File - HARRISVILLE 7
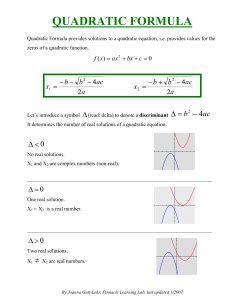
... classification or solution. In the case of a quadratic equation ax 2 + bx + c = 0, the discriminant is b 2 − 4ac; for a cubic equation x 3 + ax 2 + bx + c = 0, the discriminant is a 2b 2 + 18abc − 4b 3 − 4a 3c − 27c. The discriminant of an equation gives an idea of the number of roots and the nature ...
... classification or solution. In the case of a quadratic equation ax 2 + bx + c = 0, the discriminant is b 2 − 4ac; for a cubic equation x 3 + ax 2 + bx + c = 0, the discriminant is a 2b 2 + 18abc − 4b 3 − 4a 3c − 27c. The discriminant of an equation gives an idea of the number of roots and the nature ...
Lesson 10: Simu Eqns - Elimination
... A pair of simultaneous equations gives information about two unknown numbers. They have to be solved together to give the two solutions. ...
... A pair of simultaneous equations gives information about two unknown numbers. They have to be solved together to give the two solutions. ...
Elementary Algebra
... Translating Verbal Expressions into Algebraic Expressions Addition: Sum, add to, more than, increased by Subtraction: less than, difference, decreased by Multiplication: Product, twice, triple, half, percent Division: ratio, quotient, half ...
... Translating Verbal Expressions into Algebraic Expressions Addition: Sum, add to, more than, increased by Subtraction: less than, difference, decreased by Multiplication: Product, twice, triple, half, percent Division: ratio, quotient, half ...
[Part 2]
... This contradicts (2) and (3). Thus, 1,37,32 are 0-linearly independent Now Schmidt's theorem shows that a2 is not algebraic. The assertion is proved. REMARK. The proposition remains true if we put xn -yn x - y where A- is a quadratic Pisot number and y its conjugate. ...
... This contradicts (2) and (3). Thus, 1,37,32 are 0-linearly independent Now Schmidt's theorem shows that a2 is not algebraic. The assertion is proved. REMARK. The proposition remains true if we put xn -yn x - y where A- is a quadratic Pisot number and y its conjugate. ...
sol review notes 2
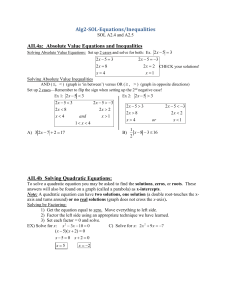
... answers will also be found on a graph (called a parabola) as x-intercepts. Note: A quadratic equation can have two solutions, one solution (a double root-touches the xaxis and turns around) or no real solutions (graph does not cross the x-axis). Solving by Factoring: 1) Get the equation equal to zer ...
... answers will also be found on a graph (called a parabola) as x-intercepts. Note: A quadratic equation can have two solutions, one solution (a double root-touches the xaxis and turns around) or no real solutions (graph does not cross the x-axis). Solving by Factoring: 1) Get the equation equal to zer ...
A Quick Review of MTH070
... – Move all linear terms to one side and all other terms to the other side. – To move a term to the other side, change its sign. – Result: ex = f ...
... – Move all linear terms to one side and all other terms to the other side. – To move a term to the other side, change its sign. – Result: ex = f ...
Lesson 1.2A Notes
... 2. The x window’s min is at -20, max at 40 increasing in increments of 5. The y window’s min is at -10, max at 30 increasing in increments of 2. ...
... 2. The x window’s min is at -20, max at 40 increasing in increments of 5. The y window’s min is at -10, max at 30 increasing in increments of 2. ...
Algebra Cheat Sheet
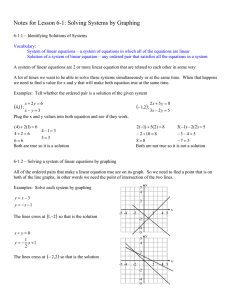
... Solving Systems of Equations Addition/Subtraction Method: Combine equations to eliminate one variable. The equations may need to be multiplied by a common multiple first. Substitution Method: Solve one equation for one variable and substitute that variable into other equations. Graphing Method: Grap ...
... Solving Systems of Equations Addition/Subtraction Method: Combine equations to eliminate one variable. The equations may need to be multiplied by a common multiple first. Substitution Method: Solve one equation for one variable and substitute that variable into other equations. Graphing Method: Grap ...














![[Part 2]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008795881_1-223d14689d3b26f32b1adfeda1303791-300x300.png)