World War II – Battles and Strategies
... heavy American casualties, the Americans were able to liberate France. – Allies were able to attack Germany from the west ...
... heavy American casualties, the Americans were able to liberate France. – Allies were able to attack Germany from the west ...
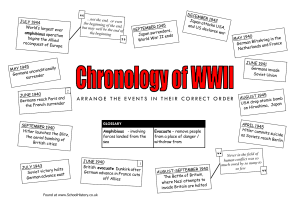
World War II - Major Events
... Italy invades France from the south and Germany takes over from the North – France surrenders 3. Battle of Britain (1940) Also known as: _____________________ _____________ __________________ Germany bombed London Massive ____________ ___________________ Germany was _______________________ ...
... Italy invades France from the south and Germany takes over from the North – France surrenders 3. Battle of Britain (1940) Also known as: _____________________ _____________ __________________ Germany bombed London Massive ____________ ___________________ Germany was _______________________ ...
How the Allies won
... COLLABORATION IN EUROPE • Hitler’s main allies: Fascist Italy, Vichy France, Romania • Spanish neutrality • Danish Resistance • Occupied Poland • Delays in the Balkans… ...
... COLLABORATION IN EUROPE • Hitler’s main allies: Fascist Italy, Vichy France, Romania • Spanish neutrality • Danish Resistance • Occupied Poland • Delays in the Balkans… ...
Ch27
... 4. Alliance with Mussolini’s Italy C. Path to War (1937-1939) 1. Annexation of Austria 2. Czechoslovakia and “Munich” 3. Invasion of Poland Course of World War II A. Victory and Stalemate (1939-1941) 1. Blitzkrieg and the British at Dunkirk 2. Fall of France and the Vichy Government 3. Winston Churc ...
... 4. Alliance with Mussolini’s Italy C. Path to War (1937-1939) 1. Annexation of Austria 2. Czechoslovakia and “Munich” 3. Invasion of Poland Course of World War II A. Victory and Stalemate (1939-1941) 1. Blitzkrieg and the British at Dunkirk 2. Fall of France and the Vichy Government 3. Winston Churc ...
Chapter VI America Before and During the Second World War Outline
... Jewish elite bartered with England and promised to bring the United States into the war in exchange for Palestine. ...
... Jewish elite bartered with England and promised to bring the United States into the war in exchange for Palestine. ...
Name Hour ____ Class - Jenks Public Schools
... c. To draw up new laws d. To terrorize his opponents 2. __________For most of World War II, Japanese American and African American troops a. Fought on the eastern front. b. Fought in segregated units. c. Stayed in the U.S. d. Tried to keep out of the war. 3. __________Just hours after they bombed Pe ...
... c. To draw up new laws d. To terrorize his opponents 2. __________For most of World War II, Japanese American and African American troops a. Fought on the eastern front. b. Fought in segregated units. c. Stayed in the U.S. d. Tried to keep out of the war. 3. __________Just hours after they bombed Pe ...
World War II (1931–1945)
... General Eisenhower was supreme commander for the invasion, Operation Overlord Heavy casualties were suffered, but by late July, nearly 2 million Allied troops were in France On August 25, 1944, Paris was liberated from German occupation. ...
... General Eisenhower was supreme commander for the invasion, Operation Overlord Heavy casualties were suffered, but by late July, nearly 2 million Allied troops were in France On August 25, 1944, Paris was liberated from German occupation. ...
World War II - SimpsonHistory
... scorched earth policy ► Drew Germans deep into USSR by winter. ...
... scorched earth policy ► Drew Germans deep into USSR by winter. ...
The End of World War II
... The main reason the United States failed to halt Fascist aggression prior to World War II was due to their policy of 17)________________. The rise of fascism was one of the causes of World War II. The term fascism is usually applied to any tyrannical or dictatorial government. The term fascist origi ...
... The main reason the United States failed to halt Fascist aggression prior to World War II was due to their policy of 17)________________. The rise of fascism was one of the causes of World War II. The term fascism is usually applied to any tyrannical or dictatorial government. The term fascist origi ...
Outline
... . Hitler and the __________________ _______________________ ________ party were voted to take over Germany - they promised to put the German people back to work and restore ________________________ stability. . Nazis invaded the __________________ _______________________. - led to the weakening of t ...
... . Hitler and the __________________ _______________________ ________ party were voted to take over Germany - they promised to put the German people back to work and restore ________________________ stability. . Nazis invaded the __________________ _______________________. - led to the weakening of t ...
Slide 1
... Mikhail Gorbachev was the leader of the U.S.S.R. who began the reforms and changes of glasnost and perestroika in the 1980’s. ...
... Mikhail Gorbachev was the leader of the U.S.S.R. who began the reforms and changes of glasnost and perestroika in the 1980’s. ...
Chapter 13 Test Review Flashcards
... What was the name for the style of warfare used by the Germans in World War II to quickly defeat their enemies using planes and tanks? Blitzkrieg (lightning war) ...
... What was the name for the style of warfare used by the Germans in World War II to quickly defeat their enemies using planes and tanks? Blitzkrieg (lightning war) ...
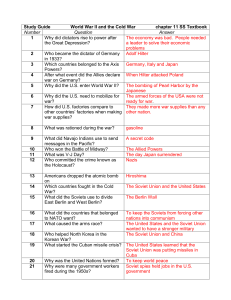
World War 2 Study Guide Answers
... 13. _________Tuskegee Airmen_____ African American fighter pilots during World War II. 14. Why did dictators rise to power after the Great Depression? _______The dictators promised to bring the countries out of the depression by creating jobs that helped the economy.____________________ 15. Who beca ...
... 13. _________Tuskegee Airmen_____ African American fighter pilots during World War II. 14. Why did dictators rise to power after the Great Depression? _______The dictators promised to bring the countries out of the depression by creating jobs that helped the economy.____________________ 15. Who beca ...
Chapter_13__1940s_files/War in Europe
... Soviets want a Second Front • Soviet leader Joseph Stalin pressed the FDR and Churchill to invade Western Europe next. He believed it would force Hitler to take soldiers out of the USSR. The Soviets has suffered terribly from the German invasion eventually losing 22 million people. The Big 3 - Stal ...
... Soviets want a Second Front • Soviet leader Joseph Stalin pressed the FDR and Churchill to invade Western Europe next. He believed it would force Hitler to take soldiers out of the USSR. The Soviets has suffered terribly from the German invasion eventually losing 22 million people. The Big 3 - Stal ...
Pearl Harbor
... Why?: We knew that Germany was working on an atomic weapon, it was important to defeat them before they could do this. ...
... Why?: We knew that Germany was working on an atomic weapon, it was important to defeat them before they could do this. ...
Test 13 - World War II and the Holocaust
... 5. The annexation of Austria by Germany began World War II. 6. Only Jews were targeted by the Nazi campaign to kill “inferior” people. 7. Germany attacking Czechoslovakia is what officially starts World War II. 8. Fascism is a type of government that bans private property, eliminates social classes ...
... 5. The annexation of Austria by Germany began World War II. 6. Only Jews were targeted by the Nazi campaign to kill “inferior” people. 7. Germany attacking Czechoslovakia is what officially starts World War II. 8. Fascism is a type of government that bans private property, eliminates social classes ...
Chapter 29 Review – World War II 1939-1945
... Atlantic Charter – Document signed between Churchill and Roosevelt, recognizing the right of all people to choose their own governments; also proposed disarmament after the war. Pearl Harbor 1941– Bombing of American Navy ships in the harbor of Hawaii on December 7, 1941 – a day that will “live in i ...
... Atlantic Charter – Document signed between Churchill and Roosevelt, recognizing the right of all people to choose their own governments; also proposed disarmament after the war. Pearl Harbor 1941– Bombing of American Navy ships in the harbor of Hawaii on December 7, 1941 – a day that will “live in i ...
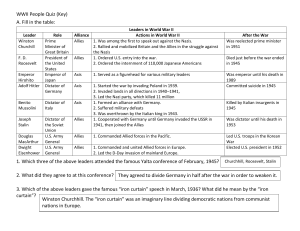
WWII Leaders Quiz Key
... Actions in World War II Allies 1. Was among the first to speak out against the Nazis. 2. Rallied and mobilized Britain and the Allies in the struggle against the Nazis Allies 1. Ordered U.S. entry into the war. 2. Ordered the internment of 110,000 Japanese Americans Axis ...
... Actions in World War II Allies 1. Was among the first to speak out against the Nazis. 2. Rallied and mobilized Britain and the Allies in the struggle against the Nazis Allies 1. Ordered U.S. entry into the war. 2. Ordered the internment of 110,000 Japanese Americans Axis ...
The Rise of Dictators - Social Studies With A Smile
... Japan and Italy feel betrayed by The Treaty of Versailles. Both helped win but were not rewarded. Established goals for territorial expansion Germany-treated harshly-blamed for war, $33 billion in reparations, colonial losses, cannot have military or enter the Rhineland ...
... Japan and Italy feel betrayed by The Treaty of Versailles. Both helped win but were not rewarded. Established goals for territorial expansion Germany-treated harshly-blamed for war, $33 billion in reparations, colonial losses, cannot have military or enter the Rhineland ...
World War II - Cloudfront.net
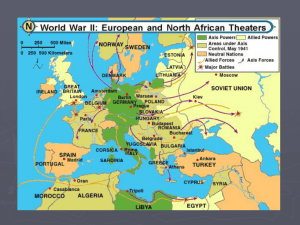
... American troops landed in Africa joined British in pushing Axis forces out of Africa Invasion of Italy in 1943 - “soft underbelly of the Axis” King Victor Emmanuel abdicated Italy withdrew from the war Northern Italy remained occupied by German forces Rome Liberated in June 1944 ...
... American troops landed in Africa joined British in pushing Axis forces out of Africa Invasion of Italy in 1943 - “soft underbelly of the Axis” King Victor Emmanuel abdicated Italy withdrew from the war Northern Italy remained occupied by German forces Rome Liberated in June 1944 ...
Foreign relations of the Axis powers

Foreign relations of the Axis powers includes states which were not officially members of the Axis but had relations with one or more Axis members.