* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Powerpoint - Blood Journal
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
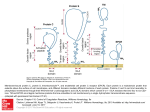
Comparison of idarubicin + ara-C–, fludarabine + ara-C–, and topotecan + ara-C–based regimens in treatment of newly diagnosed acute myeloid leukemia, refractory anemia with excess blasts in transformation, or refractory anemia with excess blasts by Elihu H. Estey, Peter F. Thall, Jorge E. Cortes, Francis J. Giles, Susan O'Brien, Sherry A. Pierce, Xuemei Wang, Hagop M. Kantarjian, and Miloslav Beran Blood Volume 98(13):3575-3583 December 15, 2001 ©2001 by American Society of Hematology Probability of event-free survival among patients achieving CR following treatment with IA, FA, or TA regimens.Kaplan-Meier estimates of the proportion of patients achieving CR who have neither relapsed nor died in CR dated from CR date. Elihu H. Estey et al. Blood 2001;98:3575-3583 ©2001 by American Society of Hematology Probability of survival following treatment with IA, FA, or TA regimens.Kaplan-Meier estimates of the proportion of patients remaining alive dated from start of treatment. Elihu H. Estey et al. Blood 2001;98:3575-3583 ©2001 by American Society of Hematology Time-varying covariate-adjusted relative risk of death following treatment with FA regimens relative to risk with IA regimens.In each cytogenetic group, the risk with IA is 1.0 (dotted line), because IA is the baseline group. Elihu H. Estey et al. Blood 2001;98:3575-3583 ©2001 by American Society of Hematology Time-varying covariate-adjusted relative risk of death following treatment with TA regimens relative to risk with IA regimens.The risk with IA, the baseline group, is 1.0 (dotted line). Elihu H. Estey et al. Blood 2001;98:3575-3583 ©2001 by American Society of Hematology Probability of survival after failure of IA, FA, or TA regimens.Kaplan-Meier estimates of the proportion of patients remaining alive dated from time of failure. Elihu H. Estey et al. Blood 2001;98:3575-3583 ©2001 by American Society of Hematology Probability of survival in younger and older patients following treatment with IA, FA, or TA regimens.Kaplan-Meier estimates of the proportion of patients aged younger than 60 years (A) and 60 years or older (B) who remain alive following treatment with the... Elihu H. Estey et al. Blood 2001;98:3575-3583 ©2001 by American Society of Hematology Probability of survival in patients with AML and patients with MDS following treatment with IA, FA, or TA regimens.Kaplan-Meier estimates of the proportion of patients with AML (A) and MDS (B) who remain alive following treatment with IA, FA, or TA regimens. Elihu H. Estey et al. Blood 2001;98:3575-3583 ©2001 by American Society of Hematology Probability of survival according to cytogenetic subgroup following treatment with IA, FA, or TA regimens.Kaplan-Meier estimates of the proportion of patients with inv(16) or t(8;21) (A), normal karyotype (B), −5/−7 (C), and other abnormal karyotypes (D) wh... Elihu H. Estey et al. Blood 2001;98:3575-3583 ©2001 by American Society of Hematology