A Pattern Language for Secure Operating System Architectures
... into segments that correspond to logical units in the programs. Use special words (descriptors) to represent access rights for these segments. • Reference Monitor. How to enforce authorizations when a process requests access to an object? Define an abstract process that intercepts all requests for r ...
... into segments that correspond to logical units in the programs. Use special words (descriptors) to represent access rights for these segments. • Reference Monitor. How to enforce authorizations when a process requests access to an object? Define an abstract process that intercepts all requests for r ...
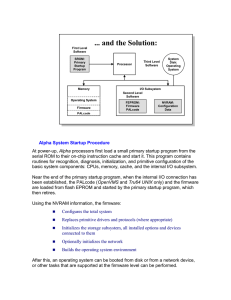
Alpha System Startup Procedure
... Configuration data, called environment variables, are stored in nonvoltile RAM. Most of these variables can be altered by the user. These settings are used by the firmware and the operating systems. Both operating system and hardware support is provided by firmware, PALcode, and environment variable ...
... Configuration data, called environment variables, are stored in nonvoltile RAM. Most of these variables can be altered by the user. These settings are used by the firmware and the operating systems. Both operating system and hardware support is provided by firmware, PALcode, and environment variable ...
Structuring of the Windows Operating System
... ! Windows Server 2003 has its own checked build ! See Knowledge base article 314743 (HOWTO: Enable Verbose Debug Tracing in Various Drivers and Subsystems) ...
... ! Windows Server 2003 has its own checked build ! See Knowledge base article 314743 (HOWTO: Enable Verbose Debug Tracing in Various Drivers and Subsystems) ...
Memory manager
... efficient use on input/output devices. The responsibilities of a device manager: Monitor every I/O device constantly to assure that the device is functioning properly. Maintains a queue for each I/O device or one or more queues for similar I/O devices. Control the different policies for accessin ...
... efficient use on input/output devices. The responsibilities of a device manager: Monitor every I/O device constantly to assure that the device is functioning properly. Maintains a queue for each I/O device or one or more queues for similar I/O devices. Control the different policies for accessin ...
Process
... libraries, rather than system calls, hence no call to OS and no interrupts to kernel One key difference with processes: when a thread is finished running for the moment, it can call thread_yield. This instruction (a) saves the thread information in the thread table itself, and (b) calls the thread s ...
... libraries, rather than system calls, hence no call to OS and no interrupts to kernel One key difference with processes: when a thread is finished running for the moment, it can call thread_yield. This instruction (a) saves the thread information in the thread table itself, and (b) calls the thread s ...
No Slide Title
... When reading a file, if a gap in the virtual cluster numbers is found, NTFS just zero-fills that portion of the caller’s buffer ...
... When reading a file, if a gap in the virtual cluster numbers is found, NTFS just zero-fills that portion of the caller’s buffer ...
File System
... When reading a file, if a gap in the virtual cluster numbers is found, NTFS just zero-fills that portion of the caller’s buffer ...
... When reading a file, if a gap in the virtual cluster numbers is found, NTFS just zero-fills that portion of the caller’s buffer ...
ch19
... hardware supports virtual to physical mapping a paging mechanism, transparent cache coherence on multiprocessor systems, and virtual ...
... hardware supports virtual to physical mapping a paging mechanism, transparent cache coherence on multiprocessor systems, and virtual ...
Introduction to Processes
... • Parent may terminate execution of child processes (abort): – Child has exceeded allocated resources. – Mission assigned to child is no longer required. – If Parent is exiting: • Some OSs do not allow child to continue if its parent terminates. • Cascading termination – all children terminated. ...
... • Parent may terminate execution of child processes (abort): – Child has exceeded allocated resources. – Mission assigned to child is no longer required. – If Parent is exiting: • Some OSs do not allow child to continue if its parent terminates. • Cascading termination – all children terminated. ...
ch4_15_Nov - Parent Directory
... Most systems now a days allow more than one process called Multiprogramming Systems. In case of uni-programming you don’t need to store information about the process as much as you would need to store information about a process being executed in multiprogramming system. ...
... Most systems now a days allow more than one process called Multiprogramming Systems. In case of uni-programming you don’t need to store information about the process as much as you would need to store information about a process being executed in multiprogramming system. ...
... Write: This test measures the performance of writing a new file. When a new file is written not only does the data need to be stored but also the overhead information for keeping track of where the data is located on the storage media. This overhead is called the “metadata” It consists of the direct ...
Operating Systems Principles and Programming More Contact
... $ man 1 command (UNIX command) $ man 2 system call (primitive system calls) $ man 3 library call (e.g., C library, system call front-end stubs) Warning: multiple entries with the same name may appear in different sections of the man pages → run $ man -k name if you are not sure The SEE ALSO section ...
... $ man 1 command (UNIX command) $ man 2 system call (primitive system calls) $ man 3 library call (e.g., C library, system call front-end stubs) Warning: multiple entries with the same name may appear in different sections of the man pages → run $ man -k name if you are not sure The SEE ALSO section ...
Chapter 3 Process Description and Control
... both main and secondary memory. • Must include this information: – Allocation of main memory to processes – Allocation of secondary memory to processes – Protection attributes for access to shared memory regions – Information needed to manage virtual memory ...
... both main and secondary memory. • Must include this information: – Allocation of main memory to processes – Allocation of secondary memory to processes – Protection attributes for access to shared memory regions – Information needed to manage virtual memory ...
Notes
... ii. User to Computer Interface – Provides an friendly environment from which user can accomplish their goals. d. OS from the viewpoint that it is User/Computer Interface – The OS acts as an intermediary between the Users/Programmers and the hardware, making it easier for users, programmers, and app ...
... ii. User to Computer Interface – Provides an friendly environment from which user can accomplish their goals. d. OS from the viewpoint that it is User/Computer Interface – The OS acts as an intermediary between the Users/Programmers and the hardware, making it easier for users, programmers, and app ...
Embedded Operating Systems for Real
... hand-held computers is a good example . ii) Single-user, multi-tasking - This is the type of operating system most of us use on our desktop and laptop computers today. Windows 98 and the MacOS are examples of OS that let a single user have several programs in operation at the same time. iii) Multi-u ...
... hand-held computers is a good example . ii) Single-user, multi-tasking - This is the type of operating system most of us use on our desktop and laptop computers today. Windows 98 and the MacOS are examples of OS that let a single user have several programs in operation at the same time. iii) Multi-u ...
Chapter 2: Operating-System Structures
... File-system manipulation - The file system is of particular interest. Programs need to read and write files and directories, create and delete them, search them, list file Information, permission management." ...
... File-system manipulation - The file system is of particular interest. Programs need to read and write files and directories, create and delete them, search them, list file Information, permission management." ...
Nagalaxmi Prasanna Gumpalli`s presentation on Enhancing
... fault handler for the capability that caused the fault. The fault handler is a function that is executed to re-establish a lost capability mapping. In order to do so, the fault handler needs to know about the type of the underlying capability and about the protocol that is used for re-establishment. ...
... fault handler for the capability that caused the fault. The fault handler is a function that is executed to re-establish a lost capability mapping. In order to do so, the fault handler needs to know about the type of the underlying capability and about the protocol that is used for re-establishment. ...
Concurrency: Mutual Exclusion and Synchronization
... section, then no other processes can be executing in their critical sections 2. Progress - If no process is executing in its critical section and there exist some processes that wish to enter their critical section, then the selection of the processes that will enter the critical section next cannot ...
... section, then no other processes can be executing in their critical sections 2. Progress - If no process is executing in its critical section and there exist some processes that wish to enter their critical section, then the selection of the processes that will enter the critical section next cannot ...
LEC6-FileSystem
... ° OS provide a way to map files into the address space of a running process; map() and unmap() • No read or write system calls are needed thereafter ...
... ° OS provide a way to map files into the address space of a running process; map() and unmap() • No read or write system calls are needed thereafter ...
File System Management
... The file system is used not only to store users’ programs and data, but also to support and represent significant portions of the operating system itself. Stallings introduces the traditional file system concepts of: fields represent the smallest logical item of data “understood” by a file-system: e ...
... The file system is used not only to store users’ programs and data, but also to support and represent significant portions of the operating system itself. Stallings introduces the traditional file system concepts of: fields represent the smallest logical item of data “understood” by a file-system: e ...
Section A: Operating Systems Basics
... experience. Discuss the ways in which the myriad options available to a user of a given application are presented via these mechanisms, and discuss how the user is, to a large degree, allowed to work the way he or she wants to, because of the many different ways that exist to perform a function. ...
... experience. Discuss the ways in which the myriad options available to a user of a given application are presented via these mechanisms, and discuss how the user is, to a large degree, allowed to work the way he or she wants to, because of the many different ways that exist to perform a function. ...
Chapter 3
... I/O operations – since user programs cannot execute I/O operations directly, the operating system must provide some means to perform I/O. File-system manipulation – program capability to read, write, create, and delete files. Communications – exchange of information between processes executing eithe ...
... I/O operations – since user programs cannot execute I/O operations directly, the operating system must provide some means to perform I/O. File-system manipulation – program capability to read, write, create, and delete files. Communications – exchange of information between processes executing eithe ...
Files and File Systems • files: persistent, named data objects – data
... – an i-number is a unique (within a file system) identifier for a file or directory – given an i-number, the file system can file the data and meta-data the file • Directories provide a way for applications to group related files • Since directories can be nested, a filesystem’s directories can be v ...
... – an i-number is a unique (within a file system) identifier for a file or directory – given an i-number, the file system can file the data and meta-data the file • Directories provide a way for applications to group related files • Since directories can be nested, a filesystem’s directories can be v ...