Lecture notes chapter 4
... Alkaline metals or earth metals (2A): Be, Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba, and Ra. They are also reactive (but less reactive than alkali metals). They are metal. They react with water in some conditions to produce the metal hydroxides. Halogens (7A): F, Cl, Br, I, and At. They are reactive (even more reactive than A ...
... Alkaline metals or earth metals (2A): Be, Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba, and Ra. They are also reactive (but less reactive than alkali metals). They are metal. They react with water in some conditions to produce the metal hydroxides. Halogens (7A): F, Cl, Br, I, and At. They are reactive (even more reactive than A ...
Chapter 10
... Predicting Products of Synthesis Reactions For Synthesis Reactions For metals that only form one cation, determine the charge on the ion of each element (metallic and nonmetallic) and form a compound from the two ions. If one of the elements forms more than one cation or 2 nonmetals are combined ...
... Predicting Products of Synthesis Reactions For Synthesis Reactions For metals that only form one cation, determine the charge on the ion of each element (metallic and nonmetallic) and form a compound from the two ions. If one of the elements forms more than one cation or 2 nonmetals are combined ...
Chapters 19 & 20
... Elements in group 1A through 8A are called representative elements because they display a wide range of physical and chemical properties. Representative elements display the range of possible valence electrons from one in group 1A to eight in group 8A. The valence electrons of representative element ...
... Elements in group 1A through 8A are called representative elements because they display a wide range of physical and chemical properties. Representative elements display the range of possible valence electrons from one in group 1A to eight in group 8A. The valence electrons of representative element ...
Group IV Elements
... Si, Ge, Sn,Pb Si most abundant element in Nature afdter O Ge, Sn, Pb are rare elements Sn,Pb have been known since long time, because they can be just melted out of their minerals Ge was discovered after its existance has been predicted. It is purified from coal and zinc ore concentrates ...
... Si, Ge, Sn,Pb Si most abundant element in Nature afdter O Ge, Sn, Pb are rare elements Sn,Pb have been known since long time, because they can be just melted out of their minerals Ge was discovered after its existance has been predicted. It is purified from coal and zinc ore concentrates ...
CHAPTER 2 ATOMS, MOLECULES, AND IONS 1 CHAPTER TWO
... If the formula is In2O3, then two times the atomic mass of In will combine with three times the atomic mass of O, or: ...
... If the formula is In2O3, then two times the atomic mass of In will combine with three times the atomic mass of O, or: ...
Semester 1 Final Exam Study Guide
... 24. A graduated cylinder has 20 ml (cm3) of water placed in it. An irregularly shaped rock is then dropped in the graduated cylinder and the volume of the rock and water in the cylinder now reads 30 ml (cm3). The mass of the rock dropped into the graduated cylinder is 23 grams. a. Find the volume o ...
... 24. A graduated cylinder has 20 ml (cm3) of water placed in it. An irregularly shaped rock is then dropped in the graduated cylinder and the volume of the rock and water in the cylinder now reads 30 ml (cm3). The mass of the rock dropped into the graduated cylinder is 23 grams. a. Find the volume o ...
Topic 4: Classifying Elements What did the early chemists use to
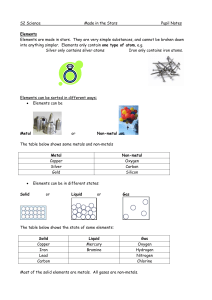
... List FOUR properties of METALS (page 118) solids (except for mercury), shiny, good conductors, malleable/ductile List FOUR properties of NON – METALS (page 118) can be solid, liquid, or gas, not shiny, ...
... List FOUR properties of METALS (page 118) solids (except for mercury), shiny, good conductors, malleable/ductile List FOUR properties of NON – METALS (page 118) can be solid, liquid, or gas, not shiny, ...
4. bonding - New Hartford Central Schools
... Elements with more than one positive oxidation number (Transition Metals) (This is called the Stock System) When the oxidation number varies we us a Roman numeral in parentheses to indicate the charge. Roman number is used for the positive element only!!! ...
... Elements with more than one positive oxidation number (Transition Metals) (This is called the Stock System) When the oxidation number varies we us a Roman numeral in parentheses to indicate the charge. Roman number is used for the positive element only!!! ...
Chemical Equations and Reactions
... into 2 or more simpler substances. Most reactions require heat, light or electricity. ...
... into 2 or more simpler substances. Most reactions require heat, light or electricity. ...
4. bonding - New Hartford Central Schools
... Elements with more than one positive oxidation number (Transition Metals) (This is called the Stock System) When the oxidation number varies we us a Roman numeral in parentheses to indicate the charge. Roman number is used for the positive element only!!! ...
... Elements with more than one positive oxidation number (Transition Metals) (This is called the Stock System) When the oxidation number varies we us a Roman numeral in parentheses to indicate the charge. Roman number is used for the positive element only!!! ...
Outline Chapter 10 The Periodic Law
... • are good conductors of heat and electricity. • Most elements are metals. Non-Metals • may be solid, liquid, or gaseous. • do not have a luster. • are transparent in thin sheets. • Solid nonmetals are brittle. • are insulators. 10-5. Chemical Activity • Active elements combine readily to form compo ...
... • are good conductors of heat and electricity. • Most elements are metals. Non-Metals • may be solid, liquid, or gaseous. • do not have a luster. • are transparent in thin sheets. • Solid nonmetals are brittle. • are insulators. 10-5. Chemical Activity • Active elements combine readily to form compo ...
Chapter 5
... general organization of the table, rows (periods) and columns (groups) main group, transition metals, lanthanides, actinides valence electrons for main group elements alkali metals, alkali earth metals, halogens, noble gases metals, nonmetals, metalloids (semimetals); general properties and location ...
... general organization of the table, rows (periods) and columns (groups) main group, transition metals, lanthanides, actinides valence electrons for main group elements alkali metals, alkali earth metals, halogens, noble gases metals, nonmetals, metalloids (semimetals); general properties and location ...
Review for second exam:
... general organization of the table, rows (periods) and columns (groups) main group, transition metals, lanthanides, actinides valence electrons for main group elements alkali metals, alkali earth metals, halogens, noble gases metals, nonmetals, metalloids (semimetals); general properties and location ...
... general organization of the table, rows (periods) and columns (groups) main group, transition metals, lanthanides, actinides valence electrons for main group elements alkali metals, alkali earth metals, halogens, noble gases metals, nonmetals, metalloids (semimetals); general properties and location ...
Chemical reactions revision
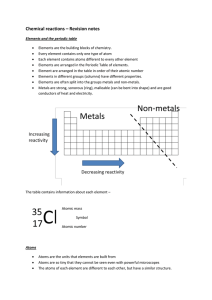
... Element are arranged in the table in order of their atomic number Elements in different groups (columns) have different properties. Elements are often split into the groups metals and non-metals. Metals are strong, sonorous (ring), malleable (can be bent into shape) and are good conductors of heat a ...
... Element are arranged in the table in order of their atomic number Elements in different groups (columns) have different properties. Elements are often split into the groups metals and non-metals. Metals are strong, sonorous (ring), malleable (can be bent into shape) and are good conductors of heat a ...
matter and its reactivity. Objects in the universe are composed of
... 3.1a Substances have characteristic properties. Some of these properties include color, odor, phase, density, solubility, heat and electrical conductivity, and boiling and freezing points. 3.1b Solubility can be affected by the nature of the solute and solvent, temperature, and pressure. The rate of ...
... 3.1a Substances have characteristic properties. Some of these properties include color, odor, phase, density, solubility, heat and electrical conductivity, and boiling and freezing points. 3.1b Solubility can be affected by the nature of the solute and solvent, temperature, and pressure. The rate of ...
Unit 3 - Chemistry
... • The sum of the number of neutrons and the number of protons in a given nucleus is called the _______________. • _______________ • atoms with the same number of protons but different numbers of _______________. • Elements on the periodic table are the most common _______________ of those ...
... • The sum of the number of neutrons and the number of protons in a given nucleus is called the _______________. • _______________ • atoms with the same number of protons but different numbers of _______________. • Elements on the periodic table are the most common _______________ of those ...
Slide 1
... Atoms of this family have 6 valence electrons. Most elements in this family share electrons when forming compounds. Oxygen is the most abundant element in the earth’s crust. It is extremely active and combines with almost all elements. ...
... Atoms of this family have 6 valence electrons. Most elements in this family share electrons when forming compounds. Oxygen is the most abundant element in the earth’s crust. It is extremely active and combines with almost all elements. ...
section_2_review_set
... 1. What is the claim to fame for the proton? 2. What is the claim to fame for the electron? 3. What is the claim to fame for the neutron? 4. What is the mass of each of the following particles?: proton; neutron; electron. 5. What is the charge for each of the following particles?: proton; neutron; e ...
... 1. What is the claim to fame for the proton? 2. What is the claim to fame for the electron? 3. What is the claim to fame for the neutron? 4. What is the mass of each of the following particles?: proton; neutron; electron. 5. What is the charge for each of the following particles?: proton; neutron; e ...
Honors Chemistry
... is essential to all living things, but not in its diatomic form. Nitrogen makes up DNA, amino acids, and therefore, proteins. Compounds containing nitrogen are what living things need and the most important one is ammonia (NH3). Ammonia (g) is prepared through the synthesis of nitrogen and hydrogen ...
... is essential to all living things, but not in its diatomic form. Nitrogen makes up DNA, amino acids, and therefore, proteins. Compounds containing nitrogen are what living things need and the most important one is ammonia (NH3). Ammonia (g) is prepared through the synthesis of nitrogen and hydrogen ...
1.Using the table above, decide if the element mercury (Hg) should
... Aluminum chloride, Al2Cl6 This forms an intermolecular Lewis acid-base dimer where one Cl atom on each AlCl3 donates a pair of electrons to the neighboring Al atom. Boron trifluoride, BF3 This forms partial pi bonds between the B and F atoms. Diborane, B2H6 B-H-B bridges are formed that use only two ...
... Aluminum chloride, Al2Cl6 This forms an intermolecular Lewis acid-base dimer where one Cl atom on each AlCl3 donates a pair of electrons to the neighboring Al atom. Boron trifluoride, BF3 This forms partial pi bonds between the B and F atoms. Diborane, B2H6 B-H-B bridges are formed that use only two ...
Nonmetal
In chemistry, a nonmetal (or non-metal) is a chemical element that mostly lacks metallic attributes. Physically, nonmetals tend to be highly volatile (easily vaporised), have low elasticity, and are good insulators of heat and electricity; chemically, they tend to have high ionization energy and electronegativity values, and gain or share electrons when they react with other elements or compounds. Seventeen elements are generally classified as nonmetals; most are gases (hydrogen, helium, nitrogen, oxygen, fluorine, neon, chlorine, argon, krypton, xenon and radon); one is a liquid (bromine); and a few are solids (carbon, phosphorus, sulfur, selenium, and iodine).Moving rightward across the standard form of periodic table, nonmetals adopt structures that have progressively fewer nearest neighbours. Polyatomic nonmetals have structures with either three nearest neighbours, as is the case (for example) with carbon (in its standard state of graphite), or two nearest neighbours (for example) in the case of sulfur. Diatomic nonmetals, such as hydrogen, have one nearest neighbour, and the monatomic noble gases, such as helium, have none. This gradual fall in the number of nearest neighbours is associated with a reduction in metallic character and an increase in nonmetallic character. The distinction between the three categories of nonmetals, in terms of receding metallicity is not absolute. Boundary overlaps occur as outlying elements in each category show (or begin to show) less-distinct, hybrid-like or atypical properties.Although five times more elements are metals than nonmetals, two of the nonmetals—hydrogen and helium—make up over 99 per cent of the observable Universe, and one—oxygen—makes up close to half of the Earth's crust, oceans and atmosphere. Living organisms are also composed almost entirely of nonmetals, and nonmetals form many more compounds than metals.