* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Recall-Lecture 7 - International Islamic University Malaysia
Spark-gap transmitter wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Ground loop (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Signal-flow graph wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Stepper motor wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Analog-to-digital converter wikipedia , lookup
Oscilloscope history wikipedia , lookup
Optical rectenna wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Semiconductor device wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Network analysis (electrical circuits) wikipedia , lookup
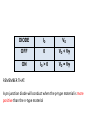
Recall Lecture 8 • Standard Clipper Circuit – Step 1: Find the clip value by doing KVL at the output branch – Step 2: Set the conditions to know whether diode is on or off – sketch your output waveform • Clipper in series – clips at zero. It is similar to half wave where the diode only turns on during one of the cycle. Clamper Clampers ● Clamping shifts the entire signal voltage by a DC level. Consider, the sinusoidal input voltage signal, vI. 1st 900, the capacitor is charged up to the peak value of VI which is VM. Then, as VI moves towards the –ve cycle, the diode is reverse biased. Ideally, capacitor cannot discharge, hence Vc = VM By KVL, we get NOTE: The input signal is shifted by a dc level; and that the peak-to-peak value is the same Clampers ● A clamping circuit that includes an independent voltage source VB. Peak value VM STEP 1: Knowing what value that the capacitor is charged to. And from the polarity of the diode, we know that it is charged during positive cycle. Using KVL, VC + VB – VS = 0 VC = VM – VB STEP 2: When the diode is reversed biased and VC is already a constant value VO – VS + VC = 0 VO = VS – VC. EXAMPLE – clampers with ideal diode For the circuit shown in figure below, sketch the waveforms of the output voltage, vout. The input voltage is a sine wave where vin = 20 sin t. Assume ideal diodes. Vin What if the diode is non-ideal? Vi C + + Vi Vo - 5V The diode is a non-ideal with V = 0.7V - 10 t -4.3 -10 -14.3 -24.3 Step 1: VC + V - VB – Vi = 0 VC = 10 + 5 – 0.7 = 14.3V Step 2: VO – Vi + VC = 0 VO = Vi – 14.3. Multiple Diode Circuits Final Exam SEM I 2013/2014 DIODE ID VD OFF 0 VD < V ON ID > 0 VD = V REMEMBER THAT: A pn junction diode will conduct when the p-type material is more positive than the n-type material OR GATE Vo = voltage across R V1 V2 VO D1 and D2 off; no current flow, 0 0 0 D1 off, D2 on, current flow, Vo – V2 + V = 0 0 5V ( 1 ) 4.3V D1 on, D2 off, current flow, Vo – V1 + V = 0 5V ( 1 ) 0 4.3V Both on, using both loops will give the same equation 5V ( 1 ) 5V ( 1 ) 4.3V AND GATE Vo = node voltage V1 V2 VO Both on, using both loops will give the same equation 0 0 0.7 D1 on, D2 off 0 5V ( 1 ) 0.7 D1 off, D2 on 5V ( 1 ) 0 0.7V Both are off; open circuit no current flowing through R since no GND destination 5V ( 1 ) 5V ( 1 ) 5V