Chapter 36. AC Circuits
... Where VC is the maximum voltage across the capacitor, also equal to the maximum emf. The instantaneous current in the circuit is ...
... Where VC is the maximum voltage across the capacitor, also equal to the maximum emf. The instantaneous current in the circuit is ...
Ohm`s Law - Power
... As the denominator increases the fraction decreases. In fact if the denominator doubles then the fraction is half the size. 1/4 is half the size of 1/2. I is the same as 1/R. This is an inverse proportion. If I is the same as 1/R and R is increased in size by three times, then the fraction 1/R is a ...
... As the denominator increases the fraction decreases. In fact if the denominator doubles then the fraction is half the size. 1/4 is half the size of 1/2. I is the same as 1/R. This is an inverse proportion. If I is the same as 1/R and R is increased in size by three times, then the fraction 1/R is a ...
Current-Mode Logic
... working with low voltages and actually taking advantage of leakage current, we hope that we can obtain the same performance of voltage logic and have low power consumption. Effectively, we would actually like to take advantage of this flaw in today’s MOSFETs. Plan: To begin we will research technolo ...
... working with low voltages and actually taking advantage of leakage current, we hope that we can obtain the same performance of voltage logic and have low power consumption. Effectively, we would actually like to take advantage of this flaw in today’s MOSFETs. Plan: To begin we will research technolo ...
Student Notes - Harrisonville Schools
... 36. What is the difference between a series circuit and a parallel circuit? ...
... 36. What is the difference between a series circuit and a parallel circuit? ...
Electricity - Logan Petlak
... electric charge and current electricity (e.g., Thales, Robert Boyle, Benjamin Franklin, Michael Faraday, Nikola Tesla, Georg Ohm, Alessandro Volta, André-Marie Ampère, James Wimshurst, and Robert Van de Graaff), and past and present careers that require an understanding of static electric charge and ...
... electric charge and current electricity (e.g., Thales, Robert Boyle, Benjamin Franklin, Michael Faraday, Nikola Tesla, Georg Ohm, Alessandro Volta, André-Marie Ampère, James Wimshurst, and Robert Van de Graaff), and past and present careers that require an understanding of static electric charge and ...
05 CMNB Block 3 Session 4
... membrane within a very small time (nannoseconds?). At 1ms, dV/dt = 0. The voltage is not changing with time during the step. Thus, from the equation, Icap = C * zero so Icap = zero. It is one of the important features of the voltage clamp technique that the capacitive current charges the membrane qu ...
... membrane within a very small time (nannoseconds?). At 1ms, dV/dt = 0. The voltage is not changing with time during the step. Thus, from the equation, Icap = C * zero so Icap = zero. It is one of the important features of the voltage clamp technique that the capacitive current charges the membrane qu ...
Lecture 20
... The frame of area A and loop number N is rotated with uniform angular velocity w. At time t=0, the angle q=0. Calculate and sketch as a function of time (a) the induced emf E(t) and (b) the power P(t) dissipated in the bulb. ...
... The frame of area A and loop number N is rotated with uniform angular velocity w. At time t=0, the angle q=0. Calculate and sketch as a function of time (a) the induced emf E(t) and (b) the power P(t) dissipated in the bulb. ...
E and M Review for Final
... 20. Why is the energy stored in a capacitor less than the energy associated with moving the same amount of total charge through the same potential difference? ...
... 20. Why is the energy stored in a capacitor less than the energy associated with moving the same amount of total charge through the same potential difference? ...
- Catalyst
... a) The conversion to decibels would be 20Log(Vout/Vin) = 20Log(2.83/1) = 9.036dB b) Vth is applied to the base and Rth is the effective resistance at this point. Vth/Rth will determine how much current available to the base. In this case, Rth = R2||R6. Vth is determined by Vcc*(R6/(R6+R2)) = Vth. c) ...
... a) The conversion to decibels would be 20Log(Vout/Vin) = 20Log(2.83/1) = 9.036dB b) Vth is applied to the base and Rth is the effective resistance at this point. Vth/Rth will determine how much current available to the base. In this case, Rth = R2||R6. Vth is determined by Vcc*(R6/(R6+R2)) = Vth. c) ...
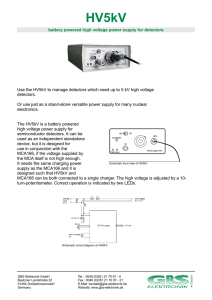
battery powered high voltage power supply for detectors Use the
... Use the HV5kV to manage detectors which need up to 5 kV high voltage detectors. Or use just as a stand-alone versatile power supply for many nuclear electronics. The HV5kV is a battery powered high voltage power supply for semiconductor detectors. It can be used as an independent standalone device, ...
... Use the HV5kV to manage detectors which need up to 5 kV high voltage detectors. Or use just as a stand-alone versatile power supply for many nuclear electronics. The HV5kV is a battery powered high voltage power supply for semiconductor detectors. It can be used as an independent standalone device, ...
Lesson 10 Steady Electric Currents 10.1 Current Density
... In the presence of an electric field E , free electrons in a conductor have a drift (average) v velocity u d . Collisions among free electrons and immobile atoms transfer energy from the v electric field to thermal vibration. Quantitatively, the work done by E in moving an amount v v v of charge Q f ...
... In the presence of an electric field E , free electrons in a conductor have a drift (average) v velocity u d . Collisions among free electrons and immobile atoms transfer energy from the v electric field to thermal vibration. Quantitatively, the work done by E in moving an amount v v v of charge Q f ...
Circuits Class Notes - Hicksville Public Schools / Homepage
... the object after it is moved. b. A constant force will be needed to keep the charge where it is. If the object were released, how much kinetic energy would it gain? ...
... the object after it is moved. b. A constant force will be needed to keep the charge where it is. If the object were released, how much kinetic energy would it gain? ...
Recall-Lecture 7 - International Islamic University Malaysia
... branch – Step 2: Set the conditions to know whether diode is on or off – sketch your output waveform ...
... branch – Step 2: Set the conditions to know whether diode is on or off – sketch your output waveform ...
Electrical Safety - the Mining Quiz List
... Electrical Shock The amount of current that flows through the ...
... Electrical Shock The amount of current that flows through the ...
Tute 2 PDF document
... (f) The rate of development of heat at this instant. (g) The rate at which the energy of the magnetic field is increasing at this instant. (h) The energy stored in the magnetic field when the current has attained its steady value. 05) A condenser of capacity 0.02F is discharged through an inductanc ...
... (f) The rate of development of heat at this instant. (g) The rate at which the energy of the magnetic field is increasing at this instant. (h) The energy stored in the magnetic field when the current has attained its steady value. 05) A condenser of capacity 0.02F is discharged through an inductanc ...
Document
... Example: If a battery cell provides 3.0 J of electrical potential energy in moving 2 coulombs of charge through the cell, what is the potential difference (or voltage) of the cell? 3.0 Joules E V 1.5 Volts q 2.0 Coulombs ...
... Example: If a battery cell provides 3.0 J of electrical potential energy in moving 2 coulombs of charge through the cell, what is the potential difference (or voltage) of the cell? 3.0 Joules E V 1.5 Volts q 2.0 Coulombs ...
Alternating Current Electricity
... The meters used to measure the voltage will give rms values, not actual voltages at a point in time The voltages across the resistor and capacitor are out of phase with each other ie they do not both reach maxs and mins at the same time. ...
... The meters used to measure the voltage will give rms values, not actual voltages at a point in time The voltages across the resistor and capacitor are out of phase with each other ie they do not both reach maxs and mins at the same time. ...
Conceptual Tools
... Note that the powers dissipated by the components inside the box sum to give the total power dissipated, 12 W. The resistor, however, is dissipating much more power than the entire box! This power creates heat. The heat from the resistor is much larger than the power dissipated by the entire box. Th ...
... Note that the powers dissipated by the components inside the box sum to give the total power dissipated, 12 W. The resistor, however, is dissipating much more power than the entire box! This power creates heat. The heat from the resistor is much larger than the power dissipated by the entire box. Th ...