File - Mr. Coach Risinger 7Y Science
... The cell’s main job is to organize the functions of the living organism. Many cells working together for a common function form tissue. There are many different kinds of tissue. Muscle tissue helps with movement. Cardiac tissue controls the heart. Nerve tissue carries messages from the brain to loca ...
... The cell’s main job is to organize the functions of the living organism. Many cells working together for a common function form tissue. There are many different kinds of tissue. Muscle tissue helps with movement. Cardiac tissue controls the heart. Nerve tissue carries messages from the brain to loca ...
File
... contains DNA -Genetic Info surrounded by a nuclear membrane that has pores visible under the compound light microscope ...
... contains DNA -Genetic Info surrounded by a nuclear membrane that has pores visible under the compound light microscope ...
TCAP review(#2)
... 14. During respiration, what two gases are exchanged in the cells? A. carbon dioxide and nitrogen B. carbon dioxide and oxygen C. oxygen and nitrogen D. oxygen and hydrogen ...
... 14. During respiration, what two gases are exchanged in the cells? A. carbon dioxide and nitrogen B. carbon dioxide and oxygen C. oxygen and nitrogen D. oxygen and hydrogen ...
Cell Structures Study Sheet
... Which organelle is responsible for storing the instructions to build an organism? Which organelle is responsible for making food? Which organelle is responsible for providing energy for chemical reactions? Which organelle is responsible for providing shape & support to plant cells? Which organelle i ...
... Which organelle is responsible for storing the instructions to build an organism? Which organelle is responsible for making food? Which organelle is responsible for providing energy for chemical reactions? Which organelle is responsible for providing shape & support to plant cells? Which organelle i ...
Outline --- Programmed Cell Death 1. Apoptosis An overview: the
... Pros and cons of each method Cell death and cancer biology Oncogene-induced apoptosis Oncogene addiction Targeting apoptosis directly 2. Non-apoptotic, programmed cell death Conceptually what is the qualification for a programmed but non-apoptotic cell death? Pathways for programmed necrosis, ...
... Pros and cons of each method Cell death and cancer biology Oncogene-induced apoptosis Oncogene addiction Targeting apoptosis directly 2. Non-apoptotic, programmed cell death Conceptually what is the qualification for a programmed but non-apoptotic cell death? Pathways for programmed necrosis, ...
Biography - Comtecmed
... The bone marrow is the natural niche of normal and malignant plasma cells. Mainly through tight cellular contacts and secretion of cytokines The Bone marrow niche appear essential for the survival, proliferation, and differentiation of malignant Multiple Myeloma (MM) cells. Via interactions through ...
... The bone marrow is the natural niche of normal and malignant plasma cells. Mainly through tight cellular contacts and secretion of cytokines The Bone marrow niche appear essential for the survival, proliferation, and differentiation of malignant Multiple Myeloma (MM) cells. Via interactions through ...
Why dread a bump on the head? October 2014 Lesson 5: What
... breaks down the DNA by cutting it at very specified places. This results in very regular DNA fragments that are 180 or multiples of 180 (i.e. 360, 540 etc.) base pairs long each. 3. The nucleus then breaks into several discrete bodies called chromatin bodies each containing condensed, systematically ...
... breaks down the DNA by cutting it at very specified places. This results in very regular DNA fragments that are 180 or multiples of 180 (i.e. 360, 540 etc.) base pairs long each. 3. The nucleus then breaks into several discrete bodies called chromatin bodies each containing condensed, systematically ...
The Cell Organelles! A Brief Summary
... RIBOSOMES: Ribosomes are small organelles. The are made of rRNA and protein. The are NOT covered by membrane. They have two main subunits, which are made in the nucleolus and then sent out to the cytoplasm. The function of ribosomes is that they are the SITE OF PROTEIN SYNTHESIS. • GOLGI APPARATUS ( ...
... RIBOSOMES: Ribosomes are small organelles. The are made of rRNA and protein. The are NOT covered by membrane. They have two main subunits, which are made in the nucleolus and then sent out to the cytoplasm. The function of ribosomes is that they are the SITE OF PROTEIN SYNTHESIS. • GOLGI APPARATUS ( ...
Supplementary Figure Legends (doc 29K)
... (A) Immunoblotting was performed to ensure that the level of YB-1 protein in HTRY cells, following a 96-hour induction, was similar to that measured across a panel of established breast cancer cell lines (SUM149, MDA-MB-231, and LCC6). HTRZ cells did not express YB-1. (B) Telomerase activity assay d ...
... (A) Immunoblotting was performed to ensure that the level of YB-1 protein in HTRY cells, following a 96-hour induction, was similar to that measured across a panel of established breast cancer cell lines (SUM149, MDA-MB-231, and LCC6). HTRZ cells did not express YB-1. (B) Telomerase activity assay d ...
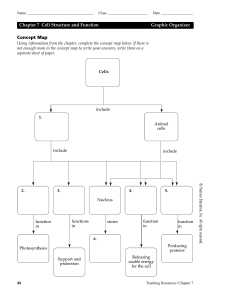
Concept Map Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function Graphic
... 8. Using Analogies The specialized cells in a multicellular organism have unique roles to play. Create an analogy that describes a situation in which specific organisms or objects have unique roles in a system. ...
... 8. Using Analogies The specialized cells in a multicellular organism have unique roles to play. Create an analogy that describes a situation in which specific organisms or objects have unique roles in a system. ...
lezione 3 bioluminescenza e proteine fluorescenti
... (A–D) Observing mitosis in dual-‐labeled normal pig kidney (LLC-‐PK1 cell line) epithelial cells stably expressing mCherry-‐ H2B (histones) and mEmerald-‐α-‐tubulin. (A) A cell in prophase is captured adjacent to cells in interphase, t = 0. (B) The cell forms a spindle and enters metaphase, t ...
... (A–D) Observing mitosis in dual-‐labeled normal pig kidney (LLC-‐PK1 cell line) epithelial cells stably expressing mCherry-‐ H2B (histones) and mEmerald-‐α-‐tubulin. (A) A cell in prophase is captured adjacent to cells in interphase, t = 0. (B) The cell forms a spindle and enters metaphase, t ...
Cells Study Guide
... Make protein? (Yes/No) Have DNA? (Yes/No) Have cell membrane? (Yes/No) DNA contained in nucleus? (Yes/No) Have membrane-bound organelles? (Yes/No) Multicellular or unicellular? ...
... Make protein? (Yes/No) Have DNA? (Yes/No) Have cell membrane? (Yes/No) DNA contained in nucleus? (Yes/No) Have membrane-bound organelles? (Yes/No) Multicellular or unicellular? ...
Since cells are the building blocks of life, understanding the different
... Rough ER (RER); H^s numerous ribosomes ^tt^ched/embedded in membr^ne so it ^ppe^rs “rough”. The ribosomes on the RER produce proteins th^t ^re collected by the ER ^nd tr^nsported throughout cell. ...
... Rough ER (RER); H^s numerous ribosomes ^tt^ched/embedded in membr^ne so it ^ppe^rs “rough”. The ribosomes on the RER produce proteins th^t ^re collected by the ER ^nd tr^nsported throughout cell. ...
AnsKey.Quiz_1
... Base, your answers to questions 17 through 20 on the diagram below and your knowledge of biology. The diagram represents details of a cross-section of a corn stem as seen through the high power objective of your microscope. ...
... Base, your answers to questions 17 through 20 on the diagram below and your knowledge of biology. The diagram represents details of a cross-section of a corn stem as seen through the high power objective of your microscope. ...
Structures outside the cell wall
... *Cytoskeleton - The cytoskeleton of the eukaryotic cell is the network of microfilaments and microtubules that give the cell its shape, the capacity to arrange its organelles, and its ability to move. Some animal cells also contain intermediate filaments as elements of the cytoskeleton. *Centrosome ...
... *Cytoskeleton - The cytoskeleton of the eukaryotic cell is the network of microfilaments and microtubules that give the cell its shape, the capacity to arrange its organelles, and its ability to move. Some animal cells also contain intermediate filaments as elements of the cytoskeleton. *Centrosome ...
Unit 2: Cell theory
... Matthias Jakob Schleiden, a German botanist, proposes that all plant tissues are composed of cells, and that cells are the basic building blocks of all plants. This statement was the first generalized statement about cells. ...
... Matthias Jakob Schleiden, a German botanist, proposes that all plant tissues are composed of cells, and that cells are the basic building blocks of all plants. This statement was the first generalized statement about cells. ...
認識微生物
... However, after four to six generations defects began to appear in the telomerase-null mice as their very long telomeres (40-60 ...
... However, after four to six generations defects began to appear in the telomerase-null mice as their very long telomeres (40-60 ...
Print Preview - C:\WINDOWS\TEMP\e3temp_5676\.aptcache
... Eukaryotic cells share many similarities. ...
... Eukaryotic cells share many similarities. ...
USMLE STEP I Review Week 1: Cell Bio & Histology
... Checkpoints control transitions between cell phases. Regulated by cyclins, cdks, and tumor suppressors. ...
... Checkpoints control transitions between cell phases. Regulated by cyclins, cdks, and tumor suppressors. ...
Structural Organization of Plants
... tissues in a plant consist of small, densely packed cells that can keep dividing to form new cells. Permanent tissues do not have the ability to divide. These cells are already differentiated in different tissue types and is now specialized to perform specific functions. ...
... tissues in a plant consist of small, densely packed cells that can keep dividing to form new cells. Permanent tissues do not have the ability to divide. These cells are already differentiated in different tissue types and is now specialized to perform specific functions. ...