3.3 Chemical Compounds
... Nucleic acids- very long organic molecules made of carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen, phosphorus ...
... Nucleic acids- very long organic molecules made of carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen, phosphorus ...
pH - Elmwood Park Public Schools
... They all have jobs, and they all work together to keep the cell alive and functioning properly, just like the organs in your body. ...
... They all have jobs, and they all work together to keep the cell alive and functioning properly, just like the organs in your body. ...
Chapter 31
... A. A plant is typically organized into a root system and a shoot system 1. The root system is typically below-ground, and the shoot system is the above-ground tissue, consisting of the stem, leaves, flowers, and fruits 2. The root and shoot system are exposed to very different environmental conditio ...
... A. A plant is typically organized into a root system and a shoot system 1. The root system is typically below-ground, and the shoot system is the above-ground tissue, consisting of the stem, leaves, flowers, and fruits 2. The root and shoot system are exposed to very different environmental conditio ...
Exam 3
... MULTIPLE CHOICE. Select the ONE choice that BEST answers the question. Circle your answer and write the letter in the blank next to the question. Please feel free to ask me to clarify any question. (2 pts. each - 70 total) ____ 1. How are adaptations beneficial to organisms? A. Adaptations help orga ...
... MULTIPLE CHOICE. Select the ONE choice that BEST answers the question. Circle your answer and write the letter in the blank next to the question. Please feel free to ask me to clarify any question. (2 pts. each - 70 total) ____ 1. How are adaptations beneficial to organisms? A. Adaptations help orga ...
Unit 2 Review Answer Key
... 26. Why are animal cell so much more variable in appearance than plant cells? because animal cells can have so many different functions 27. Name two differences between a prokaryote and a eukaryote. prokaryote – does NOT have a nucleus, no organelles, DNA is floating around in the cytoplasm; eukaryo ...
... 26. Why are animal cell so much more variable in appearance than plant cells? because animal cells can have so many different functions 27. Name two differences between a prokaryote and a eukaryote. prokaryote – does NOT have a nucleus, no organelles, DNA is floating around in the cytoplasm; eukaryo ...
Review Key - davis.k12.ut.us
... Remember here the cell theory 1. All living things are composed of one or more cell. 2. Cells are the basic unit of life 3. All cell come from other cells 3. Describe the functions of the following organelles (cell parts): a. Nucleus: the control center, DNA is housed in the Nucleus b. Cell membrane ...
... Remember here the cell theory 1. All living things are composed of one or more cell. 2. Cells are the basic unit of life 3. All cell come from other cells 3. Describe the functions of the following organelles (cell parts): a. Nucleus: the control center, DNA is housed in the Nucleus b. Cell membrane ...
ENGAGE - Galena Park ISD Moodle
... 1600s. He observed a piece of cork under a microscope and noticed the arrangement of little boxes all in a row. He called these boxes cells because they reminded him of the rooms that monks would stay in. Hooke started observing other things under the microscope and soon discovered that all living t ...
... 1600s. He observed a piece of cork under a microscope and noticed the arrangement of little boxes all in a row. He called these boxes cells because they reminded him of the rooms that monks would stay in. Hooke started observing other things under the microscope and soon discovered that all living t ...
3.1 Cell Theory
... are made of cells. Schleiden discussed the results of his work with another German scientist, Theodor Schwann, who was struck by the structural similarities between plant cells and the animal cells he had been studying. Schwann concluded that all animals are made of cells. Shortly thereafter, in 183 ...
... are made of cells. Schleiden discussed the results of his work with another German scientist, Theodor Schwann, who was struck by the structural similarities between plant cells and the animal cells he had been studying. Schwann concluded that all animals are made of cells. Shortly thereafter, in 183 ...
cells - Reocities
... Cells are the basic functional units of all living organisms. They may exist singly, as in unicellular organisms, or in aggregates, as in multicellular organisms. Living things are grouped into three domains. Bacteria and Archaea contain all prokaryotic cells (organized nucleus absent). The domain E ...
... Cells are the basic functional units of all living organisms. They may exist singly, as in unicellular organisms, or in aggregates, as in multicellular organisms. Living things are grouped into three domains. Bacteria and Archaea contain all prokaryotic cells (organized nucleus absent). The domain E ...
Cell Notes
... – Control center of the cell because it holds the genetic information or DNA – DNA contains the genes that are instructions for making proteins 2 Major demands on DNA 1. DNA must be carefully protected 2. DNA must be available for use at all times Solution for these demands: * Nuclear envelope- a do ...
... – Control center of the cell because it holds the genetic information or DNA – DNA contains the genes that are instructions for making proteins 2 Major demands on DNA 1. DNA must be carefully protected 2. DNA must be available for use at all times Solution for these demands: * Nuclear envelope- a do ...
10-1 2014 Why Cells Divide
... A.All of the DNA can’t fit within a single cell. B.DNA becomes diluted as a cell increases in size. C.The larger a cell becomes, the more demands the cell places on its DNA. D.DNA doesn’t increase in size fast enough to keep up with a cell’s growth. ...
... A.All of the DNA can’t fit within a single cell. B.DNA becomes diluted as a cell increases in size. C.The larger a cell becomes, the more demands the cell places on its DNA. D.DNA doesn’t increase in size fast enough to keep up with a cell’s growth. ...
File - Biology
... Meiosis Review 1. In human cells: a. What does diploid and haploid mean with regard to chromosomes? b. What are the diploid and haploid numbers for cells? c. Which types of cells have diploid chromosomes, and which have haploid chromosomes? 2. What are homologous chromosomes? How are they related an ...
... Meiosis Review 1. In human cells: a. What does diploid and haploid mean with regard to chromosomes? b. What are the diploid and haploid numbers for cells? c. Which types of cells have diploid chromosomes, and which have haploid chromosomes? 2. What are homologous chromosomes? How are they related an ...
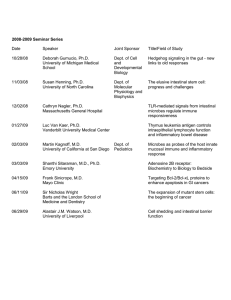
Date Speaker Joint Sponsor
... Microbes as probes of the host innate mucosal immune and inflammatory ...
... Microbes as probes of the host innate mucosal immune and inflammatory ...
BIO201 Lecture 5
... microscope – series of lenses used to magnify a specimen *magnification – ratio of object’s image to real size *resolving power – clarity of the image *magnification = 1,000X *Light microscope ...
... microscope – series of lenses used to magnify a specimen *magnification – ratio of object’s image to real size *resolving power – clarity of the image *magnification = 1,000X *Light microscope ...
Cell
... the cell. The nucleus is surrounded by its own membrane, called the nuclear membrane. The nucleus contains other organelles (chromosomes - DNA and the nucleolus). Cell activities are controlled by the nucleus ...
... the cell. The nucleus is surrounded by its own membrane, called the nuclear membrane. The nucleus contains other organelles (chromosomes - DNA and the nucleolus). Cell activities are controlled by the nucleus ...
Infection of Target Cells with Lentivirus
... 10% FBS, 1% PenStrep and the proper concentration of Puromycin. Note: The concentration of Puromycin is going to be different with each cell line as some are more sensitive to the drug than others. It is crucial to do a kill curve with each cell line and pick the lowest concentration of Puromycin th ...
... 10% FBS, 1% PenStrep and the proper concentration of Puromycin. Note: The concentration of Puromycin is going to be different with each cell line as some are more sensitive to the drug than others. It is crucial to do a kill curve with each cell line and pick the lowest concentration of Puromycin th ...
Slide 1
... These cells are found in plants, animals, and protists The eukaryotic cell is composed of 4 main parts: •cell membrane - outer boundary of the cell •cytoplasm - jelly-like fluid interior of the cell •nucleus - the "control center" of the cell, contains the cell's DNA (chromosomes) •organelles - "lit ...
... These cells are found in plants, animals, and protists The eukaryotic cell is composed of 4 main parts: •cell membrane - outer boundary of the cell •cytoplasm - jelly-like fluid interior of the cell •nucleus - the "control center" of the cell, contains the cell's DNA (chromosomes) •organelles - "lit ...
Biology Review PPT
... These cells are found in plants, animals, and protists The eukaryotic cell is composed of 4 main parts: •cell membrane - outer boundary of the cell •cytoplasm - jelly-like fluid interior of the cell •nucleus - the "control center" of the cell, contains the cell's DNA (chromosomes) •organelles - "lit ...
... These cells are found in plants, animals, and protists The eukaryotic cell is composed of 4 main parts: •cell membrane - outer boundary of the cell •cytoplasm - jelly-like fluid interior of the cell •nucleus - the "control center" of the cell, contains the cell's DNA (chromosomes) •organelles - "lit ...
Ch 4b Study Guide
... Compare the structures and functions of microfilaments, intermediate filaments, and microtubules. Relate the structure of cilia and flagella to their functions. Describe examples of environmental and genetic causes of infertility in men. Relate the structure of the extracellular matrix to its functi ...
... Compare the structures and functions of microfilaments, intermediate filaments, and microtubules. Relate the structure of cilia and flagella to their functions. Describe examples of environmental and genetic causes of infertility in men. Relate the structure of the extracellular matrix to its functi ...
CYTOLOGIC DIAGNOSIS OF CARCINOMA OF THE PROSTATE
... the group is usually sharply defined, but the cytoplasm forms one syncytial mass and shows no cellular boundaries. The nuclei are relatively small, round or oval, and not numerous. They are similar to those already described. The regularity and small size of these nuclei, together with their paucity ...
... the group is usually sharply defined, but the cytoplasm forms one syncytial mass and shows no cellular boundaries. The nuclei are relatively small, round or oval, and not numerous. They are similar to those already described. The regularity and small size of these nuclei, together with their paucity ...
Eukaryotic Cell Structure
... • The nucleus holds nearly all of the cell’s DNA and with it the coded instructions for making proteins and other important molecules • control center of the cell – Surrounded by a double membrane with pores in it nuclear envelope outer boundary of the nucleus ...
... • The nucleus holds nearly all of the cell’s DNA and with it the coded instructions for making proteins and other important molecules • control center of the cell – Surrounded by a double membrane with pores in it nuclear envelope outer boundary of the nucleus ...