Video Guide
... 14. In general, what is the role of proteins in the phospholipid bi-layer? 15. The movement of molecules from an area of __________ concentration to an area of _______ concentration is called _________________. 16. When the cell takes no energy to move molecules into or out of a cell without energy ...
... 14. In general, what is the role of proteins in the phospholipid bi-layer? 15. The movement of molecules from an area of __________ concentration to an area of _______ concentration is called _________________. 16. When the cell takes no energy to move molecules into or out of a cell without energy ...
Cell Organelle Web Quest
... Hover over all of the different organelles of the plant and animal cell to find out their names and functions. Put a check for each structure that you find in a plant or animal cell. Leave it blank if it is absent. One is done for you because it is missing from the diagram. ...
... Hover over all of the different organelles of the plant and animal cell to find out their names and functions. Put a check for each structure that you find in a plant or animal cell. Leave it blank if it is absent. One is done for you because it is missing from the diagram. ...
Tight Junctions, Desmosomes, and Gap Junctions in Animal Cells
... • also called anchoring junctions • fasten cells together into strong Sheets • Intermediate filaments made of sturdy keratin proteins anchor desmosomes in the cytoplasm. • Desmosomes attach muscle cells to each other in a muscle. • Some “muscle tears” involve the rupture of desmosomes. ...
... • also called anchoring junctions • fasten cells together into strong Sheets • Intermediate filaments made of sturdy keratin proteins anchor desmosomes in the cytoplasm. • Desmosomes attach muscle cells to each other in a muscle. • Some “muscle tears” involve the rupture of desmosomes. ...
Year 7 Plant and animal cells
... Interesting cell facts: The length of time cells live can vary. For example, white blood cells only live for thirteen days, red blood cells live for about one hundred and twenty days, liver cells live about eighteen months, and nerve cells can live up to one hundred years! ...
... Interesting cell facts: The length of time cells live can vary. For example, white blood cells only live for thirteen days, red blood cells live for about one hundred and twenty days, liver cells live about eighteen months, and nerve cells can live up to one hundred years! ...
Cell Membrane Reading Guide
... 2. Now scale down the size of your phospholipids and draw a section of the cell membrane in the space below. Use brackets to identify the hydrophobic and hydrophilic portions of the membrane. ...
... 2. Now scale down the size of your phospholipids and draw a section of the cell membrane in the space below. Use brackets to identify the hydrophobic and hydrophilic portions of the membrane. ...
Course Specifications
... 1 Students should be able to describe the characteristics of living cells, of the activities 1 of cells and of the differentiation possibilities of cells. 2 They should understand protein synthesis, apoptosis, cell division stages and cell1 cell interactions. ...
... 1 Students should be able to describe the characteristics of living cells, of the activities 1 of cells and of the differentiation possibilities of cells. 2 They should understand protein synthesis, apoptosis, cell division stages and cell1 cell interactions. ...
spontaneous generation hypothesis abiogenesis control biogenesis
... Find two young animals of the same kind whose weight is approximately the same. Feed each animal a different food, and weigh the animals at intervals. 31. The other key variables may be responsible for the observed outcome of the experiment. p. 197 1. All living things are composed of cells. Cells a ...
... Find two young animals of the same kind whose weight is approximately the same. Feed each animal a different food, and weigh the animals at intervals. 31. The other key variables may be responsible for the observed outcome of the experiment. p. 197 1. All living things are composed of cells. Cells a ...
Body in Action
... A person who is in training will notice that the factors above will return to normal resting values quicker than a person who is not in training. It can therefore be used as an indicator of fitness. ...
... A person who is in training will notice that the factors above will return to normal resting values quicker than a person who is not in training. It can therefore be used as an indicator of fitness. ...
Cell structure The basic structure of a cell The cell is the basic unit of
... up a house. They work together to keep an organism alive. There are many different types of cells. Our body alone is made up of more than 200 types of cells. The shape and size of cells vary, but some features are common to all. What is the structure of animal cells? Animal cells share the same basi ...
... up a house. They work together to keep an organism alive. There are many different types of cells. Our body alone is made up of more than 200 types of cells. The shape and size of cells vary, but some features are common to all. What is the structure of animal cells? Animal cells share the same basi ...
Multiple Choice – Chapter 1
... b. is needed so that the test will be repeated enough times. c. is the control group. d. is a backup in case some of the people getting the drug drop out of the test. e. is the experimental group. 11. _________ has characteristics that result from the organization of its component _________. a. A po ...
... b. is needed so that the test will be repeated enough times. c. is the control group. d. is a backup in case some of the people getting the drug drop out of the test. e. is the experimental group. 11. _________ has characteristics that result from the organization of its component _________. a. A po ...
File
... a rigid structure that gives support to a cell a barrier that encloses and protects the cell a web of proteins in the cytoplasm that keeps a cell’s membrane from collapsing a large organelle that produces and stores the cell’s DNA organelles that make proteins a system of folded membranes that funct ...
... a rigid structure that gives support to a cell a barrier that encloses and protects the cell a web of proteins in the cytoplasm that keeps a cell’s membrane from collapsing a large organelle that produces and stores the cell’s DNA organelles that make proteins a system of folded membranes that funct ...
Cell Cycle Analysis Questions
... 1. What 2 things does cell division (mitosis) do for multicellular organisms? 2. What is the cell cycle? How many stages are there? Name the stages. 3. What is interphase? Roughly how much of the cell’s life cycle will be spent in interphase? 4. During what part of interphase is DNA replicated (or s ...
... 1. What 2 things does cell division (mitosis) do for multicellular organisms? 2. What is the cell cycle? How many stages are there? Name the stages. 3. What is interphase? Roughly how much of the cell’s life cycle will be spent in interphase? 4. During what part of interphase is DNA replicated (or s ...
Will stem cells be a key resource for research in IBD in the future in
... Will stem cells graduate and move down the hall to the ‘big’ room? 1) Cellular therapy – addition of stem cells or their progeny 2) Use of cells for patient stratification – epithelial stem cells from patients ...
... Will stem cells graduate and move down the hall to the ‘big’ room? 1) Cellular therapy – addition of stem cells or their progeny 2) Use of cells for patient stratification – epithelial stem cells from patients ...
Chapter 7 Cells
... Cell theory states: 1. All living things are made of cells. 2. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things. 3. New cells are produced from existing cells. Microscopes: 1. Light microscope – magnifies up to 1,500 X using light. 2. Electron microscope – magnifies up to about 1 ...
... Cell theory states: 1. All living things are made of cells. 2. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things. 3. New cells are produced from existing cells. Microscopes: 1. Light microscope – magnifies up to 1,500 X using light. 2. Electron microscope – magnifies up to about 1 ...
Organelles in cellular transport
... The ribosomes on the rough endoplasmic reticulum synthesize which enter the channels of the endoplasmic reticulum packaging and shipping to the Golgi bodies. They are enveloped into pockets. These pockets, vesicles, leave the ER to transport the proteins to other parts of the cell for use. ER Video ...
... The ribosomes on the rough endoplasmic reticulum synthesize which enter the channels of the endoplasmic reticulum packaging and shipping to the Golgi bodies. They are enveloped into pockets. These pockets, vesicles, leave the ER to transport the proteins to other parts of the cell for use. ER Video ...
Section 3.5 Introduction
... Cells use active transport to obtain materials they need that they could not get by means of diffusion or facilitated diffusion. Active transport is the movement of a substance against its concentration gradient by the use of transport proteins embedded in the cell membrane and chemical energy. The ...
... Cells use active transport to obtain materials they need that they could not get by means of diffusion or facilitated diffusion. Active transport is the movement of a substance against its concentration gradient by the use of transport proteins embedded in the cell membrane and chemical energy. The ...
lecture notes-microbiology-3-Eucaryotes
... eukaryote cell, where respiration takes place. It reduces oxygen and store energy in ATP (Adenosine triphosphate). Shape: Mitochondria have cylindrical shape with 1 µm in diameter and 2-3 µm in length. ...
... eukaryote cell, where respiration takes place. It reduces oxygen and store energy in ATP (Adenosine triphosphate). Shape: Mitochondria have cylindrical shape with 1 µm in diameter and 2-3 µm in length. ...
SBI3U - misshoughton.net
... Thinner walls due to thinner layer of muscle walls stretch more easily blood under low pressure Contains valves maintain flow towards the heart (prevents back flow) ...
... Thinner walls due to thinner layer of muscle walls stretch more easily blood under low pressure Contains valves maintain flow towards the heart (prevents back flow) ...
Different Stem Cell Types used in Treating Orthopedic
... Stem Cell Risk All things being equal, the risk of a stem cell therapy increases as the source changes. The safest cells are your own. Stem cells from others can carry the good and bad of their genetic material. Embryonic cells can ...
... Stem Cell Risk All things being equal, the risk of a stem cell therapy increases as the source changes. The safest cells are your own. Stem cells from others can carry the good and bad of their genetic material. Embryonic cells can ...
Bingo
... Changes cell shape, especially during muscle contraction Allows movement of cytoplasm within the cell (cytoplasmic streaming) ...
... Changes cell shape, especially during muscle contraction Allows movement of cytoplasm within the cell (cytoplasmic streaming) ...
1.2.2 MITOSIS
... Final stage where the cytoplasm divides completely in to two, the nuclear envelopes reform, and the nuclei begin to reform resulting in two new cells. ...
... Final stage where the cytoplasm divides completely in to two, the nuclear envelopes reform, and the nuclei begin to reform resulting in two new cells. ...
Cell Growth and Division
... – Prophase (pro- means first) – Metaphase (meta- means middle/after) – Anaphase (ana- means apart) – Telophase (telo- means far away/end) ...
... – Prophase (pro- means first) – Metaphase (meta- means middle/after) – Anaphase (ana- means apart) – Telophase (telo- means far away/end) ...
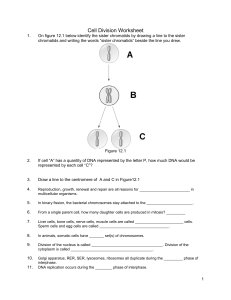
Cell Division Worksheet PDF
... If cell “A” has a quantity of DNA represented by the letter P, how much DNA would be represented by each cell “C”? ...
... If cell “A” has a quantity of DNA represented by the letter P, how much DNA would be represented by each cell “C”? ...
ch1 FA11 - Cal State LA
... Stem cells for use in cell replacement therapy • Induced pluripotent (iPS) cells has been demonstrated in culture. – Involves reprogramming a fully differentiated cell into a pluripotent stem cell. – These cells have been used to correct certain disease conditions in experimental animals. – Studies ...
... Stem cells for use in cell replacement therapy • Induced pluripotent (iPS) cells has been demonstrated in culture. – Involves reprogramming a fully differentiated cell into a pluripotent stem cell. – These cells have been used to correct certain disease conditions in experimental animals. – Studies ...
APPLIED BIOLOGY MID-TERM STUDY GUIDE
... HISTORY OF CELL Cell theory Scientists that contributed to the cell theory Prokaryotic cell Eukaryotic cell Cell membrane composition (bilayer of phospholipids) Function of cell membrane Types of microscope (electron and compound) Surface area to volume ratio Three parts of cytoske ...
... HISTORY OF CELL Cell theory Scientists that contributed to the cell theory Prokaryotic cell Eukaryotic cell Cell membrane composition (bilayer of phospholipids) Function of cell membrane Types of microscope (electron and compound) Surface area to volume ratio Three parts of cytoske ...