2017 Year 8 Term3 Programme
... Cells are the basic units of living things; they have specialised structures and functions (ACSSU149) ...
... Cells are the basic units of living things; they have specialised structures and functions (ACSSU149) ...
using animal-derived growth factors in stem cell
... Vesivirus 2117 in a bioreactor producing imiglucerase at Genzyme‘s manufacturing facility ...
... Vesivirus 2117 in a bioreactor producing imiglucerase at Genzyme‘s manufacturing facility ...
What type of cells did you observe?
... and function of cell organelles? DN: What are organelles? Name at least two organelles and describe the function of ...
... and function of cell organelles? DN: What are organelles? Name at least two organelles and describe the function of ...
The non-proteic extrusive secondary metabolites in ciliated protists F
... metabolites in ciliates function for chemical offense or defense in prey-predator interactions against unicellular or/and multicellular organisms. It is worthy of note that at least some of these secondary metabolites have been demonstrated to show antibiotic, anti-cancer and pro-apoptotic propertie ...
... metabolites in ciliates function for chemical offense or defense in prey-predator interactions against unicellular or/and multicellular organisms. It is worthy of note that at least some of these secondary metabolites have been demonstrated to show antibiotic, anti-cancer and pro-apoptotic propertie ...
Vocab Review_S14_key
... 9. Compounds that contain carbon are classified as __. 10. DNA and RNA are examples of this type of compound. 11. A weak, but very important bond (can be easily broken) 12. ‘Water fearing’ 13. A type of protein that can speed up the rate of a reaction; never used up 14. This molecule is formed when ...
... 9. Compounds that contain carbon are classified as __. 10. DNA and RNA are examples of this type of compound. 11. A weak, but very important bond (can be easily broken) 12. ‘Water fearing’ 13. A type of protein that can speed up the rate of a reaction; never used up 14. This molecule is formed when ...
Cell Boundaries
... form regions of high concentration to regions of low concentration • Pure water has a higher concentration of water than a solution does • This has important consequences for a cell ...
... form regions of high concentration to regions of low concentration • Pure water has a higher concentration of water than a solution does • This has important consequences for a cell ...
Chapter 6 PPT Notes
... • Surrounded by double membrane (nuclear envelope) • Continuous with the rough ER • Nuclear pores: control what enters/leaves nucleus • Chromatin: complex of DNA + proteins; makes up ...
... • Surrounded by double membrane (nuclear envelope) • Continuous with the rough ER • Nuclear pores: control what enters/leaves nucleus • Chromatin: complex of DNA + proteins; makes up ...
Cell wall - s3.amazonaws.com
... instrument that makes small objects look larger A compound microscope contains more than one lens ...
... instrument that makes small objects look larger A compound microscope contains more than one lens ...
organelles
... to pass in and out. • Keeps the DNA inside the nucleus • Allows other materials to pass in and out of the nucleus ...
... to pass in and out. • Keeps the DNA inside the nucleus • Allows other materials to pass in and out of the nucleus ...
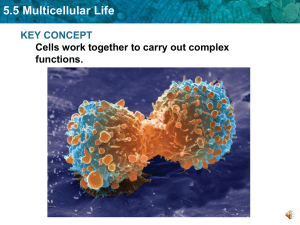
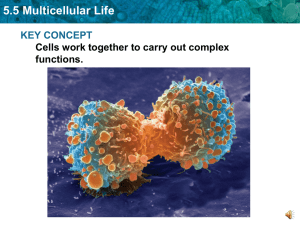
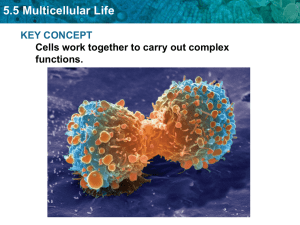
5.5 Multicellular Life KEY CONCEPT Cells work together to carry out complex functions.
... Multicellular organisms depend on interactions among different cell types. ...
... Multicellular organisms depend on interactions among different cell types. ...
Cell Organelle Notes
... Full of digestive enzymes to digest unwanted particles Help white blood cells to destroy bacteria Clean-up crew! Filled with enzymes to digest toxic substances Numerous in the liver Do not form at Golgi Body Store food, water, or waste materials In plant cells, they are very large! Found in eukaryot ...
... Full of digestive enzymes to digest unwanted particles Help white blood cells to destroy bacteria Clean-up crew! Filled with enzymes to digest toxic substances Numerous in the liver Do not form at Golgi Body Store food, water, or waste materials In plant cells, they are very large! Found in eukaryot ...
Tutorial Kit (Applied Biology and Biotechnology-100 L)
... Flatworms are acoelomate and triploblastic with organ level of organization. Digestive system is incomplete with a single opening- the mouth, anus is absent. Circulatory, respiratory and skeletal system are absent. Excretion and osmoregulation is brought about by protonephridia or flame cells. Ammon ...
... Flatworms are acoelomate and triploblastic with organ level of organization. Digestive system is incomplete with a single opening- the mouth, anus is absent. Circulatory, respiratory and skeletal system are absent. Excretion and osmoregulation is brought about by protonephridia or flame cells. Ammon ...
Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Guiding Questions: What are the
... What are some key characteristics of prokaryotic cells? ...
... What are some key characteristics of prokaryotic cells? ...
Drug absorption
... • Oral drugs must cross the cell membranes of the intestinal villi • Fat soluble molecules can pass directly through the cell membrane. • E.g. instantaneous absorption of anti-anginal drug GTN ( glyceryl trinitrate )across the buccal mucosa - lining of the cheeks and the back of the lips, inside the ...
... • Oral drugs must cross the cell membranes of the intestinal villi • Fat soluble molecules can pass directly through the cell membrane. • E.g. instantaneous absorption of anti-anginal drug GTN ( glyceryl trinitrate )across the buccal mucosa - lining of the cheeks and the back of the lips, inside the ...
Electrochemical cells
... cells are also known as rechargeable batteries and have a second recharging chemical reaction in addition to the discharging reaction ...
... cells are also known as rechargeable batteries and have a second recharging chemical reaction in addition to the discharging reaction ...
Randolph-Henry Biology Benchmark Test Six Weeks #1
... Multiple Choice: Select the best answer and mark on your answer sheet. _____1. Which of the sciences is the study of Plants? a. zoology b. botany c. mycology d. ecology _____2. Which scientist is considered to be the father of modern genetics? a. Darwin b. Pasteur c. Mendel d. Linnae _____3. In the ...
... Multiple Choice: Select the best answer and mark on your answer sheet. _____1. Which of the sciences is the study of Plants? a. zoology b. botany c. mycology d. ecology _____2. Which scientist is considered to be the father of modern genetics? a. Darwin b. Pasteur c. Mendel d. Linnae _____3. In the ...
Jenga Review Questions What organ pumps the blood? What type
... 22. Where in the body would you find smooth muscle? 23. Where in the body would you find cardiac muscle? 24. Where in the body would you find skeletal muscle? 25. What type of muscles can you control? 26. What type of muscles do you not control? 27. What is the function of the Muscular System? ...
... 22. Where in the body would you find smooth muscle? 23. Where in the body would you find cardiac muscle? 24. Where in the body would you find skeletal muscle? 25. What type of muscles can you control? 26. What type of muscles do you not control? 27. What is the function of the Muscular System? ...
Protective Antigens
... Protective Antigen 1. This term has several meanings. 2. One example is the anthrax toxin. It is composed of three parts that each play a role in destroying the cell (PA or protective is the first). The antigen is called protective because it is protected from immune destruction once inside the cell ...
... Protective Antigen 1. This term has several meanings. 2. One example is the anthrax toxin. It is composed of three parts that each play a role in destroying the cell (PA or protective is the first). The antigen is called protective because it is protected from immune destruction once inside the cell ...
Cell Organelles
... B. They breakdown lipids, carbohydrates, and proteins into small molecules that the rest of the cells uses ...
... B. They breakdown lipids, carbohydrates, and proteins into small molecules that the rest of the cells uses ...
Slide ()
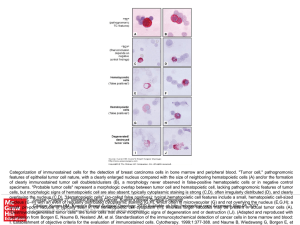
... Categorization of immunostained cells for the detection of breast carcinoma cells in bone marrow and peripheral blood. "Tumor cell," pathognomonic features of epithelial tumor cell nature, with a clearly enlarged nucleus compared with the size of neighboring hematopoietic cells (A) and/or the format ...
... Categorization of immunostained cells for the detection of breast carcinoma cells in bone marrow and peripheral blood. "Tumor cell," pathognomonic features of epithelial tumor cell nature, with a clearly enlarged nucleus compared with the size of neighboring hematopoietic cells (A) and/or the format ...
Title goes in here
... First Stem Cell Drug Prochymal • Prochymal is a preparation of mesenchymal stem cells, obtained from the bone marrow of healthy young adults • The first SC product approved by the FDA as pharmaceutical product • The target disorders of this therapeutic are GVHD and Crohn’s disease • For the repair ...
... First Stem Cell Drug Prochymal • Prochymal is a preparation of mesenchymal stem cells, obtained from the bone marrow of healthy young adults • The first SC product approved by the FDA as pharmaceutical product • The target disorders of this therapeutic are GVHD and Crohn’s disease • For the repair ...
File - Biology with Radjewski
... 1. What 1 drawing was an animal cell? 2. What 2 drawing(s) were plant cells? 3. What 3 drawing(s) were eukaryotic cells? 4. What 1 drawing was prokaryotic cells? 5. What 1 drawing was unicellular? 6. Describe the shape of the cheek cell. 7. What did you find living in yogurt? Are they prokaryotic or ...
... 1. What 1 drawing was an animal cell? 2. What 2 drawing(s) were plant cells? 3. What 3 drawing(s) were eukaryotic cells? 4. What 1 drawing was prokaryotic cells? 5. What 1 drawing was unicellular? 6. Describe the shape of the cheek cell. 7. What did you find living in yogurt? Are they prokaryotic or ...
Cell organelles you need to know for unit test
... Cell organelles= parts of the cell 1. Cytoplasm-mostly made up of water, this jelly like organelle found inside the cell that holds all the other cells in place. 2. Cell wall- Found only in plants it is a rigid structure that gives the cell its shape, it also provides support which helps plants grow ...
... Cell organelles= parts of the cell 1. Cytoplasm-mostly made up of water, this jelly like organelle found inside the cell that holds all the other cells in place. 2. Cell wall- Found only in plants it is a rigid structure that gives the cell its shape, it also provides support which helps plants grow ...