PlantFunction-English
... Dicot plants have broad leaves with a net-type of veins. Stems are often long and branching. They may be woody or non-woody, depending on the plant species. ...
... Dicot plants have broad leaves with a net-type of veins. Stems are often long and branching. They may be woody or non-woody, depending on the plant species. ...
Week Nine notes
... deliberately got holes in them) and others design trickle irrigation systems. The problem with these can be that once you have buried them its really easy to put your fork through them. We tried using them in the Large greenhouse but eventurally gave up due to this problem. Plants try to save water. ...
... deliberately got holes in them) and others design trickle irrigation systems. The problem with these can be that once you have buried them its really easy to put your fork through them. We tried using them in the Large greenhouse but eventurally gave up due to this problem. Plants try to save water. ...
Water Plants How-To.pub
... Submerged or Oxygena ng Plants: The roots of these plants are anchored in soil, but the leaves stay underwater. Their foliage is usually fern‐like, lacy, or hairy. They play a vital role in maintaining the pond's natural balance. These plants use waste nutrients and help purify the water. This, in t ...
... Submerged or Oxygena ng Plants: The roots of these plants are anchored in soil, but the leaves stay underwater. Their foliage is usually fern‐like, lacy, or hairy. They play a vital role in maintaining the pond's natural balance. These plants use waste nutrients and help purify the water. This, in t ...
vascular plants
... SPORE - in the life cycle of a plant or alga undergoing alternat ion of generations, a meiotically produced haploid cell that divides mitotically, generating a multicellular individual, the gametophyte, without fusing with another cell SORUS (pl=sori): a cluster of sporangia on a fern sporophyll. ST ...
... SPORE - in the life cycle of a plant or alga undergoing alternat ion of generations, a meiotically produced haploid cell that divides mitotically, generating a multicellular individual, the gametophyte, without fusing with another cell SORUS (pl=sori): a cluster of sporangia on a fern sporophyll. ST ...
Plant Test
... the nutrient found in the cotyledons which nourishes the embryo that part of any plant which is the growing part having vessels which transport nutrients and water to plant cells a plant have one seed leaf a plant which has vascular tissue but does not reproduce using seeds the holes on the bottom o ...
... the nutrient found in the cotyledons which nourishes the embryo that part of any plant which is the growing part having vessels which transport nutrients and water to plant cells a plant have one seed leaf a plant which has vascular tissue but does not reproduce using seeds the holes on the bottom o ...
Care of Holiday Plants
... -Keep soil evenly moist -Do not let water settle in center of bulb Reblooming: -Very difficult!! -After flowering, reduce watering so that foliage dies. Withhold water for 6-8 weeks -When watering resumes, place in cool window -As new leaves develop, place in sunny location; water Holiday Cactus: Ca ...
... -Keep soil evenly moist -Do not let water settle in center of bulb Reblooming: -Very difficult!! -After flowering, reduce watering so that foliage dies. Withhold water for 6-8 weeks -When watering resumes, place in cool window -As new leaves develop, place in sunny location; water Holiday Cactus: Ca ...
Plants - GZ @ Science Class Online
... the Seeds are mature they then also need to be dispersed so they are not competing with the parent plant for space, light, water and nutrients. There are various ways that plants have evolved to disperse their seeds; forming inside fruit that animals will eat and spread, forming structures on the se ...
... the Seeds are mature they then also need to be dispersed so they are not competing with the parent plant for space, light, water and nutrients. There are various ways that plants have evolved to disperse their seeds; forming inside fruit that animals will eat and spread, forming structures on the se ...
Plant_Anatomy
... the environment Cotyledons contain the endosperm, a nutritive tissue that accumulates starch, protein, and fats to provide for the growth of the embryo Epicotyl in most plants develop into the leaves Hypocotyl develops into the stem Radicle first to emerge from the seed and develops into the root ...
... the environment Cotyledons contain the endosperm, a nutritive tissue that accumulates starch, protein, and fats to provide for the growth of the embryo Epicotyl in most plants develop into the leaves Hypocotyl develops into the stem Radicle first to emerge from the seed and develops into the root ...
Plant Structure and Growth
... support for plant organs like leaves and stems without secondary growth - e.g. strings in celery Sclerenchyma - usually nonliving cells - cell walls reinforced with lignin fibers - long slender cells grouped together into strands that provide support - e.g. linen fibers from flax addition of fibers ...
... support for plant organs like leaves and stems without secondary growth - e.g. strings in celery Sclerenchyma - usually nonliving cells - cell walls reinforced with lignin fibers - long slender cells grouped together into strands that provide support - e.g. linen fibers from flax addition of fibers ...
Plant Study Questions
... a. Make their own food (photosynthesis) b. Has a cuticle c. Has a cell wall d. Reproduces using spores or sex cells 2. What is the organelle where photosynthesis occurs? a. Chloroplast 3. What makes a plant green? a. chlorophyll 4. What is the purpose of a cuticle? a. Waxy layer that holds the moist ...
... a. Make their own food (photosynthesis) b. Has a cuticle c. Has a cell wall d. Reproduces using spores or sex cells 2. What is the organelle where photosynthesis occurs? a. Chloroplast 3. What makes a plant green? a. chlorophyll 4. What is the purpose of a cuticle? a. Waxy layer that holds the moist ...
plant form and function
... There are 2 types of lateral meristems: a. Vascular cambiums: this produces secondary xylem and phloems which are actually wood. The vascular cambium is the source of both the secondary xylem the secondary phloem. b. Cork cambiums – replace the epidermis with peridermis which is bark or cork in some ...
... There are 2 types of lateral meristems: a. Vascular cambiums: this produces secondary xylem and phloems which are actually wood. The vascular cambium is the source of both the secondary xylem the secondary phloem. b. Cork cambiums – replace the epidermis with peridermis which is bark or cork in some ...
chapt 22
... later, captain of his own vessel, owner of a small freighter fleet and with a major interest in a few oil tankers, he indulged in a nostalgic whim and returned for the first time ever, to his old hometown. Imagine his joy, when he discovered his old sweetheart living there, now a widow.One thing led ...
... later, captain of his own vessel, owner of a small freighter fleet and with a major interest in a few oil tankers, he indulged in a nostalgic whim and returned for the first time ever, to his old hometown. Imagine his joy, when he discovered his old sweetheart living there, now a widow.One thing led ...
lecture outline
... o Some parenchyma cells in the stems and roots have colorless plastids that store starch. o The fleshy tissue of most fruit is composed of parenchyma cells. Most parenchyma cells retain the ability to divide and differentiate into other cell types under special conditions, such as the repair and rep ...
... o Some parenchyma cells in the stems and roots have colorless plastids that store starch. o The fleshy tissue of most fruit is composed of parenchyma cells. Most parenchyma cells retain the ability to divide and differentiate into other cell types under special conditions, such as the repair and rep ...
Introduction to Plants
... which are comprised of tissues that form internal passageways through which water and dissolved nutrients can traverse the entire plant. Vascular plants are thus far less reliant on moist environments for survival. At the same time, Vascular systems also provide a strong system of support to the pla ...
... which are comprised of tissues that form internal passageways through which water and dissolved nutrients can traverse the entire plant. Vascular plants are thus far less reliant on moist environments for survival. At the same time, Vascular systems also provide a strong system of support to the pla ...
Introductions to the Kingdoms of Life
... Nutrition – Heterotrophs with digestive tract Reproduction – Sexual with external eggs needing water Growth and Development – endoskeleton; ...
... Nutrition – Heterotrophs with digestive tract Reproduction – Sexual with external eggs needing water Growth and Development – endoskeleton; ...
NOTES FOR THE MIGHTY PLANTOFE
... The three types of lichens (Not Plant Kingdom –Fungi and Protist) Crustose: Forms a crust, difficult to remove without crumbling. Foliose: Leafy, can be peeled off rock with knife. ...
... The three types of lichens (Not Plant Kingdom –Fungi and Protist) Crustose: Forms a crust, difficult to remove without crumbling. Foliose: Leafy, can be peeled off rock with knife. ...
Care of Holiday Plants, Wreaths and Trees Flowering Holiday Plants
... -Cut back tall growth & old flower stems -During spring and summer provide bright light -Fertilize monthly -Give the plant 6 weeks of short days (8-10 hours of light) and long nights (14-16 hours of complete dark). When buds are visible, day length is no longer critical ...
... -Cut back tall growth & old flower stems -During spring and summer provide bright light -Fertilize monthly -Give the plant 6 weeks of short days (8-10 hours of light) and long nights (14-16 hours of complete dark). When buds are visible, day length is no longer critical ...
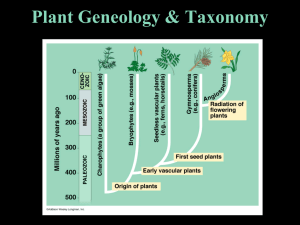
Plant Geneology & Taxonomy
... Special vessel-like system for transmission of fluids internally. A. Non-Seed Bearing Reproduce through spores • Examples: Horsetail, Ferns ...
... Special vessel-like system for transmission of fluids internally. A. Non-Seed Bearing Reproduce through spores • Examples: Horsetail, Ferns ...
Aquatic Weed Control - Identification
... groups; algae and flowering plants. Algae are usually structurally very simple with no apparent roots, leaves, or stems. However, some (for example, Chara) can resemble flowering plants. Flowering plants have roots, shoots, shoots, and stems. You must be able to distinguish between algae and floweri ...
... groups; algae and flowering plants. Algae are usually structurally very simple with no apparent roots, leaves, or stems. However, some (for example, Chara) can resemble flowering plants. Flowering plants have roots, shoots, shoots, and stems. You must be able to distinguish between algae and floweri ...
THE GREAT PLANT ESCAPE
... Seed producing vascular plants-All other plants are seed plants. They can produce seeds in cones(cones in pine trees) or have seeds in flowers. ...
... Seed producing vascular plants-All other plants are seed plants. They can produce seeds in cones(cones in pine trees) or have seeds in flowers. ...
The Plant Kingdom
... The cells are quite transparent and permit most of the light that strikes them to pass through to the underlying cells. The upper surface is covered with a waxy, waterproof _________________________, which serves to reduce water loss from the leaf. 2. _______________ ______________: This consists of ...
... The cells are quite transparent and permit most of the light that strikes them to pass through to the underlying cells. The upper surface is covered with a waxy, waterproof _________________________, which serves to reduce water loss from the leaf. 2. _______________ ______________: This consists of ...
Life Processes and Living Systems
... are later found inside the fruit. Mosses and ferns reproduce from spores. Spores are special cells that can live a long time without water. When spores do get enough water, they grow into new plants. ...
... are later found inside the fruit. Mosses and ferns reproduce from spores. Spores are special cells that can live a long time without water. When spores do get enough water, they grow into new plants. ...
Xylem
Xylem is one of the two types of transport tissue in vascular plants, phloem being the other. The word xylem is derived from the Greek word ξύλον (xylon), meaning ""wood""; the best-known xylem tissue is wood, though it is found throughout the plant.The basic function of xylem is to transport water, but it also transports some nutrients.