Cells: Prokaryote vs Eukaryote
... Pathogenic – feed on living things The kind that make you sick! Decomposers – feed on dead things ...
... Pathogenic – feed on living things The kind that make you sick! Decomposers – feed on dead things ...
Cell Biology Study Guide - Westerville City Schools
... Cell Biology Study Guide (Test is Monday, October 3rd) ...
... Cell Biology Study Guide (Test is Monday, October 3rd) ...
The drug colchicine inhibits the formation of spindle fibers. If you
... The drug colchicine inhibits the formation of spindle fibers. If you treat dividing cells with colchicine, what would you expect the result to be? A ...
... The drug colchicine inhibits the formation of spindle fibers. If you treat dividing cells with colchicine, what would you expect the result to be? A ...
Prokaryotes vs. Eukaryotes
... – Pathogenic – feed on living things ! • The kind that make you sick!! ...
... – Pathogenic – feed on living things ! • The kind that make you sick!! ...
Prokaryote and Eukaryote Touch Up
... 1. Most people know about blood types, some also know about tissue types. However, now we may need to consider intestinal bacteria types as well. As part of a large, international research consortium, scientists from the University of Copenhagen have recently contributed to map special ”enterotypes” ...
... 1. Most people know about blood types, some also know about tissue types. However, now we may need to consider intestinal bacteria types as well. As part of a large, international research consortium, scientists from the University of Copenhagen have recently contributed to map special ”enterotypes” ...
6th Grade
... Essential Question/Purpose: Purpose: To become more familiar with cells and their importance ...
... Essential Question/Purpose: Purpose: To become more familiar with cells and their importance ...
Cells and Stuff - Mr. Cloud`s Class
... unicellular. Organisms made up of many cells are called multi-cellular. Large organisms, such as humans, have billions of cells. Students might think that most organisms on Earth are multi-cellular. In fact, the majority of organisms are microscopic, single-celled organisms such as bacteria, algae, ...
... unicellular. Organisms made up of many cells are called multi-cellular. Large organisms, such as humans, have billions of cells. Students might think that most organisms on Earth are multi-cellular. In fact, the majority of organisms are microscopic, single-celled organisms such as bacteria, algae, ...
Plant Cells vs. Animal Cells
... 4. There is compelling evidence that mitochondria and chloroplasts were once primitive bacterial cells. This evidence is described in the endosymbiotic theory. Symbiosis occurs when two different species benefit from living and working together. When one organism actually lives inside the other it's ...
... 4. There is compelling evidence that mitochondria and chloroplasts were once primitive bacterial cells. This evidence is described in the endosymbiotic theory. Symbiosis occurs when two different species benefit from living and working together. When one organism actually lives inside the other it's ...
Cett5 frLluZ * c4tv1
... 7. Plant cellwalls are made of cellulose. List some ways people use cellulose. ...
... 7. Plant cellwalls are made of cellulose. List some ways people use cellulose. ...
LAB 4-A - BrainMass
... 4- Are nuclei visible in the bacterium lactobacillus and the cyanobacterium anabaena? 5- Knowing that Anabaena is photosynthetic, do you think that the color when observed under magnification is due to the presence of chloroplates? Explain? LAB 4-C 1- Since onion cells and elodea leaf cells are both ...
... 4- Are nuclei visible in the bacterium lactobacillus and the cyanobacterium anabaena? 5- Knowing that Anabaena is photosynthetic, do you think that the color when observed under magnification is due to the presence of chloroplates? Explain? LAB 4-C 1- Since onion cells and elodea leaf cells are both ...
7-2 - Cloudfront.net
... digest and breakdown lipids, carbohydrates, and proteins • Also breakdown worn-out organelles • Ex: Ms. Tracy – Ex: tay-sachs disease ...
... digest and breakdown lipids, carbohydrates, and proteins • Also breakdown worn-out organelles • Ex: Ms. Tracy – Ex: tay-sachs disease ...
Cells, Tissues, Organs and Body Systems
... Ribosomes: Proteins (needed for growth, repair and reproduction) are put together on endoplasmic reticulum Endoplasmic Reticulum: carry materials through the cytoplasm Golgi Apparatus: stores protein molecules Lysosomes: Breaks down large molecules and destroys damaged or worn-out cells ...
... Ribosomes: Proteins (needed for growth, repair and reproduction) are put together on endoplasmic reticulum Endoplasmic Reticulum: carry materials through the cytoplasm Golgi Apparatus: stores protein molecules Lysosomes: Breaks down large molecules and destroys damaged or worn-out cells ...
the_cell_theory_questions_0809
... 10. What did Schwann summarize as the 3 parts of the cell theory? ...
... 10. What did Schwann summarize as the 3 parts of the cell theory? ...
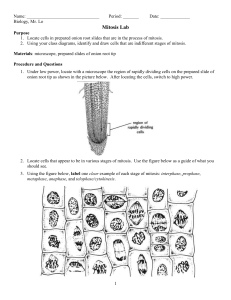
Name
... The invention of the microscope in the late 1500s revealed to early scientists a whole new world of tiny cells. Most cells are so small that they cannot be seen without a microscope. The discoveries of scientists from the 1600s through the 1800s led to the cell theory, which is a unifying concept of ...
... The invention of the microscope in the late 1500s revealed to early scientists a whole new world of tiny cells. Most cells are so small that they cannot be seen without a microscope. The discoveries of scientists from the 1600s through the 1800s led to the cell theory, which is a unifying concept of ...
Activity 8 Information Sheet - The Road to Cancer What is cancer
... Each instruction is carried on a unique piece of DNA called a gene. Our cells grow and multiply by a process called mitosis. Cell growth and multiplication is part of a continual process called the cell cycle. To move through the different stages of the cell cycle each cell has to go through a serie ...
... Each instruction is carried on a unique piece of DNA called a gene. Our cells grow and multiply by a process called mitosis. Cell growth and multiplication is part of a continual process called the cell cycle. To move through the different stages of the cell cycle each cell has to go through a serie ...
Cell Reproduction
... metabolizes, and spends a majority of its life is _______________ INTERPHASE Also, during this period, the chromosomes are duplicated to prepare for cell division. ...
... metabolizes, and spends a majority of its life is _______________ INTERPHASE Also, during this period, the chromosomes are duplicated to prepare for cell division. ...
1.2 The Cell Cycle and Mitosis
... 14. A cell is in _____ when it is preparing for cell division. 15. A cell that divides uncontrollably is called a _____ cell. 16. During this phase, the cell makes (synthesizes) an entire copy of the DNA of the cell. 17. A _____ is a long piece of coiled DNA and proteins. 18. Cancer cells can seem t ...
... 14. A cell is in _____ when it is preparing for cell division. 15. A cell that divides uncontrollably is called a _____ cell. 16. During this phase, the cell makes (synthesizes) an entire copy of the DNA of the cell. 17. A _____ is a long piece of coiled DNA and proteins. 18. Cancer cells can seem t ...
Cell Type and Form - Southmoreland School District
... respiration produces the energy carrier ATP. The distinctive organelle of a eukaryotic cell, consisting of a membranous envelope in which the chromosomes reside Membrane surrounding the cytoplasm that consists of a phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins; functions to regulate the entrance and e ...
... respiration produces the energy carrier ATP. The distinctive organelle of a eukaryotic cell, consisting of a membranous envelope in which the chromosomes reside Membrane surrounding the cytoplasm that consists of a phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins; functions to regulate the entrance and e ...
Name
... 9. A double layer of these molecules makes up the plasma membrane 10. Smallest unit of life 12. Cell structures that perform specific functions for the cell 14. First person to see and draw living cells 15. Genetic material found inside the nucleus of a cell 17. Unattached ribosomes in the cytosol 1 ...
... 9. A double layer of these molecules makes up the plasma membrane 10. Smallest unit of life 12. Cell structures that perform specific functions for the cell 14. First person to see and draw living cells 15. Genetic material found inside the nucleus of a cell 17. Unattached ribosomes in the cytosol 1 ...
Cells - Biology Junction
... 9. A double layer of these molecules makes up the plasma membrane 10. Smallest unit of life 12. Cell structures that perform specific functions for the cell 14. First person to see and draw living cells 15. Genetic material found inside the nucleus of a cell 17. Unattached ribosomes in the cytosol 1 ...
... 9. A double layer of these molecules makes up the plasma membrane 10. Smallest unit of life 12. Cell structures that perform specific functions for the cell 14. First person to see and draw living cells 15. Genetic material found inside the nucleus of a cell 17. Unattached ribosomes in the cytosol 1 ...