Plant Cell Tissue and Organ Culture Biotechnology and Its
... aims to provide a brief overview of the role of plant cell tissue and organ biotechnology in the field of the conservation and improvement of Medicinal and Aromatic Plants (MAPs). Several textbooks and review articles have been described this topic more comprehensively than is possible in this edito ...
... aims to provide a brief overview of the role of plant cell tissue and organ biotechnology in the field of the conservation and improvement of Medicinal and Aromatic Plants (MAPs). Several textbooks and review articles have been described this topic more comprehensively than is possible in this edito ...
Kingdom Protista A Mixed Bag of Organisms
... •They contain __________________________ and carry on ________________________________, so they are an important ________________________ source for many _____________________ ...
... •They contain __________________________ and carry on ________________________________, so they are an important ________________________ source for many _____________________ ...
Dynamic Organization of DNA Replication in Mammalian Cell Nuclei
... labeling with in situhybridization of DNA sequences and examining by confocal microscopy, we can determine when these sequences replicate within a cell in relation to the replication patterns and assess the differences and/or similarities in replication between individual cells within a population . ...
... labeling with in situhybridization of DNA sequences and examining by confocal microscopy, we can determine when these sequences replicate within a cell in relation to the replication patterns and assess the differences and/or similarities in replication between individual cells within a population . ...
Whole mount in situ hybridization shows Endo 16
... uniformly distributed throughout the cytoplasm of the vegetal plate cells. Fig. 1A,B shows clearly that Endo 16 message is restricted to a ring of approximately 28 cells in 20 h embryos. The absence of staining in the center of the vegetal plate territory shows that the skeletogenic territory in the ...
... uniformly distributed throughout the cytoplasm of the vegetal plate cells. Fig. 1A,B shows clearly that Endo 16 message is restricted to a ring of approximately 28 cells in 20 h embryos. The absence of staining in the center of the vegetal plate territory shows that the skeletogenic territory in the ...
Ion-channel blocker sensitivity of voltage-gated
... diltiazem, enhanced Ca2+ accumulation unexpectedly (Fig. 4a). A possible explanation for this unexpected observation is that diltiazem may specifically bind to Cch1 to activate Ca2+ entry, instead of blocking it. The second possibility is that diltiazem, at high concentrations, may be a stress for y ...
... diltiazem, enhanced Ca2+ accumulation unexpectedly (Fig. 4a). A possible explanation for this unexpected observation is that diltiazem may specifically bind to Cch1 to activate Ca2+ entry, instead of blocking it. The second possibility is that diltiazem, at high concentrations, may be a stress for y ...
Direct conversion of root primordium into shoot meristem relies on
... switches for the initiation of novel meristematic structures. Although such transitions are often assumed to involve a dedifferentiation phase, the de novo organogenesis observed in CIM/SIM systems is thought to be a transdifferentiation process, whereby a cell is directly transformed into another c ...
... switches for the initiation of novel meristematic structures. Although such transitions are often assumed to involve a dedifferentiation phase, the de novo organogenesis observed in CIM/SIM systems is thought to be a transdifferentiation process, whereby a cell is directly transformed into another c ...
Zinc-induced Inactivation of the Yeast ZRT1 Zinc Transporter
... This response attenuates the effects of mating pheromone during periods of prolonged exposure. Several nutrient transporters are endocytosed in response to the increased availability of a preferred substrate. Glucose, the preferred carbon source for yeast, signals the endocytosis of the GAL2 galacto ...
... This response attenuates the effects of mating pheromone during periods of prolonged exposure. Several nutrient transporters are endocytosed in response to the increased availability of a preferred substrate. Glucose, the preferred carbon source for yeast, signals the endocytosis of the GAL2 galacto ...
Unit 1.2: The Study of Life
... Competition is a relationship between living things that depend on the same resources. The resources may be food, water, or anything else they both need. Competition occurs whenever they both try to get the same resources in the same place and at the same time. The two organisms are likely to come i ...
... Competition is a relationship between living things that depend on the same resources. The resources may be food, water, or anything else they both need. Competition occurs whenever they both try to get the same resources in the same place and at the same time. The two organisms are likely to come i ...
Chapter 9 - Fullfrontalanatomy.com
... not be able to express your wishes to others, nor could you ask questions to find out more about your environment. Social organization is dependent on communication between the individuals that comprise that society; without communication, society would fall apart. As with people, it is vital for in ...
... not be able to express your wishes to others, nor could you ask questions to find out more about your environment. Social organization is dependent on communication between the individuals that comprise that society; without communication, society would fall apart. As with people, it is vital for in ...
Making parallel lines meet
... to spaces both fascinating and useful. A contemporary case of parallel lines whose meeting is impossible but informative is offered by the humble vascular plant. Perhaps of doubtful utility for readers of Cell Adhesion and Migration, this case nevertheless could fascinate them, concerning as it does ...
... to spaces both fascinating and useful. A contemporary case of parallel lines whose meeting is impossible but informative is offered by the humble vascular plant. Perhaps of doubtful utility for readers of Cell Adhesion and Migration, this case nevertheless could fascinate them, concerning as it does ...
Expression of the Fgf6 gene is restricted to
... sections of prefixed mouse embryos at various postimplantation stages of development were hybridized in situ to either antisense or sense Fgf6 probes. No signal above background was ever observed at any time using the sense probe (data not shown). No Fgf6 signal was detected at stages between 6.5 an ...
... sections of prefixed mouse embryos at various postimplantation stages of development were hybridized in situ to either antisense or sense Fgf6 probes. No signal above background was ever observed at any time using the sense probe (data not shown). No Fgf6 signal was detected at stages between 6.5 an ...
Plastid Ontogeny during Petal Development in Arabidopsis
... clearly observed (Fig. 8, arrowheads) and made up more than 50% of the total plastid population. Such dividing plastids were seen in only these basal cells of the petal stalk, and images of green chloroplasts at earlier stages of petal development did not show large numbers of the dumbbell shapes (d ...
... clearly observed (Fig. 8, arrowheads) and made up more than 50% of the total plastid population. Such dividing plastids were seen in only these basal cells of the petal stalk, and images of green chloroplasts at earlier stages of petal development did not show large numbers of the dumbbell shapes (d ...
to get the file - Chair of Computational Biology
... initiation and the initial number of free DnaA monomers. The duration of the replication phase in individual cells is more closely related to the free dNTP content at the start of replication than to the dNTP content at the start of the cell cycle The durations of the initiation and replication phas ...
... initiation and the initial number of free DnaA monomers. The duration of the replication phase in individual cells is more closely related to the free dNTP content at the start of replication than to the dNTP content at the start of the cell cycle The durations of the initiation and replication phas ...
Asymmetric Cell Division as a Route to Reduction in Cell Length
... trypanosome SCC1 demonstrated that it is the orthologue of yeast SCC1 (Gluenz, Sharma, Gull ...
... trypanosome SCC1 demonstrated that it is the orthologue of yeast SCC1 (Gluenz, Sharma, Gull ...
MOVEMENT OF SUBSTANCES ACROSS THE PLASMA MEMBRANE
... As raw materials for protein synthesis For cell metabolism and osmoregulation ...
... As raw materials for protein synthesis For cell metabolism and osmoregulation ...
C 2. Electrical properties of the heart a. Explain
... The sinus nodal fibres fuse with the atrial cardiac muscle fibres, carrying the action potential throughout the atria. There are several condensation of muscle fibres which carry the action potential more rapidly: the anterior interatrial band and the internodal pathways which run to the AV node. Th ...
... The sinus nodal fibres fuse with the atrial cardiac muscle fibres, carrying the action potential throughout the atria. There are several condensation of muscle fibres which carry the action potential more rapidly: the anterior interatrial band and the internodal pathways which run to the AV node. Th ...
Intracellular marking of physiologically characterized cells in the
... nucleus neurons are thought to be, at least in part, dependent on the different spatial arrangements of presynaptic endings on the postsynaptic cells (Kiang et al., ’65b, ’73; Morest et al., ’73; Kiang, ’75; Tsuchitani, ’78). The difficulty in determining synaptic geometry, however, has prompted res ...
... nucleus neurons are thought to be, at least in part, dependent on the different spatial arrangements of presynaptic endings on the postsynaptic cells (Kiang et al., ’65b, ’73; Morest et al., ’73; Kiang, ’75; Tsuchitani, ’78). The difficulty in determining synaptic geometry, however, has prompted res ...
Module 17 / Skeletal Muscle Tissue and Fiber Types
... high amounts of glycogen, which is used in glycolysis to generate ATP quickly; thus, they produce high levels ...
... high amounts of glycogen, which is used in glycolysis to generate ATP quickly; thus, they produce high levels ...
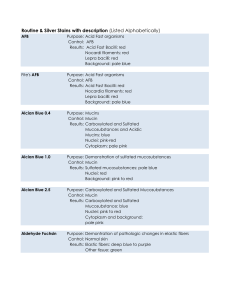
Special Stain Content.xlsx
... Purpose: For Connective tissue Control: Normal Skin Results: Nuclei: deep blue Cytoplasm of epidermis and smooth muscle: light blue Collagen: rose pink Elastic fibers: dark brown Mast cell granules and many Mucoid substances: purple Eosinophilic granules and erythrocytes: bright red ...
... Purpose: For Connective tissue Control: Normal Skin Results: Nuclei: deep blue Cytoplasm of epidermis and smooth muscle: light blue Collagen: rose pink Elastic fibers: dark brown Mast cell granules and many Mucoid substances: purple Eosinophilic granules and erythrocytes: bright red ...
Supplement Supporting Materials and Methods Site
... A, The inhibitory efficiency of the shRNA directed against P300 or CBP evaluated by Western blot analysis. At 48 h after shRNA transfection, total cell lysates were prepared and normalized for protein concentration. The expression of gapdh was used to control equal protein loading. Results shown are ...
... A, The inhibitory efficiency of the shRNA directed against P300 or CBP evaluated by Western blot analysis. At 48 h after shRNA transfection, total cell lysates were prepared and normalized for protein concentration. The expression of gapdh was used to control equal protein loading. Results shown are ...
Sos recruitment system for the analysis of the
... We sought information on SUMF2 localization and whether its subtypes could interact with whIL-13 and mhIL-13. The Sos recruitment system takes advantage of Ras-activation through membrane-localized hSos in yeast (Kruse et al., 2006; Aronheim et al., 2006). The SUMF2 subtypes are particularly well su ...
... We sought information on SUMF2 localization and whether its subtypes could interact with whIL-13 and mhIL-13. The Sos recruitment system takes advantage of Ras-activation through membrane-localized hSos in yeast (Kruse et al., 2006; Aronheim et al., 2006). The SUMF2 subtypes are particularly well su ...
Growing wrist mass
... masses of the musculoskeletal system. It is particularly useful for assessing masses in the hand and wrist, where benign lesions predominate.1 2 A specific diagnosis may be made, or strongly suspected, from the characteristic MRI features of certain lesions, such as ganglion, haemangioma, arterioven ...
... masses of the musculoskeletal system. It is particularly useful for assessing masses in the hand and wrist, where benign lesions predominate.1 2 A specific diagnosis may be made, or strongly suspected, from the characteristic MRI features of certain lesions, such as ganglion, haemangioma, arterioven ...
- Wiley Online Library
... (Bulloch and Kingston, 2014). Screening such candidates with the classic BEVS is a time-, labor-, and cost-intensive (Jarvis, 2014) process as sufficient recombinant baculoviral material of adequate quality for each construct is required for analysis of the expression efficiency. Hence, screening targ ...
... (Bulloch and Kingston, 2014). Screening such candidates with the classic BEVS is a time-, labor-, and cost-intensive (Jarvis, 2014) process as sufficient recombinant baculoviral material of adequate quality for each construct is required for analysis of the expression efficiency. Hence, screening targ ...