this PDF file. - barton musical circuits
... The outputs of these pots are mixed together by two unity gain inverting op-amp stages. The output of the second stage is then sent to another schottky diode voltage limiting circuit, and a .1uf capacitor which filters out high frequency noise from the CV and the diodes. To the left is the output ci ...
... The outputs of these pots are mixed together by two unity gain inverting op-amp stages. The output of the second stage is then sent to another schottky diode voltage limiting circuit, and a .1uf capacitor which filters out high frequency noise from the CV and the diodes. To the left is the output ci ...
Buck-Boost Converter Introduction A Buck
... gradually decreasing as the battery charge is used up. At full charge, where the battery voltage may be higher than actually needed by the circuit being powered, a buck regulator would be ideal to keep the supply voltage steady. However as the charge diminishes, the input voltage falls below the lev ...
... gradually decreasing as the battery charge is used up. At full charge, where the battery voltage may be higher than actually needed by the circuit being powered, a buck regulator would be ideal to keep the supply voltage steady. However as the charge diminishes, the input voltage falls below the lev ...
In Problems 1 and 2, find the Thévenin and Norton equivalent
... b. Find the impedance for Zmatch that will force the voltage vR to be 180o out of phase with the current iR. In phase is a condition where the phase angle of the voltage is equal to the phase angle of the current. Note that this does not mean that the phase angle will be equal to 0o. This will never ...
... b. Find the impedance for Zmatch that will force the voltage vR to be 180o out of phase with the current iR. In phase is a condition where the phase angle of the voltage is equal to the phase angle of the current. Note that this does not mean that the phase angle will be equal to 0o. This will never ...
1 (Vahid 4.1) Given a timer ... frequency of 10 MHz: (a)Determine ...
... second. (b) Provide values for a pulse width and period that achieve this duty cycle. You do not need to consider whether the frequency is too high or too low although the values should be reasonable. There is no one correct answer. ...
... second. (b) Provide values for a pulse width and period that achieve this duty cycle. You do not need to consider whether the frequency is too high or too low although the values should be reasonable. There is no one correct answer. ...
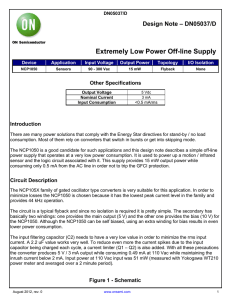
Test Procedure for the NCP690, 1A, Adjustable LDO Test Setup:
... The feedback resistors R1 and R2 have to be soldered before any measurement could be started (Figure 1). Please use the following equation to determine the appropriate value of feedback resistors to be soldered on the demoboard: VOUT = 1.25(1 + ...
... The feedback resistors R1 and R2 have to be soldered before any measurement could be started (Figure 1). Please use the following equation to determine the appropriate value of feedback resistors to be soldered on the demoboard: VOUT = 1.25(1 + ...
Experiment No. 3 Clipping and Clamping Circuits
... the Figure (l) shows a biased clipper, for the diode to turn in the input voltage must be greater +V, when Vm is greater than +V , the diode acts like a closed switch (ideally) & the voltage across the output equals +V , this output stays at +V as long as the input voltage exceeds +V. when the input ...
... the Figure (l) shows a biased clipper, for the diode to turn in the input voltage must be greater +V, when Vm is greater than +V , the diode acts like a closed switch (ideally) & the voltage across the output equals +V , this output stays at +V as long as the input voltage exceeds +V. when the input ...
Bidirectional Single Power-Conversion DC-AC
... This project presents a bidirectional single power-conversion dc-ac converter with noncomplementary active-clamp circuits. In order to interface the grid with low voltage energy storage through only single power-conversion, the bidirectional fly back converter transforms the low voltage directly int ...
... This project presents a bidirectional single power-conversion dc-ac converter with noncomplementary active-clamp circuits. In order to interface the grid with low voltage energy storage through only single power-conversion, the bidirectional fly back converter transforms the low voltage directly int ...
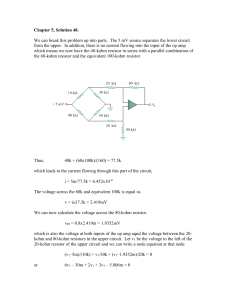
Soln0548 051017
... We can break this problem up into parts. The 5 mV source separates the lower circuit from the upper. In addition, there is no current flowing into the input of the op amp which means we now have the 40-kohm resistor in series with a parallel combination of the 60-kohm resistor and the equivalent 100 ...
... We can break this problem up into parts. The 5 mV source separates the lower circuit from the upper. In addition, there is no current flowing into the input of the op amp which means we now have the 40-kohm resistor in series with a parallel combination of the 60-kohm resistor and the equivalent 100 ...
UNIT-V DAC: Principles – weighted-resistor network, R
... output returns to zero (the run-down period). The input voltage is computed as a function of the reference voltage, the constant run-up time period, and the measured run-down time period. The run-down time measurement is usually made in units of the converter's clock, so longer integration times all ...
... output returns to zero (the run-down period). The input voltage is computed as a function of the reference voltage, the constant run-up time period, and the measured run-down time period. The run-down time measurement is usually made in units of the converter's clock, so longer integration times all ...
EUP2410 1.6A, 500KHz Synchronous Step-up Converter
... conduction path from SW to OUT is fully blocked and the OUT pin is isolated from the battery. This output disconnect feature reduces the shutdown current to typically only 50nA. The 500KHz switching frequency allows for smaller external components producing a compact solution for a wide range of loa ...
... conduction path from SW to OUT is fully blocked and the OUT pin is isolated from the battery. This output disconnect feature reduces the shutdown current to typically only 50nA. The 500KHz switching frequency allows for smaller external components producing a compact solution for a wide range of loa ...
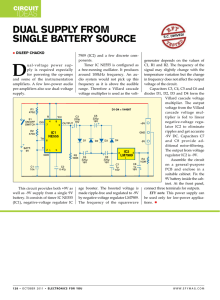
Dual Supply From Single Battery SourCe
... around 100kHz frequency. An audio system would not pick up this frequency as it is above the audible range. Therefore a Villard cascade voltage multiplier is used as the volt- ...
... around 100kHz frequency. An audio system would not pick up this frequency as it is above the audible range. Therefore a Villard cascade voltage multiplier is used as the volt- ...
Cascaded Op Amp Circuits
... This is due to the fact that each (ideal) op amp circuit has infinite input resistance and zero output resistance. Although the cascade connection does not affect the op amp input-output relationships, care must be exercised in the design of an actual op amp circuit to ensure that the load due t ...
... This is due to the fact that each (ideal) op amp circuit has infinite input resistance and zero output resistance. Although the cascade connection does not affect the op amp input-output relationships, care must be exercised in the design of an actual op amp circuit to ensure that the load due t ...
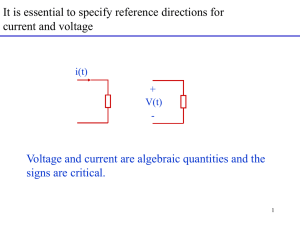
Basic EE
... Voltage is the electrical potential energy a charge has due to its position in space • potential energy per unit of charge • "path independent“ Voltage is measured in Joules/Coulomb or Volts (V) ...
... Voltage is the electrical potential energy a charge has due to its position in space • potential energy per unit of charge • "path independent“ Voltage is measured in Joules/Coulomb or Volts (V) ...
슬라이드 1
... (4) Essentially zero output for zero input offset voltage is the input voltage required to produce a zero output potential. -They are employed to perform such mathematical operations as summing, multiplying, differentiating and integrating. ...
... (4) Essentially zero output for zero input offset voltage is the input voltage required to produce a zero output potential. -They are employed to perform such mathematical operations as summing, multiplying, differentiating and integrating. ...
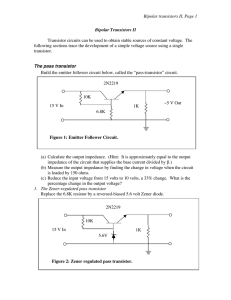
Bipolar transistors II, Page 1 Bipolar Transistors II
... Plot I vs. V for this supply by loading it. Note: The zener-regulated pass transistor developed in this lab is an acceptable source of stable voltage to be used when circumstances are not demanding. Transistorized power supplies with two or three transistors in a fast negative feedback circuit are u ...
... Plot I vs. V for this supply by loading it. Note: The zener-regulated pass transistor developed in this lab is an acceptable source of stable voltage to be used when circumstances are not demanding. Transistorized power supplies with two or three transistors in a fast negative feedback circuit are u ...
Analog to Digital Converters Electronics Unit – Lecture 7
... (A/D) and digital-to-analog (D/A) converters. They provide a means for summing currents at the input and converting a current to a voltage at the output of converter circuits. • The methods of A/D conversion used are many! In the successive method, bits are tested to see if they contribute an equiva ...
... (A/D) and digital-to-analog (D/A) converters. They provide a means for summing currents at the input and converting a current to a voltage at the output of converter circuits. • The methods of A/D conversion used are many! In the successive method, bits are tested to see if they contribute an equiva ...
Integrating ADC
An integrating ADC is a type of analog-to-digital converter that converts an unknown input voltage into a digital representation through the use of an integrator. In its most basic implementation, the unknown input voltage is applied to the input of the integrator and allowed to ramp for a fixed time period (the run-up period). Then a known reference voltage of opposite polarity is applied to the integrator and is allowed to ramp until the integrator output returns to zero (the run-down period). The input voltage is computed as a function of the reference voltage, the constant run-up time period, and the measured run-down time period. The run-down time measurement is usually made in units of the converter's clock, so longer integration times allow for higher resolutions. Likewise, the speed of the converter can be improved by sacrificing resolution.Converters of this type can achieve high resolution, but often do so at the expense of speed. For this reason, these converters are not found in audio or signal processing applications. Their use is typically limited to digital voltmeters and other instruments requiring highly accurate measurements.