Cells Structure and Function
... Inner and outer compartments formed by the membranes are important in energy transformation. Mitochondria resemble bacteria in size and ...
... Inner and outer compartments formed by the membranes are important in energy transformation. Mitochondria resemble bacteria in size and ...
chapter 3 powerpoint
... • movement of water through a selectively permeable membrane from regions of higher concentration to regions of lower concentration • water moves toward a higher concentration of ...
... • movement of water through a selectively permeable membrane from regions of higher concentration to regions of lower concentration • water moves toward a higher concentration of ...
7th Grade Review for Benchmark
... Know the basic function of the following body systems: circulatory, respiratory, integumentary, nervous, endocrine, excretory, digestive, skeletal and muscular systems. Review the MAIN organs of each system listed above. ****See my teacher web page for a concept map of these systems**** All body sys ...
... Know the basic function of the following body systems: circulatory, respiratory, integumentary, nervous, endocrine, excretory, digestive, skeletal and muscular systems. Review the MAIN organs of each system listed above. ****See my teacher web page for a concept map of these systems**** All body sys ...
The Cell Study Guide KEY
... 17. What is the function of the Mitochondria? POWERHOUSE OF THE CELL! The Mitochondria’s role is in the production of energy in the form of ATP for cellular use. a. Do plants have them? Yes. 18. Both prokaryotes (70S) and eukaryotes (80s) have ribosomes. What would happen to the prokaryote if their ...
... 17. What is the function of the Mitochondria? POWERHOUSE OF THE CELL! The Mitochondria’s role is in the production of energy in the form of ATP for cellular use. a. Do plants have them? Yes. 18. Both prokaryotes (70S) and eukaryotes (80s) have ribosomes. What would happen to the prokaryote if their ...
Section: Passive Transport
... Read the passages below. Notice that the sentences are numbered. Then answer the questions that follow. ...
... Read the passages below. Notice that the sentences are numbered. Then answer the questions that follow. ...
Ch. 3- Cells, The Living Units Theory Cell
... -Divides into two cells Interphase * Period from cell formation to cell ______________ * Nuclear material called _______________ * Three subphases: * G1 (gap 1)—vigorous growth and metabolism * Cells that permanently cease dividing said to be in G0 phase * S (synthetic)—DNA replication occurs * G2 ( ...
... -Divides into two cells Interphase * Period from cell formation to cell ______________ * Nuclear material called _______________ * Three subphases: * G1 (gap 1)—vigorous growth and metabolism * Cells that permanently cease dividing said to be in G0 phase * S (synthetic)—DNA replication occurs * G2 ( ...
Epithelial Tissues
... Collagenous fibers- thick fibers made of collagen, grouped in parallel bundles, holds tissues together, found in tendons Elastic fibers- thin fibers, stretch easily, build networks, made of elastin Reticular fibers- very thin fibers, delicate support ...
... Collagenous fibers- thick fibers made of collagen, grouped in parallel bundles, holds tissues together, found in tendons Elastic fibers- thin fibers, stretch easily, build networks, made of elastin Reticular fibers- very thin fibers, delicate support ...
What`s in a Cell?
... could get it inside of a beach ball. That’s kind of what the ER is. Instead of newspaper…it’s a network of membranes. Substances like nutrients and wastes move along the surface to get from one place to another within a cell. There’s smooth ER and rough ER. The rough ER has ribosomes stuck in it. Ho ...
... could get it inside of a beach ball. That’s kind of what the ER is. Instead of newspaper…it’s a network of membranes. Substances like nutrients and wastes move along the surface to get from one place to another within a cell. There’s smooth ER and rough ER. The rough ER has ribosomes stuck in it. Ho ...
Microbiology Part 1 Study Guide Tell what contribution the following
... b. viruses genetic material takes over the cell functions of the bacterium c. Proteins and genetics material assemble into new viruses that fill the bacterium d. The bacterium burst open, releasing new viruses to infect more cells. 16. Name two characteristics of a virus. a. Considered non living be ...
... b. viruses genetic material takes over the cell functions of the bacterium c. Proteins and genetics material assemble into new viruses that fill the bacterium d. The bacterium burst open, releasing new viruses to infect more cells. 16. Name two characteristics of a virus. a. Considered non living be ...
A cell analogy
... An analogy is a comparison between two different items where one is more familiar than the other to help in understanding the less familiar item. In the lesson an analogy was used that compared a cell to a city. ...
... An analogy is a comparison between two different items where one is more familiar than the other to help in understanding the less familiar item. In the lesson an analogy was used that compared a cell to a city. ...
Anatomy and Physiology - MOC-FV
... from an original. Genetically identical 46 chromosomes. 1. Prophase: Chromatin condenses into chromosomes, centrioles move to opposite sides of cytoplasm, nuclar membrane and nucleous disperse, microtubules appear and associate with centrioles and chromatids of chromosomes. 2. Metaphase: Spindle fib ...
... from an original. Genetically identical 46 chromosomes. 1. Prophase: Chromatin condenses into chromosomes, centrioles move to opposite sides of cytoplasm, nuclar membrane and nucleous disperse, microtubules appear and associate with centrioles and chromatids of chromosomes. 2. Metaphase: Spindle fib ...
CP Biology
... the plasma membrane together 6 The bond that holds amino acids together 8 The liquid that fills the cell 9 Smallest basic unit of matter 10 Process where a cell divides its nucleus and contents ...
... the plasma membrane together 6 The bond that holds amino acids together 8 The liquid that fills the cell 9 Smallest basic unit of matter 10 Process where a cell divides its nucleus and contents ...
Chapter 3: Section 3 – Carbon Compounds
... A. Building Blocks of Cells 1. The parts of a cell are made of large, complex molecules called __________________ ____________ _______________. 2. Large, complex biomolecules or organic molecules are built from smaller, simpler molecules called ___________________. 3. These simple molecules or monom ...
... A. Building Blocks of Cells 1. The parts of a cell are made of large, complex molecules called __________________ ____________ _______________. 2. Large, complex biomolecules or organic molecules are built from smaller, simpler molecules called ___________________. 3. These simple molecules or monom ...
Chromosomal basis of inheritance cell division – mitosis and meiosis
... 2N = number of chromosomes in somatic cells of diploid species • number and size of chromosomes is unrelated to complexity of organism (e.g., nematode N varies from 1 to 48) ...
... 2N = number of chromosomes in somatic cells of diploid species • number and size of chromosomes is unrelated to complexity of organism (e.g., nematode N varies from 1 to 48) ...
evolution_of_cells
... World to DNA>Protein world is difficult, because it would have been during this transitional time that the “language” that is the Genetic Code evolved. Languages evolve communally, and I accept the Carl Woese hypothesis of a community of pre-cellular entities that worked out a genetic code together. ...
... World to DNA>Protein world is difficult, because it would have been during this transitional time that the “language” that is the Genetic Code evolved. Languages evolve communally, and I accept the Carl Woese hypothesis of a community of pre-cellular entities that worked out a genetic code together. ...
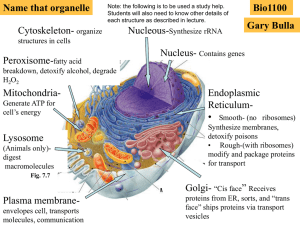
Cells - Images
... The word "lysosome" is Latin for "kill body." The purpose of the lysosome is to digest things. They might be used to digest food or break down the cell when it dies. Break down food molecules, cell wastes & worn out cell parts ...
... The word "lysosome" is Latin for "kill body." The purpose of the lysosome is to digest things. They might be used to digest food or break down the cell when it dies. Break down food molecules, cell wastes & worn out cell parts ...
Beyond the light microscope
... Anton van Leeuwenhoek 1670 - Anton van Leeuwenhoek looks at pond water and becomes the first person to see living cells with a simple microscope. ...
... Anton van Leeuwenhoek 1670 - Anton van Leeuwenhoek looks at pond water and becomes the first person to see living cells with a simple microscope. ...
Cells as Units of Life
... Animals utilize osmosis to control internal fluid and solute levels. The blood of marine fishes has 1/3 the salt content of the water. They are hypoosmotic to seawater. Freshwater fishes have blood that is saltier than the water. They are hyperosmotic to the water. If the solute concentratio ...
... Animals utilize osmosis to control internal fluid and solute levels. The blood of marine fishes has 1/3 the salt content of the water. They are hypoosmotic to seawater. Freshwater fishes have blood that is saltier than the water. They are hyperosmotic to the water. If the solute concentratio ...
The Cell
... 3. As a cell grows, its need for oxygen increases faster than its ability to get oxygen. So the cell must divide or suffocate ...
... 3. As a cell grows, its need for oxygen increases faster than its ability to get oxygen. So the cell must divide or suffocate ...
CELLS: The smallest living things
... have already learned about the parts of these cells in class; in this lab we will observe celery cells (plant cells) and human cheek cells (animal cells) under the microscope. Remember that whenever you use the microscope you always start with the _______ X objective (fill in the blank). Background: ...
... have already learned about the parts of these cells in class; in this lab we will observe celery cells (plant cells) and human cheek cells (animal cells) under the microscope. Remember that whenever you use the microscope you always start with the _______ X objective (fill in the blank). Background: ...
Viewing Cells Microscopes are used to magnify cells. The number of
... be supported by evidence, including experimental evidence and observations. A theory proves its value when it explains new discoveries and observations. Theories are important for a number of reasons. Certainly they satisfy scientists’ desire to understand the natural world, and they serve as founda ...
... be supported by evidence, including experimental evidence and observations. A theory proves its value when it explains new discoveries and observations. Theories are important for a number of reasons. Certainly they satisfy scientists’ desire to understand the natural world, and they serve as founda ...
REVISED Handout
... have already learned about the parts of these cells in class; in this lab we will observe celery cells (plant cells) and human cheek cells (animal cells) under the microscope. Remember that whenever you use the microscope you always start with the _______ X objective (fill in the blank). Background: ...
... have already learned about the parts of these cells in class; in this lab we will observe celery cells (plant cells) and human cheek cells (animal cells) under the microscope. Remember that whenever you use the microscope you always start with the _______ X objective (fill in the blank). Background: ...
Transport in Plants
... Phloem cells are also called sieve tubes. Cells are joined by small holes in the cell wall at the end of each cell, forming a continuous system. The end cell walls are called sieve plates. ...
... Phloem cells are also called sieve tubes. Cells are joined by small holes in the cell wall at the end of each cell, forming a continuous system. The end cell walls are called sieve plates. ...