activator to gain kinase activity [13, 14]. One major activator for Cdk5 is p35, which was first reported in postmitotic neurons [15]. The critical role of the Cdk5-p35 complex is to support the development of the central nervous system, especially through th ...
Iridocorneal Endothelial Syndrome • abnormal corneal endothelium
... Glaucoma occurs in approximately 50% more severe in patients who have the progressive iris atrophy and Cogan-Reese variations, as opposed to those who have Chandler's syndrome. The degree of angle closure does not always correlate to the elevation in intraocular pressure (IOP), since some angles may ...
... Glaucoma occurs in approximately 50% more severe in patients who have the progressive iris atrophy and Cogan-Reese variations, as opposed to those who have Chandler's syndrome. The degree of angle closure does not always correlate to the elevation in intraocular pressure (IOP), since some angles may ...
Respiratory Physiology
... Respiratory system impairment causes acid-base imbalance (respiratory acidosis or respiratory alkalosis) Respiratory Acidosis and Alkalosis Result from failure of the respiratory system to balance pH pCO2 is the single most important indicator of respiratory inadequacy Blood pCO2 levels: Normal pCO2 ...
... Respiratory system impairment causes acid-base imbalance (respiratory acidosis or respiratory alkalosis) Respiratory Acidosis and Alkalosis Result from failure of the respiratory system to balance pH pCO2 is the single most important indicator of respiratory inadequacy Blood pCO2 levels: Normal pCO2 ...
Progressive divergence of definitive haematopoietic stem cells from
... have suggested the origin of HSCs from sub-endothelial patches/mesenchyme (Bertrand et al., 2005; North et al., 2002). However, the relation of these cells to the endothelial lineage has yet to be unveiled. There is also some experimental evidence suggesting the existence of the haemangioblast in th ...
... have suggested the origin of HSCs from sub-endothelial patches/mesenchyme (Bertrand et al., 2005; North et al., 2002). However, the relation of these cells to the endothelial lineage has yet to be unveiled. There is also some experimental evidence suggesting the existence of the haemangioblast in th ...
Determination of Symmetric and Asymmetric Division Planes in
... cell layers, or cell types. They are oriented in planes that would not be predicted by mother cell shape and generate daughters with distinct sizes, shapes, and/or developmental fates. For example, asymmetric cell divisions in root meristems follow a stereotyped pattern that establishes distinct cel ...
... cell layers, or cell types. They are oriented in planes that would not be predicted by mother cell shape and generate daughters with distinct sizes, shapes, and/or developmental fates. For example, asymmetric cell divisions in root meristems follow a stereotyped pattern that establishes distinct cel ...
Dissociation of Centrosome Replication Events from Cycles of DNA
... (1990) have demonstrated that centriole duplication in somatic cells is a semi-conservative process with each progeny cell receiving a parental and daughter centriole at cell division. Finally, studies have shown that unlike unfertilized eggs, in which centriole formation can occur de novo (Palazzo ...
... (1990) have demonstrated that centriole duplication in somatic cells is a semi-conservative process with each progeny cell receiving a parental and daughter centriole at cell division. Finally, studies have shown that unlike unfertilized eggs, in which centriole formation can occur de novo (Palazzo ...
BIOLOGY 206 CHAPTER 20: BLOOD VESSELS
... Medium-sized arteries which carry blood from elastic arteries to ...
... Medium-sized arteries which carry blood from elastic arteries to ...
Resident and infiltrating immune cells in the uveal tract in the
... (MHC) class II molecules on the membrane of antigen-presenting cells (APC), such as dendritic cells (DC). This peptide-MHC class II complex interacts with the T-cell receptor14 and is aided by accessory cell adhesion and co-stimulatory molecules.1516 Although it is well known that uveitis is T cell- ...
... (MHC) class II molecules on the membrane of antigen-presenting cells (APC), such as dendritic cells (DC). This peptide-MHC class II complex interacts with the T-cell receptor14 and is aided by accessory cell adhesion and co-stimulatory molecules.1516 Although it is well known that uveitis is T cell- ...
Cells ppt - Decatur ISD
... Functions in cholesterol synthesis and breakdown, fat metabolism, and detoxification of drugs Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
... Functions in cholesterol synthesis and breakdown, fat metabolism, and detoxification of drugs Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
Nerve activates contraction
... Functions in cholesterol synthesis and breakdown, fat metabolism, and detoxification of drugs Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
... Functions in cholesterol synthesis and breakdown, fat metabolism, and detoxification of drugs Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
The Role of Lipid Domains in Bacterial Cell Processes
... selection in the two systems to be brought closer together. A longitudinal concentration gradient of MinCD, a cell division inhibition complex, can be built up either by oscillation of these proteins on lipid helices or by preferential attraction to the poles along an anionic helical track. In both ...
... selection in the two systems to be brought closer together. A longitudinal concentration gradient of MinCD, a cell division inhibition complex, can be built up either by oscillation of these proteins on lipid helices or by preferential attraction to the poles along an anionic helical track. In both ...
this PDF file
... The basal rate of H excretion was monitored for 5min, then 100|xM was added to measure the contribution of protons from plasma membrane ...
... The basal rate of H excretion was monitored for 5min, then 100|xM was added to measure the contribution of protons from plasma membrane ...
The Respiratory System
... harder, and they need more oxygen. They also produce more carbon dioxide. That's why you breathe faster when you exercise! You have probably noticed that when you're exercising, your heart beats more quickly. That's so that the blood can carry oxygen to your cells faster! • Your heart and lungs work ...
... harder, and they need more oxygen. They also produce more carbon dioxide. That's why you breathe faster when you exercise! You have probably noticed that when you're exercising, your heart beats more quickly. That's so that the blood can carry oxygen to your cells faster! • Your heart and lungs work ...
PDF
... shape during which time the luminal surface of the neuroepithelial sheet is curved in the opposite direction from its eventual definitive form. From this point until approximately the 5-somite stage, the folds continue to elevate and gradually lose their convexity. Then, at the 5-somite stage, they ...
... shape during which time the luminal surface of the neuroepithelial sheet is curved in the opposite direction from its eventual definitive form. From this point until approximately the 5-somite stage, the folds continue to elevate and gradually lose their convexity. Then, at the 5-somite stage, they ...