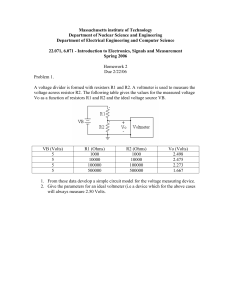
Muddiest Points Week 8 2016
... terminal, effectively creating a difference between the negative and positive voltage that is close to 0, but not quite. In doing so the output voltage can be controlled and is usually equal to the input voltage. Question: How to find out the values of Vs and Rs when a complicated circuit is connect ...
... terminal, effectively creating a difference between the negative and positive voltage that is close to 0, but not quite. In doing so the output voltage can be controlled and is usually equal to the input voltage. Question: How to find out the values of Vs and Rs when a complicated circuit is connect ...
RC and RL Circuits
... equation for q(t), the charge on the capacitor as a function of time. If you have time, you may wish to write down the equation and show that a solution for the voltage on the capacitor, VC = q(t)/C, consistent with no initial charge on the capacitor, is: ...
... equation for q(t), the charge on the capacitor as a function of time. If you have time, you may wish to write down the equation and show that a solution for the voltage on the capacitor, VC = q(t)/C, consistent with no initial charge on the capacitor, is: ...
ANALOGUE COMPUTERS INTRODUCTION There are 2 main types
... Clearly, the voltage is now simulating time -at a ratio of 1:1. The circuit of Fig. 1 can also be thought of ~s a clock with displays the passage of time following the closure of S. The 1:1 ratio can be changed by changing the forward gain of the integrator. THE EXPERIMENT: Set up the circuit of Fig ...
... Clearly, the voltage is now simulating time -at a ratio of 1:1. The circuit of Fig. 1 can also be thought of ~s a clock with displays the passage of time following the closure of S. The 1:1 ratio can be changed by changing the forward gain of the integrator. THE EXPERIMENT: Set up the circuit of Fig ...
AN9637: Simple Phase Meter Operates to 10MHz
... verify that the Application Note or Technical Brief is current before proceeding. ...
... verify that the Application Note or Technical Brief is current before proceeding. ...
Boost converter Operation - San Jose State University
... VIN +VL from the charge on C1. Although the charge C1 drains away through the load during this period, C1 is recharged each time the MOSFET switches off, so maintaining an almost steady output voltage across the load. The theoretical DC output voltage is determined by the input voltage (VIN) divided ...
... VIN +VL from the charge on C1. Although the charge C1 drains away through the load during this period, C1 is recharged each time the MOSFET switches off, so maintaining an almost steady output voltage across the load. The theoretical DC output voltage is determined by the input voltage (VIN) divided ...
Single-Phase Test Circuit
... 10.6.5 Alternate circuit for high voltage delta-connected windings For two-winding transformers with delta-connected high voltage windings, a single phase induced test executed three times may be used in lieu of the applied test on the HV winding. Each phase is tested separately at the required appl ...
... 10.6.5 Alternate circuit for high voltage delta-connected windings For two-winding transformers with delta-connected high voltage windings, a single phase induced test executed three times may be used in lieu of the applied test on the HV winding. Each phase is tested separately at the required appl ...
Existing method
... and cascaded converters are commonly used. Multi-level converters have lower dv/dt and reduced harmonic distortion along with lower semiconductor switching device blocking voltage requirements, thus multi-level converters are advantageous in medium voltage, high power or low voltage, high frequency ...
... and cascaded converters are commonly used. Multi-level converters have lower dv/dt and reduced harmonic distortion along with lower semiconductor switching device blocking voltage requirements, thus multi-level converters are advantageous in medium voltage, high power or low voltage, high frequency ...
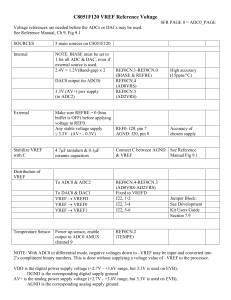
DN190 - Op Amp, Comparator and Reference IC Provides Micropower Monitoring Capability
... amplifier’s output swings high, biasing Q1 on. Hysteresis, provided by the 10M resistor, ensures clean transitions, while the diodes clamp static generated voltages to the rails. The 100k–2.2µF RC filters the signal to the amplifier. The comparator (“C”) monitors the battery voltage via the 2M–1M di ...
... amplifier’s output swings high, biasing Q1 on. Hysteresis, provided by the 10M resistor, ensures clean transitions, while the diodes clamp static generated voltages to the rails. The 100k–2.2µF RC filters the signal to the amplifier. The comparator (“C”) monitors the battery voltage via the 2M–1M di ...
factors that affect the charging time of a capacitor
... resistance between B and C __________________ and hence the voltage across B and C will _____________________ . At the same time, the resistance between A and C will __________________ and so hence the voltage across A and ...
... resistance between B and C __________________ and hence the voltage across B and C will _____________________ . At the same time, the resistance between A and C will __________________ and so hence the voltage across A and ...
High Voltage MLCC for use in Power Supplies
... D: Tank capacitor, usually a high capacitance value for smoothing, low voltage low frequency devices would use an electrolytic capacitor but at higher voltage and higher frequencies where charge/discharge rates are important and lower ESR is required an MLCC would be suitable, Syfer can offer an 181 ...
... D: Tank capacitor, usually a high capacitance value for smoothing, low voltage low frequency devices would use an electrolytic capacitor but at higher voltage and higher frequencies where charge/discharge rates are important and lower ESR is required an MLCC would be suitable, Syfer can offer an 181 ...
Portable Appliance Testing Course Pre-Study Revision
... The candidate will need to understand basic electrical symbols and measurement units. i.e.… voltage (V) measured in volts (V), current (I) measured in Amperes (or amps for short) (A), resistance (R) measured in ohm’s (), power (P) measured in watts (W) The candidate will need to understand basi ...
... The candidate will need to understand basic electrical symbols and measurement units. i.e.… voltage (V) measured in volts (V), current (I) measured in Amperes (or amps for short) (A), resistance (R) measured in ohm’s (), power (P) measured in watts (W) The candidate will need to understand basi ...
Pre-lab4 Problems
... (d) RF = 0 and R = infinity (the voltage follower)Gain:1 BW: 5MHz Be careful about which equations you use here. Make sure you justify when you can use an approximate equation i.e., what you get from the golden rules for an ideal op-amp, and when you need to do some extra work. The point of the co ...
... (d) RF = 0 and R = infinity (the voltage follower)Gain:1 BW: 5MHz Be careful about which equations you use here. Make sure you justify when you can use an approximate equation i.e., what you get from the golden rules for an ideal op-amp, and when you need to do some extra work. The point of the co ...
A Switch is Pressed, So W hat??? Debouncing Light Dependent
... Use charge-redistribution technique ...
... Use charge-redistribution technique ...
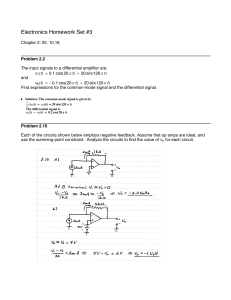
Solutions #3
... v1 HtL = 0.1 cosH20 p tL + 20 sinH120 p tL and v2 HtL = -0.1 cosH20 p tL + 20 sinH120 p tL Find expressions for the common-mode signal and the differential signal. ü Solution: The common-mode signal is given by ...
... v1 HtL = 0.1 cosH20 p tL + 20 sinH120 p tL and v2 HtL = -0.1 cosH20 p tL + 20 sinH120 p tL Find expressions for the common-mode signal and the differential signal. ü Solution: The common-mode signal is given by ...
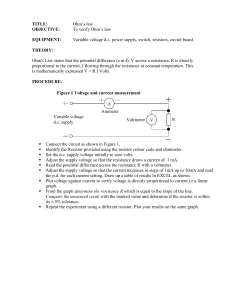
L3 Ohms_law
... Connect the circuit as shown in Figure 1. Identify the Resistor provided using the resistor colour code and ohmmeter. Set the d.c. supply voltage initially to zero volts. Adjust the supply voltage so that the resistance draws a current of 1 mA. Read the potential difference across the resistance R w ...
... Connect the circuit as shown in Figure 1. Identify the Resistor provided using the resistor colour code and ohmmeter. Set the d.c. supply voltage initially to zero volts. Adjust the supply voltage so that the resistance draws a current of 1 mA. Read the potential difference across the resistance R w ...
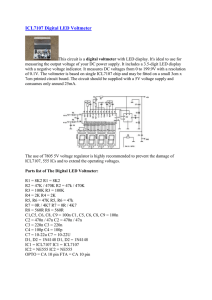
H91-23 Inverter Converter
... signals generated by devices that might have switch bounce so the output will only respond once to each input. The output voltage will remain on for the duration that the corresponding input voltage is present. Before using the H91-23, be sure the power supply is connected to the H91-23 and a main v ...
... signals generated by devices that might have switch bounce so the output will only respond once to each input. The output voltage will remain on for the duration that the corresponding input voltage is present. Before using the H91-23, be sure the power supply is connected to the H91-23 and a main v ...
Integrating ADC
An integrating ADC is a type of analog-to-digital converter that converts an unknown input voltage into a digital representation through the use of an integrator. In its most basic implementation, the unknown input voltage is applied to the input of the integrator and allowed to ramp for a fixed time period (the run-up period). Then a known reference voltage of opposite polarity is applied to the integrator and is allowed to ramp until the integrator output returns to zero (the run-down period). The input voltage is computed as a function of the reference voltage, the constant run-up time period, and the measured run-down time period. The run-down time measurement is usually made in units of the converter's clock, so longer integration times allow for higher resolutions. Likewise, the speed of the converter can be improved by sacrificing resolution.Converters of this type can achieve high resolution, but often do so at the expense of speed. For this reason, these converters are not found in audio or signal processing applications. Their use is typically limited to digital voltmeters and other instruments requiring highly accurate measurements.