MPM1D Exam Outline 2009
... solve for the value of a variable in an equation involving one step done to both sides Solving Multi-Step Equations solving polynomial equations by simplifying/expanding/multiplying (distributive property) first solving equations by using ‘reverse’ order operations Solving Equations involving Fracti ...
... solve for the value of a variable in an equation involving one step done to both sides Solving Multi-Step Equations solving polynomial equations by simplifying/expanding/multiplying (distributive property) first solving equations by using ‘reverse’ order operations Solving Equations involving Fracti ...
Midterm Review Notes - Spring
... - Distribute if needed - Combine like terms - Isolate your variable - Remember to flip the inequality sign if you multiply or divide by a negative - Your solutions are usually graphed on a number line with shading. ...
... - Distribute if needed - Combine like terms - Isolate your variable - Remember to flip the inequality sign if you multiply or divide by a negative - Your solutions are usually graphed on a number line with shading. ...
Section 10
... Opposites of Polynomials: Two polynomials are opposites (additive inverses) if their sum is zero. We can find the opposite of a polynomial by replacing each term with its opposite, (ie, change the sign of every term). Examples: Find the opposite polynomial a) 3x2 + 7x – 9 ...
... Opposites of Polynomials: Two polynomials are opposites (additive inverses) if their sum is zero. We can find the opposite of a polynomial by replacing each term with its opposite, (ie, change the sign of every term). Examples: Find the opposite polynomial a) 3x2 + 7x – 9 ...
quintessence
... 59. What will be the equation of the circle (x2 + y2 – 6x – 6y) = 0 if the origin is shifted to (3, 3)? (a) x2 + y2 = 0 (b) x2 + y2 – 6x – 6y = 18 (c) x2 + y2 – 6x – 6y – 36 = 0 (d) x2 + y2 = 18 60. The mean of a Poisson random variant X is 6. Then Pr (X = 7) / Pr(X = 5) is (a) 13 sq. cm (b) 16 sq. ...
... 59. What will be the equation of the circle (x2 + y2 – 6x – 6y) = 0 if the origin is shifted to (3, 3)? (a) x2 + y2 = 0 (b) x2 + y2 – 6x – 6y = 18 (c) x2 + y2 – 6x – 6y – 36 = 0 (d) x2 + y2 = 18 60. The mean of a Poisson random variant X is 6. Then Pr (X = 7) / Pr(X = 5) is (a) 13 sq. cm (b) 16 sq. ...
Karnataka PUC-II Maths Exam Syllabus
... looking at natural numbers as the least inductive subset of real numbers. The principle of mathematical induction and simple applications. 2. Complex Numbers and Quadratic Equations: Need for complex numbers, especially, -1 to be motivated by inability to solve every quadratic equation. Brief descri ...
... looking at natural numbers as the least inductive subset of real numbers. The principle of mathematical induction and simple applications. 2. Complex Numbers and Quadratic Equations: Need for complex numbers, especially, -1 to be motivated by inability to solve every quadratic equation. Brief descri ...
Unit 7: Algebra 1A Semester Review
... rule that represents the helicopter’s height, h, above the ground as a function of time, t. what is the helicopter’s height after 45 s? ...
... rule that represents the helicopter’s height, h, above the ground as a function of time, t. what is the helicopter’s height after 45 s? ...
FERM - Interjetics
... Next we show how to devise an algorithm for proving that the two distinct polynomial equations in R cannot have a solution other than R=0. Though it is important to note that the polynomials in powers are not true polynomials in the sense that we assume that there is only one value of R that satisfi ...
... Next we show how to devise an algorithm for proving that the two distinct polynomial equations in R cannot have a solution other than R=0. Though it is important to note that the polynomials in powers are not true polynomials in the sense that we assume that there is only one value of R that satisfi ...
MTH 098
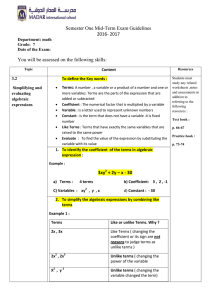
... Simplifying an Algebraic Expression • An algebraic expression consists of 1. variables with “counting number” exponents 2. coefficients 3. constants 4. arithmetic operations and grouping symbols • An expression will not have an equal sign. • To simplify an algebraic expression: 1. Apply the distrib ...
... Simplifying an Algebraic Expression • An algebraic expression consists of 1. variables with “counting number” exponents 2. coefficients 3. constants 4. arithmetic operations and grouping symbols • An expression will not have an equal sign. • To simplify an algebraic expression: 1. Apply the distrib ...