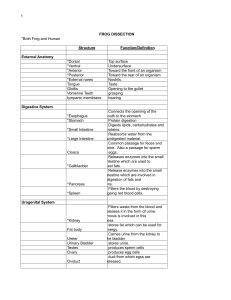
frog dissection
... Releases enzymes into the small intestine which are used to digest fats. Release enzymes into the small intestine which are involved in the digestion of fats and proteins. Filters the blood by destroying ageing red blood cells. ...
... Releases enzymes into the small intestine which are used to digest fats. Release enzymes into the small intestine which are involved in the digestion of fats and proteins. Filters the blood by destroying ageing red blood cells. ...
Quiz (multiple choice) * Chapter 3
... _______ can cause pressure-related problems such as stroke and kidney failure. ...
... _______ can cause pressure-related problems such as stroke and kidney failure. ...
cell membrane - Demarest School
... What are cells? An organism is a living thing. A cell is the smallest unit of living things that can carry out the basic processes of life. Cells come from other cells. A unicellular organism is made of a single cell. A multicellular organism is made up of more than one cell. Created by I. Cavalli ...
... What are cells? An organism is a living thing. A cell is the smallest unit of living things that can carry out the basic processes of life. Cells come from other cells. A unicellular organism is made of a single cell. A multicellular organism is made up of more than one cell. Created by I. Cavalli ...
doc
... collecting dead animals. I became much more popular when I concluded that all animals are made of cells based on my research. Theodor Schwann I unfortunately was not popular with the ladies due to my unique look, but this kept my night free to work in my lab observing cork using my new microscope wi ...
... collecting dead animals. I became much more popular when I concluded that all animals are made of cells based on my research. Theodor Schwann I unfortunately was not popular with the ladies due to my unique look, but this kept my night free to work in my lab observing cork using my new microscope wi ...
Cell Observations Lab
... 1. Peel a translucent piece of tissue from the onion. (The smaller the piece the better.) Translucent means that you can see light through the specimen, but it is not transparent. 2. Place the piece of onion on a glass slide and add a drop or two of the Lugol's solution. ( iodine is a specific stain ...
... 1. Peel a translucent piece of tissue from the onion. (The smaller the piece the better.) Translucent means that you can see light through the specimen, but it is not transparent. 2. Place the piece of onion on a glass slide and add a drop or two of the Lugol's solution. ( iodine is a specific stain ...
cells - Old Saybrook Public Schools
... • Have a nucleus where DNA is protected away from the rest of the cell ...
... • Have a nucleus where DNA is protected away from the rest of the cell ...
Scientist/Senior Scientist for Immunology
... advance a new wave of medicines that control expression of disease-driving genes. Syros has built a proprietary platform to systematically and efficiently analyze this unexploited region of DNA in human disease tissue to identify and drug novel targets linked to genomically defined patient populatio ...
... advance a new wave of medicines that control expression of disease-driving genes. Syros has built a proprietary platform to systematically and efficiently analyze this unexploited region of DNA in human disease tissue to identify and drug novel targets linked to genomically defined patient populatio ...
Guyton and Hall Textbook of Medical Physiology
... E. Vascular smooth muscle cell F. Skeletal muscle cell ...
... E. Vascular smooth muscle cell F. Skeletal muscle cell ...
name: period - Spring Branch ISD
... 7. List and briefly describe the four tissue types. 8. The lungs are and organ composed of all four tissue types. Describe the interaction of the tissues in the lungs. What is the function of the cilia on the cells that make up the epithelial lung tissue? 9. What organ systems must work together to ...
... 7. List and briefly describe the four tissue types. 8. The lungs are and organ composed of all four tissue types. Describe the interaction of the tissues in the lungs. What is the function of the cilia on the cells that make up the epithelial lung tissue? 9. What organ systems must work together to ...
Structures of Eukaryotic Cells
... used by a cell to do “work”. -12 to 1000 mitochondria per cell -plant cells have less than animal cells. Why? -less active -require less energy -Which cells in our body would have the most mitochondria? -muscle cells ~ very active ...
... used by a cell to do “work”. -12 to 1000 mitochondria per cell -plant cells have less than animal cells. Why? -less active -require less energy -Which cells in our body would have the most mitochondria? -muscle cells ~ very active ...
Basic Cell Structure
... Observe each cell type as directed below. For each type of cell perform the following and record your results in the data table. Measure the length, width, and/or diameter of each cell. Record the presence or absence of the listed organelles and structures that you observe. Draw, while on high power ...
... Observe each cell type as directed below. For each type of cell perform the following and record your results in the data table. Measure the length, width, and/or diameter of each cell. Record the presence or absence of the listed organelles and structures that you observe. Draw, while on high power ...
Unit 3 Powerpoint
... C. The typical cell – The cell membrane separates: 1. Extracellular (Interstitial) fluid – Watery medium surrounding the cell ...
... C. The typical cell – The cell membrane separates: 1. Extracellular (Interstitial) fluid – Watery medium surrounding the cell ...
organelles
... C. They build muscle and bone tissues. D. They carry the code for all of an organism's ...
... C. They build muscle and bone tissues. D. They carry the code for all of an organism's ...
Hypertonic, Hypotonic and Isotonic
... • Facilitated diffusion is the process in which molecules that cannot directly diffuse across the membrane pass through special protein channels. o Examples: glucose and water ...
... • Facilitated diffusion is the process in which molecules that cannot directly diffuse across the membrane pass through special protein channels. o Examples: glucose and water ...
cell - Demarest School District
... What are cells? An organism is a living thing. A cell is the smallest unit of living things that can carry out the basic processes of life. Cells come from other cells. A unicellular organism is made of a single cell. A multicellular organism is made up of more than one cell. Created by I. Cavalli ...
... What are cells? An organism is a living thing. A cell is the smallest unit of living things that can carry out the basic processes of life. Cells come from other cells. A unicellular organism is made of a single cell. A multicellular organism is made up of more than one cell. Created by I. Cavalli ...
Active Transport
... • Energy (by way of ATP) forces materials through a protein in the membrane against concentration gradient. ...
... • Energy (by way of ATP) forces materials through a protein in the membrane against concentration gradient. ...
White Blood Cells
... neutrophils, although other cell types may also be increased. This increase in leukocytes can be caused by a normal physiologic response or a disease condition. ...
... neutrophils, although other cell types may also be increased. This increase in leukocytes can be caused by a normal physiologic response or a disease condition. ...
Human (mammalian) Body Systems
... Remember that all of your body systems are integrated and regulated by the neuroendocrine system (the coordination of the nervous and endocrine (hormones) systems. As time is limited, focus on the figures indicated. Digestive System ...
... Remember that all of your body systems are integrated and regulated by the neuroendocrine system (the coordination of the nervous and endocrine (hormones) systems. As time is limited, focus on the figures indicated. Digestive System ...
Cell Structures
... Provides support for the cell, has two “subparts” Name for the collection of DNA in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells Consist of hollow tubes which provide support for the cell Small hair-like structures used for movement or sensing things Composed of a phospholipid bilayer Longer whip-like structures ...
... Provides support for the cell, has two “subparts” Name for the collection of DNA in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells Consist of hollow tubes which provide support for the cell Small hair-like structures used for movement or sensing things Composed of a phospholipid bilayer Longer whip-like structures ...
FOSS Science
... digestion – process of breaking down food into nutrients that can be used by cells mouth and teeth – where food is taken in and what is used to moisten (by saliva), chew and bite, and cut it; first step in the digestion process esophagus – tube connecting the mouth and the stomach stomach – organ wh ...
... digestion – process of breaking down food into nutrients that can be used by cells mouth and teeth – where food is taken in and what is used to moisten (by saliva), chew and bite, and cut it; first step in the digestion process esophagus – tube connecting the mouth and the stomach stomach – organ wh ...
Cells and Organisms Study Guide 5.5
... Animal- many celled; mobile; feeds on other organisms; reproduces by eggs or live birth Cell- the smallest unit within a living thing in which life functions occur Cell membrane- the thin, bag-like structure that allows certain materials to pass in and out of cells (it surrounds animal cells, and is ...
... Animal- many celled; mobile; feeds on other organisms; reproduces by eggs or live birth Cell- the smallest unit within a living thing in which life functions occur Cell membrane- the thin, bag-like structure that allows certain materials to pass in and out of cells (it surrounds animal cells, and is ...
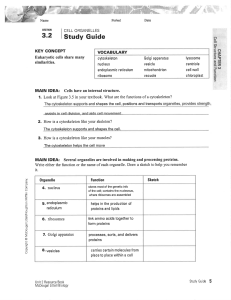
3.2 Study Guide KEY
... All cells are surrounded by a cell membrane that is flex¡ble and ¡nteracts w¡th the env¡ronmênt only certa¡n cells have a cell wâll wh¡ch ìs rigid and provides shape and support toEells ...
... All cells are surrounded by a cell membrane that is flex¡ble and ¡nteracts w¡th the env¡ronmênt only certa¡n cells have a cell wâll wh¡ch ìs rigid and provides shape and support toEells ...
Dying for a living: plants do it too
... comparison to animal systems are dealt with by all of the reviewers. While caspases, so crucial to animal cell death, have not been definitively identified in plants, other proteases and the ubiquitin system may play important roles, as pointed out by Beers (1997) and Fukuda (1997). Morel and Dangl ...
... comparison to animal systems are dealt with by all of the reviewers. While caspases, so crucial to animal cell death, have not been definitively identified in plants, other proteases and the ubiquitin system may play important roles, as pointed out by Beers (1997) and Fukuda (1997). Morel and Dangl ...