Unit 2 Objectives: Cells and the Cell Membrane By the conclusion of
... increasing surface area where reactions can occur. b. Membranes and membrane-bound organelles in eukaryotic cells localize (compartmentalize) intracellular metabolic processes and specific enzymatic reactions. To foster student understanding of this concept, instructors can choose an illustrative ex ...
... increasing surface area where reactions can occur. b. Membranes and membrane-bound organelles in eukaryotic cells localize (compartmentalize) intracellular metabolic processes and specific enzymatic reactions. To foster student understanding of this concept, instructors can choose an illustrative ex ...
CELL
... A. The first to describe living single cells; results were checked and confirmed by Hooke B. Saw “animalcules” in pond water using the scopes that he made III. 1830s - full & widespread importance of cells realized A. Matthias Schleiden,realized that, despite differences in tissue structures, all pl ...
... A. The first to describe living single cells; results were checked and confirmed by Hooke B. Saw “animalcules” in pond water using the scopes that he made III. 1830s - full & widespread importance of cells realized A. Matthias Schleiden,realized that, despite differences in tissue structures, all pl ...
Cell Structures - Central Magnet School
... Nuclear envelope • Double membrane layer surrounding the cell • Has pores which allows material into and out of the cell ...
... Nuclear envelope • Double membrane layer surrounding the cell • Has pores which allows material into and out of the cell ...
Introduction:
... The students will need to create an essay based on the information that they have found and the project that they have created. It will need to include an introductory statement or paragraph, the body paragraph(s) which will include any information about their specific cell type along with all of th ...
... The students will need to create an essay based on the information that they have found and the project that they have created. It will need to include an introductory statement or paragraph, the body paragraph(s) which will include any information about their specific cell type along with all of th ...
What is a Cell? All living things are made up of cells. Each of us has
... Are all cells the same? No, they're not. Plant cells are different than animal cells. Plant cells in a root are different to those in the stem or in the leaf. Animal cells, including the cells in our bodies are all sorts of different shapes and sizes. Cells are the units which all organisms are made ...
... Are all cells the same? No, they're not. Plant cells are different than animal cells. Plant cells in a root are different to those in the stem or in the leaf. Animal cells, including the cells in our bodies are all sorts of different shapes and sizes. Cells are the units which all organisms are made ...
Stanford Notes Modeled for section 7.1, pages 193 and 194
... flexible barrier that surrounds all cells and controls movement of materials in and out of the cell. Nucleus—a part of eukaryotic cells which is a compartment (separated area) that is enclosed in a membrane & contains genetic material called DNA Micrometer—1 millionth of a meter; the unit of measure ...
... flexible barrier that surrounds all cells and controls movement of materials in and out of the cell. Nucleus—a part of eukaryotic cells which is a compartment (separated area) that is enclosed in a membrane & contains genetic material called DNA Micrometer—1 millionth of a meter; the unit of measure ...
Document
... •In the development of most multicellular organisms, a single cell (fertilized egg) gives rise to many different types of cells, each with a different structure and corresponding function. •As cell division proceeds, the cells not only increase in number but also undergo differentiation becoming spe ...
... •In the development of most multicellular organisms, a single cell (fertilized egg) gives rise to many different types of cells, each with a different structure and corresponding function. •As cell division proceeds, the cells not only increase in number but also undergo differentiation becoming spe ...
Immune cells
... Contains histamine for increased capillary permeability to WBC’s, and heparin for anticoagulant properties. ...
... Contains histamine for increased capillary permeability to WBC’s, and heparin for anticoagulant properties. ...
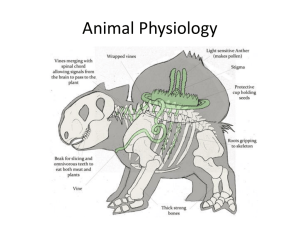
Animal Physiology Powerpoint
... think is most closely related of these three organisms? – Seagull – Fruit Bat – Common Rat ...
... think is most closely related of these three organisms? – Seagull – Fruit Bat – Common Rat ...
Chapter 5 Review Answers (1)
... 1. What is the basic unit of all life? The basic unit of all life is the cell. 2. How does a plant cell differ from an animal cell? (Identify 3 differences) Plant cells differ from animal cells because they have chloroplasts, cell walls, large vacuoles, and lack centrioles. 3. What is the purpose of ...
... 1. What is the basic unit of all life? The basic unit of all life is the cell. 2. How does a plant cell differ from an animal cell? (Identify 3 differences) Plant cells differ from animal cells because they have chloroplasts, cell walls, large vacuoles, and lack centrioles. 3. What is the purpose of ...
cell walls containing peptidoglycan
... Protista This prickly character was discovered to be composed of many spike-shaped, eukaryotic cells stuck together in the middle. Surprisingly, its cells were surrounded by cell walls that were not made of chitin. It was also seen ingesting (eating) small bits of food from the ...
... Protista This prickly character was discovered to be composed of many spike-shaped, eukaryotic cells stuck together in the middle. Surprisingly, its cells were surrounded by cell walls that were not made of chitin. It was also seen ingesting (eating) small bits of food from the ...
Name Date Period
... o Determines the cell’s function o Determines what activities the cell can perform Molecules in a cell do different activities o Cells produce certain molecules when they need to do different activities o If a cell can’t produce certain molecules then it will not be able to perform the activities ...
... o Determines the cell’s function o Determines what activities the cell can perform Molecules in a cell do different activities o Cells produce certain molecules when they need to do different activities o If a cell can’t produce certain molecules then it will not be able to perform the activities ...
Biology Glossary
... a diagram representing a system of connections or interrelations among two or more things by a number of distinctive dots, lines, bars, etc. a transitional biome that is found between a desert and a forest destruction or fragmentation of an area that supports living organisms sex cells with 1/2 as m ...
... a diagram representing a system of connections or interrelations among two or more things by a number of distinctive dots, lines, bars, etc. a transitional biome that is found between a desert and a forest destruction or fragmentation of an area that supports living organisms sex cells with 1/2 as m ...
Cell Cycle PPT
... • cancer cells do not stop dividing when growth factors are depleted either because they manufacture their own, have an abnormality in the signaling pathway, or have a problem in the cell cycle control ...
... • cancer cells do not stop dividing when growth factors are depleted either because they manufacture their own, have an abnormality in the signaling pathway, or have a problem in the cell cycle control ...
Part 6
... wall: • Primary cell wall - laid down first • Secondary cell wall - deposited between plasma membrane and primary wall, more rigid for support • Parenchyma cells - most abundant cell, for food storage, photosynthesis. Only primary cell walls. • Collenchyma cells - provide support in growing parts of ...
... wall: • Primary cell wall - laid down first • Secondary cell wall - deposited between plasma membrane and primary wall, more rigid for support • Parenchyma cells - most abundant cell, for food storage, photosynthesis. Only primary cell walls. • Collenchyma cells - provide support in growing parts of ...
OB41 - OB42
... If living organisms are composed of cells, what do they need in order to grow bigger? … ...
... If living organisms are composed of cells, what do they need in order to grow bigger? … ...
Quiz – Mitosis
... In all cases, the cells are dragon in origin. Dragons have a diploid number of 16. Diploid is 2n, or the total number of chromosomes in both sets of chromosomes. _______ 15) How many chromosomes are in a female dragon’s muscle cell that is in metaphase of mitosis? What kind of chromosomes? (SAC or D ...
... In all cases, the cells are dragon in origin. Dragons have a diploid number of 16. Diploid is 2n, or the total number of chromosomes in both sets of chromosomes. _______ 15) How many chromosomes are in a female dragon’s muscle cell that is in metaphase of mitosis? What kind of chromosomes? (SAC or D ...
CellUnitReview2014KEY2
... 7. Why is photosynthesis important to all living things on earth? ALL LIVING THINGS MUST BREATHE OXYGEN AND ALL CONSUMERS MUST EAT PLANTS OR SOMETHING THAT ATE PLANTS 8. What is an organelle found in plant cells that captures energy from sunlight? CHLOROPLAST 9. What are the raw materials needed for ...
... 7. Why is photosynthesis important to all living things on earth? ALL LIVING THINGS MUST BREATHE OXYGEN AND ALL CONSUMERS MUST EAT PLANTS OR SOMETHING THAT ATE PLANTS 8. What is an organelle found in plant cells that captures energy from sunlight? CHLOROPLAST 9. What are the raw materials needed for ...
Cell Boundaries
... cell surrounds and takes in material from environment. Material does not pass through the membrane; instead, it is engulfed and closed by a portion of membrane and cytoplasm. ...
... cell surrounds and takes in material from environment. Material does not pass through the membrane; instead, it is engulfed and closed by a portion of membrane and cytoplasm. ...
Chap 23 –Nutrition, Part III
... What is ATP? • An organic molecule known as • _______________ that releases and stores chemical energy for use in body cells • You will die without its production Check out “Metabolic Poisons” page 849 in the section called, “Homeostatic Imbalance”. ...
... What is ATP? • An organic molecule known as • _______________ that releases and stores chemical energy for use in body cells • You will die without its production Check out “Metabolic Poisons” page 849 in the section called, “Homeostatic Imbalance”. ...
Quiz Review
... Organ: two or more tissues working together. Remember: The body is organized into cells, tissues, organs, and organ systems. ...
... Organ: two or more tissues working together. Remember: The body is organized into cells, tissues, organs, and organ systems. ...
Classification Domains Review questions
... 5. The domains Archae and Bacteria are all unicellular. What does this mean? a. They are made up of more than one cell b. They are complex cells c. They are single celled organisms ...
... 5. The domains Archae and Bacteria are all unicellular. What does this mean? a. They are made up of more than one cell b. They are complex cells c. They are single celled organisms ...