Modification of Cell Surface/ Cell Communication
... Essential knowledge 3.D.3: Signal transduction pathways link signal reception with cellular response. a. Signaling begins with the recognition of a chemical messenger, a ligand, by a receptor protein. Evidence of student learning is a demonstrated understanding of each of the following: 1. Differen ...
... Essential knowledge 3.D.3: Signal transduction pathways link signal reception with cellular response. a. Signaling begins with the recognition of a chemical messenger, a ligand, by a receptor protein. Evidence of student learning is a demonstrated understanding of each of the following: 1. Differen ...
SCIENCE AS A PROCESS- Science is a way of knowing
... Evolution accounts for the diversity of life on Earth. Example: Widespread use of antibiotics has selected for antibiotic resistance in disease-causing bacteria. ENDOSYMBIOTIC THEORY- idea that the incorporation of photosynthesizing and respiring bacteria by other early bacteria resulted in the evol ...
... Evolution accounts for the diversity of life on Earth. Example: Widespread use of antibiotics has selected for antibiotic resistance in disease-causing bacteria. ENDOSYMBIOTIC THEORY- idea that the incorporation of photosynthesizing and respiring bacteria by other early bacteria resulted in the evol ...
The basic unit of life
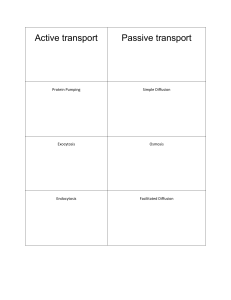
... concentration gradient. • Actively: moving items against a concentration gradient, energy is required • Facilitated diffusion: No energy, just using helpers (like proteins) to move things in or out of a cell that are large. • The two most common passive movement processes are diffusion (solutions) a ...
... concentration gradient. • Actively: moving items against a concentration gradient, energy is required • Facilitated diffusion: No energy, just using helpers (like proteins) to move things in or out of a cell that are large. • The two most common passive movement processes are diffusion (solutions) a ...
week9
... 5A Describe the stages of the cell cycle and its importance to the growth of organisms. 5D Recognize that disruptions of the cell cycle can lead to diseases such as cancer. ...
... 5A Describe the stages of the cell cycle and its importance to the growth of organisms. 5D Recognize that disruptions of the cell cycle can lead to diseases such as cancer. ...
SI-revised - AIP FTP Server
... Therefore, the cell cycle analysis is powerful to reflect the influence of cellular endocytosis on cell proliferation. Several studies have been focused on the influence of the particles, genes and inhibitors on the cell cycle.[1-4] Since G2 and M phases could not be distinguished only by DNA conten ...
... Therefore, the cell cycle analysis is powerful to reflect the influence of cellular endocytosis on cell proliferation. Several studies have been focused on the influence of the particles, genes and inhibitors on the cell cycle.[1-4] Since G2 and M phases could not be distinguished only by DNA conten ...
Summary Sheet for Introductory Animal, Plant and Protist Reading
... Animals are multicellular/unicellular organisms. They need to eat to obtain energy so they are hetertrophs/autotrophs. Their cells contain nuclei so they are prokaryotes/eukaryotes. 3. Complete the graphic organizer to show the basic classification of animals. ...
... Animals are multicellular/unicellular organisms. They need to eat to obtain energy so they are hetertrophs/autotrophs. Their cells contain nuclei so they are prokaryotes/eukaryotes. 3. Complete the graphic organizer to show the basic classification of animals. ...
2 organelles
... Ribosomes make proteins. (remember-from amino acids) Ribosomes can be found alone in the cytoplasm (free), in groups, or attached (bound) to the endoplasmic reticulum. Plant ...
... Ribosomes make proteins. (remember-from amino acids) Ribosomes can be found alone in the cytoplasm (free), in groups, or attached (bound) to the endoplasmic reticulum. Plant ...
Chapter 7 - Angelfire
... • All these scientists (plus others) contributed ideas that are now summed up in what we call the cell theory ...
... • All these scientists (plus others) contributed ideas that are now summed up in what we call the cell theory ...
mac to mic mac_to_mic_review_lessons_1-71
... Dr. Matthews has worked with WOWBugs for many years WOWBug is a parasitic insect Lays its eggs in a host Usually damages or kills the host ...
... Dr. Matthews has worked with WOWBugs for many years WOWBug is a parasitic insect Lays its eggs in a host Usually damages or kills the host ...
CHAPTER 7 A TOUR OF THE CELL Section B: A Panoramic View of
... this exchange. • Rates of chemical exchange may be inadequate to maintain a cell with a very large cytoplasm. • The need for a surface sufficiently large to accommodate the volume explains the microscopic size of most cells. • Larger organisms do not generally have larger cells than smaller organism ...
... this exchange. • Rates of chemical exchange may be inadequate to maintain a cell with a very large cytoplasm. • The need for a surface sufficiently large to accommodate the volume explains the microscopic size of most cells. • Larger organisms do not generally have larger cells than smaller organism ...
eukaryotic
... Telophase 1: Two daughter cells are formed with each daughter containing only one chromosome of the homologous pair. Second division of meiosis: Gamete formation Prophase 2: DNA does not replicate. Metaphase 2: Chromosomes align at the equatorial plate. Anaphase 2: Centromeres divide and sister chro ...
... Telophase 1: Two daughter cells are formed with each daughter containing only one chromosome of the homologous pair. Second division of meiosis: Gamete formation Prophase 2: DNA does not replicate. Metaphase 2: Chromosomes align at the equatorial plate. Anaphase 2: Centromeres divide and sister chro ...
Cells Powerpoint
... • All organisms are made of one or more cells. • Cells are the basic unit of life in all living things. • All cells come from existing cells. ...
... • All organisms are made of one or more cells. • Cells are the basic unit of life in all living things. • All cells come from existing cells. ...
Immunity - Seattle Central College
... – B-cells: released into bloodstream and migrate to lymph organs – Pre T-cells: migrate to thymus & mature there • Mature T-cells migrate to lymph organs ...
... – B-cells: released into bloodstream and migrate to lymph organs – Pre T-cells: migrate to thymus & mature there • Mature T-cells migrate to lymph organs ...
Notable Inventions - Lemelson
... changes in glycosylation that accompany cancer onset and progression. Using zebrafish as a model organism, Bertozzi was able to show that sugars can be imaged during the process of embryogenesis, a major breakthrough that might facilitate studies of stem cell differentiation in live animals. ...
... changes in glycosylation that accompany cancer onset and progression. Using zebrafish as a model organism, Bertozzi was able to show that sugars can be imaged during the process of embryogenesis, a major breakthrough that might facilitate studies of stem cell differentiation in live animals. ...
Cells - Steven Lin`s Websites
... A Constitution: Plan on how to run the city Image Courtesy of http://www.archives.gov/education/lessons/constitution-day/images/constitution01.gif ...
... A Constitution: Plan on how to run the city Image Courtesy of http://www.archives.gov/education/lessons/constitution-day/images/constitution01.gif ...
Both Both Both Both Both Both
... Without cytoplasm in the cell the organelles would not have organization and support and organelles would lack nutrients. Without ribosomes the cell could not maintain homeostasis because it would not have the proteins needed to build all the other organelles! All cells need liquid within them to su ...
... Without cytoplasm in the cell the organelles would not have organization and support and organelles would lack nutrients. Without ribosomes the cell could not maintain homeostasis because it would not have the proteins needed to build all the other organelles! All cells need liquid within them to su ...
1 Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
... Cells with different functions often vary in shape. They may also vary in size. However, all cells are very small. Even the largest organisms have microscopic cells. Cells are so small that their diameter is measured in micrometers. A micrometer is just one-millionth of a meter. Use the sliding scal ...
... Cells with different functions often vary in shape. They may also vary in size. However, all cells are very small. Even the largest organisms have microscopic cells. Cells are so small that their diameter is measured in micrometers. A micrometer is just one-millionth of a meter. Use the sliding scal ...
Presentation
... blots and cortical ERK blots because the saturation point for band intensities was 12.5μL › curve was very sensitive to fluctuations at ...
... blots and cortical ERK blots because the saturation point for band intensities was 12.5μL › curve was very sensitive to fluctuations at ...
The Science of Biology
... o Relationship between cell respiration and photosynthesis o Mitochondria o Yeast metabolism Cell Division (Chapter 10) o Surface area, volume, ratio of surface area to volume, % absorption o Cell cycle o Disadvantages of large cell size o Events that take place during interphase, mitosis and cytoki ...
... o Relationship between cell respiration and photosynthesis o Mitochondria o Yeast metabolism Cell Division (Chapter 10) o Surface area, volume, ratio of surface area to volume, % absorption o Cell cycle o Disadvantages of large cell size o Events that take place during interphase, mitosis and cytoki ...
Lecture 013--Organelles 4 (Cytoskeleton)
... in animal cells, pair of centrioles organize microtubules guiding chromosomes in cell division ...
... in animal cells, pair of centrioles organize microtubules guiding chromosomes in cell division ...
Eukaryotic Cells- Part 2 - Westerville City Schools
... organelle called the mitochondrion (mite oh kahn dree uhn). Since cells have more than one mitochondrion, you might see them called mitochondria (many mitochondrions). The mitochondria break down sugar from our food to make a special type of cell energy called ATP (that’s short for Adenosintriphosph ...
... organelle called the mitochondrion (mite oh kahn dree uhn). Since cells have more than one mitochondrion, you might see them called mitochondria (many mitochondrions). The mitochondria break down sugar from our food to make a special type of cell energy called ATP (that’s short for Adenosintriphosph ...