Demonstration - Faculty Pages
... Show that when t is 5 times the time constant, , the capacitor voltage is 99.33% of the peak voltage. ...
... Show that when t is 5 times the time constant, , the capacitor voltage is 99.33% of the peak voltage. ...
Test Procedure for the LV5683PGEVB Evaluation Board SANYO Semiconductors
... Refer to Fig1, In initial setting, “USB_EN”, “SWU_EN”, “AUDIO_EN” pins are shorted GND. And USB, AUDIO and SWU-OUT are low potential. 2. Measurement Connect VCC/VCC1 cable and GND cable. Bias VCC/VCC1 voltage. Regarding bias voltage range, refer to Application note. Next step remove 3 “Shorted Ring” ...
... Refer to Fig1, In initial setting, “USB_EN”, “SWU_EN”, “AUDIO_EN” pins are shorted GND. And USB, AUDIO and SWU-OUT are low potential. 2. Measurement Connect VCC/VCC1 cable and GND cable. Bias VCC/VCC1 voltage. Regarding bias voltage range, refer to Application note. Next step remove 3 “Shorted Ring” ...
RC Time Constant Lab
... The purpose of this lab is to verify that a series RC circuit does in fact decay exponentially. To do this, we measure a resistance and capacitance (out of circuit), and then we measure the voltage on the capacitor as a function of time when it is decaying in series through the resistor. Is R times ...
... The purpose of this lab is to verify that a series RC circuit does in fact decay exponentially. To do this, we measure a resistance and capacitance (out of circuit), and then we measure the voltage on the capacitor as a function of time when it is decaying in series through the resistor. Is R times ...
wiSCAPETM Photo Sensor - Hubbell Control Solutions
... this sensor continuously measures daylight levels and sends the information to the module. The applicable foot-candle range is selected by using a jumper beneath the front cover. ...
... this sensor continuously measures daylight levels and sends the information to the module. The applicable foot-candle range is selected by using a jumper beneath the front cover. ...
Abstract - Rockwell Automation Knowledgebase
... the main menu of Emonitor Odyssey. “Bias Voltage” should be selected as the input type with units of Vdc and Calibration value of 1000. ...
... the main menu of Emonitor Odyssey. “Bias Voltage” should be selected as the input type with units of Vdc and Calibration value of 1000. ...
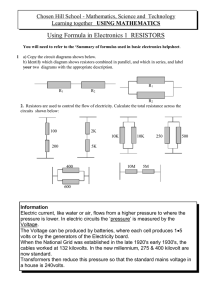
Voltage Divider circuits
... much current through Vout it will affect the output voltage. Therefore this shouldn’t be used for high-current applications like power supplies (voltage regulators are a much better option). To pick resistors, use the following equation: ...
... much current through Vout it will affect the output voltage. Therefore this shouldn’t be used for high-current applications like power supplies (voltage regulators are a much better option). To pick resistors, use the following equation: ...
Physics 2102 Spring 2002 Lecture 8
... RC Circuits: Charging a Capacitor In these circuits, current will change for a while, and then stay constant. We want to solve for current as a function of time i(t)=dq/dt. The charge on the capacitor will also be a function of time: q(t). The voltage across the resistor and the capacitor also chan ...
... RC Circuits: Charging a Capacitor In these circuits, current will change for a while, and then stay constant. We want to solve for current as a function of time i(t)=dq/dt. The charge on the capacitor will also be a function of time: q(t). The voltage across the resistor and the capacitor also chan ...
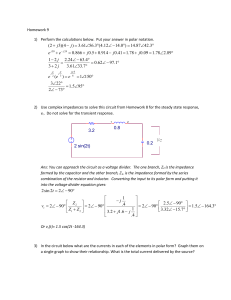
2 sin 2 2 90 1 2.5 90 .4 2 90 2 90 2 90 1.5 164.3 1 3.32 15.7 3.2 1.6
... Ans: We can combine the impedance of the inductor in series with the resistor to form the total impedance in the circuit. The current is then the voltage source divided by this impedance. We can then find the voltage across the inductor and the resistor in turn by multiplying the impedance of each e ...
... Ans: We can combine the impedance of the inductor in series with the resistor to form the total impedance in the circuit. The current is then the voltage source divided by this impedance. We can then find the voltage across the inductor and the resistor in turn by multiplying the impedance of each e ...
Test Procedure for the LV56801PGEVB Evaluation Board SANYO Semiconductors
... varied through the specified range. It is measured by changing the input voltage and measuring the minimum/maximum voltage of the output. Line regulation is defined as the difference between maximum and minimum voltage. ...
... varied through the specified range. It is measured by changing the input voltage and measuring the minimum/maximum voltage of the output. Line regulation is defined as the difference between maximum and minimum voltage. ...
Voltage tuning
... For the PAC Chargers Tuning The Output Voltage: If The battery is charged in a very cold place or desired constant voltage didn’t found from the charging algorithm list, then there is a need to tune the output voltage. The output voltage can be tuned +/-5% from its nominal value. ...
... For the PAC Chargers Tuning The Output Voltage: If The battery is charged in a very cold place or desired constant voltage didn’t found from the charging algorithm list, then there is a need to tune the output voltage. The output voltage can be tuned +/-5% from its nominal value. ...
Current – Voltage Graphs
... (a) define resistance; (b) select and use the equation for resistance (c) define the ohm; (d) state and use Ohm’s law; (e) describe an experiment to obtain the I–V characteristics of a resistor at constant temperature, filament lamp and light-emitting diode (LED); ...
... (a) define resistance; (b) select and use the equation for resistance (c) define the ohm; (d) state and use Ohm’s law; (e) describe an experiment to obtain the I–V characteristics of a resistor at constant temperature, filament lamp and light-emitting diode (LED); ...
GS-R400/2 Family
... a 32°C temperature increase of the module surface for 4W of internal power dissipation. Depending on the ambient temperature and/or on the power dissipation, an additional heatsink or forced ventilation may be required. Input Impedance The module has an internal capacitor connected between the input ...
... a 32°C temperature increase of the module surface for 4W of internal power dissipation. Depending on the ambient temperature and/or on the power dissipation, an additional heatsink or forced ventilation may be required. Input Impedance The module has an internal capacitor connected between the input ...
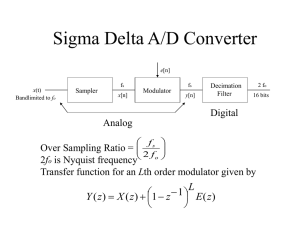
Sigma Delta A/D converters
... – Finite DC gain (“integrator leakage”) causes DC offset and increased baseband noise – Always build the best possible op-amp for the first integrator ...
... – Finite DC gain (“integrator leakage”) causes DC offset and increased baseband noise – Always build the best possible op-amp for the first integrator ...
STATE UNIVERSITY OF NEW YORK COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY CANTON, NEW YORK
... ACTIVITY: Two hours lecture and two hours laboratory per week H. CATALOG DESCRIPTION: This course is designed to prepare students with industrial power electronics skills necessary to function as technologist. Topics include: Solid States Devices, Photo-Electronics, Inverters, Operational Amplifie ...
... ACTIVITY: Two hours lecture and two hours laboratory per week H. CATALOG DESCRIPTION: This course is designed to prepare students with industrial power electronics skills necessary to function as technologist. Topics include: Solid States Devices, Photo-Electronics, Inverters, Operational Amplifie ...
emitter-follower
... CC Amplifier or Emitter Follower The common-collector(CC) amplifier is usually referred to as an emitter-follower(EF). The input is applied to the base through a coupling capacitor, and the output is at the emitter. The voltage gain of a CC amplifier is approximately 1, and its main advantages are ...
... CC Amplifier or Emitter Follower The common-collector(CC) amplifier is usually referred to as an emitter-follower(EF). The input is applied to the base through a coupling capacitor, and the output is at the emitter. The voltage gain of a CC amplifier is approximately 1, and its main advantages are ...
HIGH/LOW VOLTAGE OR CURRENT ALARM UNIT
... With the monitoring unit pe9003µC-G as desktop version it is possible to monitor DC output voltages or currents of DC power supplies ...
... With the monitoring unit pe9003µC-G as desktop version it is possible to monitor DC output voltages or currents of DC power supplies ...
Test Procedure for the LV5693PGEVB Evaluation Board SANYO Semiconductors TEST Procedure
... Line regulation is defined as the maximum change in output voltage as the input voltage is varied through the specified range. It is measured by changing the input voltage and measuring the minimum/maximum voltage of the output. Line regulation is defined as the difference between maximum and minimu ...
... Line regulation is defined as the maximum change in output voltage as the input voltage is varied through the specified range. It is measured by changing the input voltage and measuring the minimum/maximum voltage of the output. Line regulation is defined as the difference between maximum and minimu ...
Abstract - PG Embedded systems
... inductor of the transformer will cause serious problems such as voltage spike on the main switch and high power dissipation. In order to improve the conversion efficiency and obtain high stepup voltage gain, many converter structures have been presented. Switched capacitor and voltage lift technique ...
... inductor of the transformer will cause serious problems such as voltage spike on the main switch and high power dissipation. In order to improve the conversion efficiency and obtain high stepup voltage gain, many converter structures have been presented. Switched capacitor and voltage lift technique ...
Absorb current spikes and noise with a simple technique
... Noise is one error that you cannot calibrate with your processor or controller. The reference noise at the output of the converter grows larger with the analog input voltage (Figure 2). Data sheets for most voltage references have an output-voltage-noise specification over a 0.1- to 10-Hz frequency ...
... Noise is one error that you cannot calibrate with your processor or controller. The reference noise at the output of the converter grows larger with the analog input voltage (Figure 2). Data sheets for most voltage references have an output-voltage-noise specification over a 0.1- to 10-Hz frequency ...
Presentation no 1 - Group5Weatherstation
... The Wheatstone bridge is a measurement instrument used to measure an unknown electrical resistance by balancing two legs of a bridge circuit, one leg of which includes the unknown component. It is an extremely accurate way of measuring resistances and has an unlimited array of applications in indus ...
... The Wheatstone bridge is a measurement instrument used to measure an unknown electrical resistance by balancing two legs of a bridge circuit, one leg of which includes the unknown component. It is an extremely accurate way of measuring resistances and has an unlimited array of applications in indus ...
review
... is sum of voltage of two series dc sources. In this state, because both two sources are active, D1 and D2 are forward biased and D3 and D4 are reverse biased. Thus the sources current enters in Z-network through D1 and D2 and after passing load impedance, comes back into sources through negative pol ...
... is sum of voltage of two series dc sources. In this state, because both two sources are active, D1 and D2 are forward biased and D3 and D4 are reverse biased. Thus the sources current enters in Z-network through D1 and D2 and after passing load impedance, comes back into sources through negative pol ...
Integrating ADC
An integrating ADC is a type of analog-to-digital converter that converts an unknown input voltage into a digital representation through the use of an integrator. In its most basic implementation, the unknown input voltage is applied to the input of the integrator and allowed to ramp for a fixed time period (the run-up period). Then a known reference voltage of opposite polarity is applied to the integrator and is allowed to ramp until the integrator output returns to zero (the run-down period). The input voltage is computed as a function of the reference voltage, the constant run-up time period, and the measured run-down time period. The run-down time measurement is usually made in units of the converter's clock, so longer integration times allow for higher resolutions. Likewise, the speed of the converter can be improved by sacrificing resolution.Converters of this type can achieve high resolution, but often do so at the expense of speed. For this reason, these converters are not found in audio or signal processing applications. Their use is typically limited to digital voltmeters and other instruments requiring highly accurate measurements.