Biochemistry 6/e
... Fetal red blood cells have a higher oxygen affinity than that of maternal red blood cells because fetal hemoglobin does not bind 2,3-BPG as well as maternal hemoglobin does ...
... Fetal red blood cells have a higher oxygen affinity than that of maternal red blood cells because fetal hemoglobin does not bind 2,3-BPG as well as maternal hemoglobin does ...
A Possible Correlation Between the Type of bcr-abl
... leukemic cells of more than 90% of chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) patients.’ The Phl chromosome, which can be considered to be the first karyotypic marker consistently present in a human neoplasm, is the result of a reciprocal translocation between chromosomes 9 and 22, t(9;22) (q34;qll).*This t ...
... leukemic cells of more than 90% of chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) patients.’ The Phl chromosome, which can be considered to be the first karyotypic marker consistently present in a human neoplasm, is the result of a reciprocal translocation between chromosomes 9 and 22, t(9;22) (q34;qll).*This t ...
Vascular Specialization in Fish, but No Evidence for
... Fig. 1. Scanning electron micrographs o f material from Osphronemus goramy. Similar results have been obtained in all fish studied, (a) Corrosion cast of a segmental artery (SA) from which several shunt vessels originate (arrows). The shunts unite to feed a small secondary artery, (b) Wall o f a seg ...
... Fig. 1. Scanning electron micrographs o f material from Osphronemus goramy. Similar results have been obtained in all fish studied, (a) Corrosion cast of a segmental artery (SA) from which several shunt vessels originate (arrows). The shunts unite to feed a small secondary artery, (b) Wall o f a seg ...
Blood Vessels PowerPoint
... • Blood flow across the capillary bed is regulated by a sphincter muscle on the arteriole side. Whenever there is little need to supply blood to a given capillary bed, the sphincter closes and blood bypasses the capillary bed via an arteriovenal shunt. ...
... • Blood flow across the capillary bed is regulated by a sphincter muscle on the arteriole side. Whenever there is little need to supply blood to a given capillary bed, the sphincter closes and blood bypasses the capillary bed via an arteriovenal shunt. ...
fanconi familial hypoplastic anaemia
... addition reticulum cells and plasma cells were also found. Roentgenogram of the skull, cervical spine and chest were normal except for synostosis between C3 and C4 vertebrae. Electrocardiogram was normal and coupled with X-ray and on auscultatory findings it was concluded that she had a functional h ...
... addition reticulum cells and plasma cells were also found. Roentgenogram of the skull, cervical spine and chest were normal except for synostosis between C3 and C4 vertebrae. Electrocardiogram was normal and coupled with X-ray and on auscultatory findings it was concluded that she had a functional h ...
platelet proteins from diabetic subjects cause phenotypic changes in
... membrane receptors which are instrumental for platelet-platelet, platelet leukocyte and plateletendothelial interactions5. Platelet endothelium interaction takes place via several molecules like Pselectin, CD40L etc. Role of these molecules is long being investigated in metabolic condition like diab ...
... membrane receptors which are instrumental for platelet-platelet, platelet leukocyte and plateletendothelial interactions5. Platelet endothelium interaction takes place via several molecules like Pselectin, CD40L etc. Role of these molecules is long being investigated in metabolic condition like diab ...
document
... Since they generally function outside of the circulatory system, primarily in the connective tissues of other organs, All leukocytes can leave (and most can also reenter) the blood vessels by a process called ...
... Since they generally function outside of the circulatory system, primarily in the connective tissues of other organs, All leukocytes can leave (and most can also reenter) the blood vessels by a process called ...
Lecture 1
... prevent blood from clotting prior to test. – Separate cells from plasma by centrifugation – Add excess of Ca and known amount of prothrombin to plasma – Record time required for clot formation. ...
... prevent blood from clotting prior to test. – Separate cells from plasma by centrifugation – Add excess of Ca and known amount of prothrombin to plasma – Record time required for clot formation. ...
2014 Annual Report - LIFELINE Blood Services
... learn more about the need for platelets and how they can become a platelet donor. As the provider of blood and blood products for 16 West Tennessee hospitals, LIFELINE Blood Services collects blood each year to meet patient needs. In addition to red cell donations (the most commonly used blood produ ...
... learn more about the need for platelets and how they can become a platelet donor. As the provider of blood and blood products for 16 West Tennessee hospitals, LIFELINE Blood Services collects blood each year to meet patient needs. In addition to red cell donations (the most commonly used blood produ ...
Take home Quiz #5 - San Diego Mesa College
... Q. 8: Which of the following statements about the heritable disorder familial Hypercholesterolemia (fHC) is/are correct? A) Only homozygous recessive individuals are affected B) It is caused by mutations of the gene coding for the LDL receptor C) It is caused by mutations of the gene coding for hemo ...
... Q. 8: Which of the following statements about the heritable disorder familial Hypercholesterolemia (fHC) is/are correct? A) Only homozygous recessive individuals are affected B) It is caused by mutations of the gene coding for the LDL receptor C) It is caused by mutations of the gene coding for hemo ...
Parental Consent
... Your child has expressed an interest in donating blood. Donating blood is safe, easy and saves lives. Over 200 blood and platelet donations are needed everyday, year round. Donors can help save up to three lives in just one hour. We hope you will support your child’s decision to help those in need w ...
... Your child has expressed an interest in donating blood. Donating blood is safe, easy and saves lives. Over 200 blood and platelet donations are needed everyday, year round. Donors can help save up to three lives in just one hour. We hope you will support your child’s decision to help those in need w ...
INFECTION CONTROL - Oregon Institute of Technology
... Others by blood or body fluids Hep B , C and D can be chronic Acute demonstrated as flu-like symptoms then in 1-2 weeks becomes jaundiced, liver enlarges, liver cells die Can regenerate unless it turns chronic ...
... Others by blood or body fluids Hep B , C and D can be chronic Acute demonstrated as flu-like symptoms then in 1-2 weeks becomes jaundiced, liver enlarges, liver cells die Can regenerate unless it turns chronic ...
Blood Types - MrsSconyersAnatomy
... • Transfusion – transfer of whole blood or blood components (RBC or plasma) • Agglutination – clumping of RBCs, hemolysis occurs, kidney damage and death can result – This only causes problems between recipient antibodies and donor antigens – Donor antibodies become diluted in blood plasma ...
... • Transfusion – transfer of whole blood or blood components (RBC or plasma) • Agglutination – clumping of RBCs, hemolysis occurs, kidney damage and death can result – This only causes problems between recipient antibodies and donor antigens – Donor antibodies become diluted in blood plasma ...
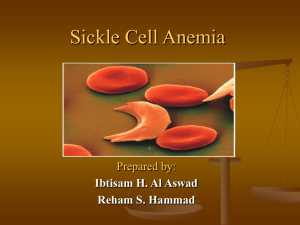
Sickle cell test
... This process produces periodic episodes of pain and ultimately can damage tissues and vital organs and lead to other serious medical problems . ...
... This process produces periodic episodes of pain and ultimately can damage tissues and vital organs and lead to other serious medical problems . ...
Powerpoint - Blood Journal
... Time-varying covariate-adjusted relative risk of death following treatment with FA regimens relative to risk with IA regimens.In each cytogenetic group, the risk with IA is 1.0 (dotted line), because IA is the baseline group. ...
... Time-varying covariate-adjusted relative risk of death following treatment with FA regimens relative to risk with IA regimens.In each cytogenetic group, the risk with IA is 1.0 (dotted line), because IA is the baseline group. ...
Identification of the hemoglobin scavenger receptor
... Glucocorticoids, interleukin (IL)-6 and IL-10 (but not IL-4 or IL-13) induce increased expression of both messenger RNA and surface receptor protein.5-7 Furthermore, antibody-mediated HbSR cross-linkage induces intracellular signaling and secretion of IL-6 and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulati ...
... Glucocorticoids, interleukin (IL)-6 and IL-10 (but not IL-4 or IL-13) induce increased expression of both messenger RNA and surface receptor protein.5-7 Furthermore, antibody-mediated HbSR cross-linkage induces intracellular signaling and secretion of IL-6 and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulati ...
live blood analysis - Neogenesis Systems
... Live blood analysis is especially useful in preventive health care. The red blood cells carry oxygen and the plasma carries nutrients to every cell in the body. The state of health or ill-health of the blood therefore affects every cell in the body, so it is clear that by improving the health of the ...
... Live blood analysis is especially useful in preventive health care. The red blood cells carry oxygen and the plasma carries nutrients to every cell in the body. The state of health or ill-health of the blood therefore affects every cell in the body, so it is clear that by improving the health of the ...
Ibrutinib treatment affects collagen and von Willebrand Factor-dependent platelet functions
... platelets (Figure 1D). Ibrutinib also inhibited collagen-induced platelet aggregation in PRP (Figure 1E), with an IC50 value of 0.5 µM, nearly the peak dose in plasma of treated patients.6,13 Mixing experiments in PRP showed a correction of the aggregation defect to collagen and Tyr223-Btk autophosp ...
... platelets (Figure 1D). Ibrutinib also inhibited collagen-induced platelet aggregation in PRP (Figure 1E), with an IC50 value of 0.5 µM, nearly the peak dose in plasma of treated patients.6,13 Mixing experiments in PRP showed a correction of the aggregation defect to collagen and Tyr223-Btk autophosp ...
Blood Vessels: biology homework revision questions
... Describe the function of the collagen fibres. ...
... Describe the function of the collagen fibres. ...
BLOOD Blood Volume Blood Composition Origin of Blood Cells
... • triggered by thromboplastin (not found in blood) • triggered when blood contacts damaged tissue Intrinsic Clotting Mechanism • chemical inside blood triggers blood coagulation • triggered by Hageman factor (found inside blood) • triggered when blood contacts a foreign surface ...
... • triggered by thromboplastin (not found in blood) • triggered when blood contacts damaged tissue Intrinsic Clotting Mechanism • chemical inside blood triggers blood coagulation • triggered by Hageman factor (found inside blood) • triggered when blood contacts a foreign surface ...
Chapter 19- The Cardiovascular System: The Blood
... B) eosinophil C) monocyte D) lymphocyte E) neutrophil 18) Two doctors, trained in different decades and different parts of the country, call the critical care nurses’ station and ask for a report on a patient’s blood work. One doctor is particularly interested in the patient’s “segs” and the other i ...
... B) eosinophil C) monocyte D) lymphocyte E) neutrophil 18) Two doctors, trained in different decades and different parts of the country, call the critical care nurses’ station and ask for a report on a patient’s blood work. One doctor is particularly interested in the patient’s “segs” and the other i ...
Blood Typing
... she carries that has Rh + (positive) blood. In subsequent pregnancies, if the fetus is Rh +, Rh antibodies produced in maternal blood may cross the placenta and destroy fetal cells, causing erythroblastosis fetalis. ...
... she carries that has Rh + (positive) blood. In subsequent pregnancies, if the fetus is Rh +, Rh antibodies produced in maternal blood may cross the placenta and destroy fetal cells, causing erythroblastosis fetalis. ...
Avascular Necrosis - BC Children`s Hospital
... deterioration of the bone, which can collapse. When AVN occurs in the hip joint, the top of the femoral head (the ball portion) collapses and begins to flatten. As the damage occurs to the bone, it can be painful and cause difficulty moving the hip. The AVN can cause significant damage to the bone; ...
... deterioration of the bone, which can collapse. When AVN occurs in the hip joint, the top of the femoral head (the ball portion) collapses and begins to flatten. As the damage occurs to the bone, it can be painful and cause difficulty moving the hip. The AVN can cause significant damage to the bone; ...
The effects of anti-diabetic agents on white blood cells
... and cyclosporine. Interferons used to treat multiple sclerosis, like Rebif, Avonex, and Betaseron, can also cause leukopenia. Oral hypogycemic agents also can cause leukopenia .[9] Fixed leukocytes: Some leukocytes migrate into the tissues of the body to take up a permanent residence at that locatio ...
... and cyclosporine. Interferons used to treat multiple sclerosis, like Rebif, Avonex, and Betaseron, can also cause leukopenia. Oral hypogycemic agents also can cause leukopenia .[9] Fixed leukocytes: Some leukocytes migrate into the tissues of the body to take up a permanent residence at that locatio ...
Hemolytic-uremic syndrome
Hemolytic-uremic syndrome (or haemolytic-uraemic syndrome), abbreviated HUS, is a disease characterized by hemolytic anemia (anemia caused by destruction of red blood cells), acute kidney failure (uremia), and a low platelet count (thrombocytopenia). It predominantly, but not exclusively, affects children. Most cases are preceded by an episode of infectious, sometimes bloody, diarrhea acquired as a foodborne illness or from a contaminated water supply and caused by E. coli O157:H7, although Shigella, Campylobacter and a variety of viruses have also been implicated. It is now the most common cause of acquired acute renal failure in childhood. It is a medical emergency and carries a 5–10% mortality; of the remainder, the majority recover without major consequences but a small proportion develop chronic kidney disease and become reliant on renal replacement therapy.The primary target appears to be the vascular endothelial cell. This may explain the pathogenesis of HUS, in which a characteristic renal lesion is capillary microangiopathy.HUS was first defined as a syndrome in 1955. The more common form of the disease, Shiga-like toxin-producing E. coli HUS (STEC-HUS), is triggered by the infectious agent E. coli O157:H7. Certain Shiga toxin secreting strains of Shigella dysenteriae can also cause HUS. Approximately 5% of cases are classified as pneumococcal HUS, which results from infection by Streptococcus pneumoniae, the agent that causes traditional lobar pneumonia. There is also a rare, chronic, and severe form known as atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome (aHUS), which is caused by genetic defects resulting in chronic, uncontrolled complement activation. Both STEC-HUS and aHUS cause endothelial damage, leukocyte activation, platelet activation, and widespread inflammation and multiple thromboses in the small blood vessels, a condition known as systemic thrombotic microangiopathy (TMA), which leads to thrombotic events as well as organ damage/failure and death.