* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Meet #5
Computational electromagnetics wikipedia , lookup
Plateau principle wikipedia , lookup
Mathematical descriptions of the electromagnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Two-body Dirac equations wikipedia , lookup
Computational fluid dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Routhian mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Perturbation theory wikipedia , lookup
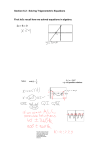
Park Forest Math Team Meet #5 Self-study Packet Problem Categories for this Meet (in addition to topics of earlier meets): 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Mystery: Problem solving Geometry: Solid Geometry (Volume and Surface Area) Number Theory: Set Theory and Venn Diagrams Arithmetic: Combinatorics and Probability Algebra: Solving Quadratics with Rational Solutions, including word problems Important things you need to know about ALGEBRA: Solving quadratics with rational solutions, including word problems • If xy = 0, then x = 0 or y = 0. This is called the Zero Product Property • If (x – 3) (x + 2) = 0, then x – 3 = 0 or x + 2 = 0. The solutions to this problem are x =3 and x = -2 • When a graph crosses the x-axis, y = 0. • To multiply binomials, such as (x – 4) (x + 6), we can use the distributive property. A mnemonic is FOIL. Foil means multiply the First, Outside, Inside, and Last Terms. (x – 4) (x + 6) = x2 + 6x – 4x – 24 = x2 + 2x – 24 • You should notice that in the above example, the -4 and 6 add to equal 2 and multiply to equal -24. Use this knowledge to work backward to factor a trinomial. • Factor x2 – 7x + 12 (Think: What are two numbers that multiply to equal 12 and add to equal -7? -3 and -4) So, x2 – 7x + 12 = (x – 3) (x – 4) • If x2 – 7x + 12 = 0, then (x – 3) (x – 4) = 0, so x = 3 or x = 4 • The quadratic formula can also be used to solve quadratic equations. If Ax2 + Bx + C = 0, then Example: How many units are in the shortest length of the right triangle below? 2x + 3 x 2x + 2 By Pythagorean Theorem, x + (2x + 2)2 = (2x + 3)2 So, x2 + (2x + 2)(2x + 2) = (2x + 3)(2x + 3) Using FOIL, x2 + 4x2 + 4x + 4x + 4 = 4x2 + 6x = 6x + 9 Combining like terms, 5x2 + 8x + 4 = 4x2 + 12x + 9 Subtracting the right side to get everything on the left, we get x2 – 4x – 5 = 0 So (x – 5)(x+1) = 0, Therefore, x = 5 or x = -1 A side length cannot be negative, so x must be 5. 2 2 2 ! Check. If x = 5, 2x + 2 = 12 and 2x + 3 = 13. 5 + 12 = 13 2 Meet #5 March 2011 Category 5 ± Algebra 1. If we add Ͷ inches to a square¶s length, and shorten its width by Ͷ inches, we get a new rectangle whose area is ͷΨ RIWKHRULJLQDOVTXDUH¶s area. +RZPDQ\LQFKHVDUHLQWKHOHQJWKRIWKHVTXDUH¶VVLGH" 2. One of the solutions to the equation ݔଶ ܤȉ ݔെ ͺ ൌ Ͳ is ݔൌ ʹ. What is the value of the other solution? 3. The product of the solutions of the equation ݔଶ െ ͻ ݔ ܥൌ Ͳ, is twice as much as their sum. What is the larger of the two solutions? Answers 1. _______________ 2. _______________ 3. _______________ www.imlem.org Meet #5 March 2011 Solutions to Category 5 - Algebra Answers 1. ,IZHFDOOWKHVTXDUH¶VOHQJWKݔ, then we can write: ଷ ሺ ݔ Ͷሻ ȉ ሺ ݔെ Ͷሻ ൌ ݔଶ െ ͳ ൌ ȉ ݔଶ ସ and so ݔଶ ൌ Ͷ and ݔൌ ͺ݄݅݊ܿ݁ݏǤ 6LQFHZH¶UHORRNLQJIRUD lenJWKZH¶UHLQWHUHVWHGRQO\LQWKHSRVLWLYHVROXWLRQ 1. ͺ 2. െͶ 3. 2. Since we know that ݔൌ ʹ is a solution, we can use this value in the original equation to get ʹଶ ܤȉ ʹ െ ͺ ൌ Ͳ and solve to get ܤൌ ʹ. Now the original equation is known to be ݔଶ ʹ ȉ ݔെ ͺ ൌ Ͳ and the other solution for this is ݔൌ െͶ. 3. In the general case of a quadratic equation ܣȉ ݔଶ ܤȉ ݔ ܥൌ Ͳ we know that the sum of solutions is Ȃ ܤ, and their product is ܣȉ ܥ. In our case ܣൌ ͳ and ܤൌ െͻ, and so the sum of solutions is ͻ, and their product is ͳͺ ൌ ܥ. Our equation then is ݔଶ െ ͻ ȉ ݔ ͳͺ ൌ ሺ ݔെ ͵ሻ ȉ ሺ ݔെ ሻ ൌ Ͳ. The solutions are of course ݔൌ ͵ and ݔൌ . www.imlem.org You may use a calculator today. Category 5 Algebra Meet #5, March 2009 1. What is the positive difference between the two solutions to the equation below? 2. The diagram below is a large rectangle which is made up of a square and 2 rectangles as shown. The area of the entire figure is 756. What is the area of the square? 3 4 3. The difference between a positive number and times its reciprocal is equal to . What is the number? Express your answer as a common fraction. Answers 1. _______________ 2. _______________ 3. _______________ Solutions to Category 5 Algebra Meet #5, March 2009 Dividing both sides of the equation by 3 gives us: or or The positive difference between two solutions is 1. Answers 1. 10 2. 576 3. 2. If we call the side of the square , the square has area , the rectangle to the right of the square has area and the area of the rectangle below the square is The total area of the three shapes is or or Since the side length of the square cannot be negative, the side of the square is 24 and the area of the square is 242 = 576. 3. Multiplying both sides of the equation by gives us: or or or Since we know is positive, it must be . Category 5 Algebra Meet #5, March 2007 You may use a calculator. 1. Give the lesser of the two solutions to the following equation. x(7 + x) + 312 − 4 x = 3(x + 137) + 526 2. The length and width of a certain rectangle are whole numbers of units, and the length is one more than four times the width. If the area of the rectangle is 105 square units, how many units are in the perimeter of the rectangle? y 3. The graph of the quadratic equation shown at right crosses the x-axis at the points (–5, 0) and (7, 0), and its vertex is at the point (1, –36). Give the coordinates of the two points where the graph of this same equation crosses the line y = 13. Reminder: The 20 10 x -20 coordinates of the two points should be written as 20 -10 ordered pairs in parentheses. -20 Answers 1. ____________________ 2. ____________________ 3. ________ and ________ -30 -40 www.imlem.org Solutions to Category 5 Algebra Meet #5, March 2007 Answers 1. –25 1. The equation can be simplified as follows: x(7 + x) + 312 − 4 x = 3(x + 137) + 526 7x + x 2 + 312 − 4 x = 3x + 411+ 526 2. 52 x 2 + 3x + 312 = 3x + 937 x 2 + 312 = 937 3. (8, 13) and (–6, 13) x 2 = 625 The two solutions are x = 25 and x = –25. We want –25. 2. If we call the width x, then the length is 4x + 1. Since length times width gives the area of a rectangle, we can write the quadratic equation x(4 x + 1) = 105 . Distributing on the left, we can rewrite this as 4x 2 + x = 105 . Now we subtract 105 from each side to set the equation equal to zero: 4 x 2 + x −105 = 0 . At this point we can use the quadratic formula or try to factor the trinomial into a product of two binomials. Our template for factoring is: (__ x + ___ )(__ x − ___ ) = 0 . The prime factorization of 4 is 2 × 2 and that of 105 is 3 × 5 × 7. We need to place these factors in the blanks so that the difference is 1 for the middle term. We note that 2 × 2 × 5 = 20 and 3 × 7 = 21, so our equation must be (4 x + 21)(x − 5) = 0 . The two solutions are x = − 21 and x = 5 . Only 5 units make sense for the width, so 4 the length must be 4 × 5 + 1 = 21 units. The perimeter of the rectangle is 2 × (5 + 21) = 2 × 26 = 52 units. 3. We are told that the equation is quadratic and we are given the roots of the equation. We can assume that the equation has the form y = a (x + 5)(x − 7), where a is not yet determined. We can use the vertex, (1, –36), as a point to help us determine the value of a. First we substitute y = -36 and x = 1 into the equation to get −36 = a (1 + 5)(1− 7). Now we simplify and get −36 = −36a , which shows us that a = 1. Now we want to find the values of x when y = 13. We have to solve the equation 13 = 1(x + 5)(x − 7). Expanding on the right, we get 13 = x 2 − 2x − 35 . Now we set this equal to zero and factor the new equation as follows: 0 = x 2 − 2x − 48 = (x − 8)(x + 6). From this, we find that the desired x values are 8 and –6. The coordinates of the two points where the graph crosses the line y = 13 are (8, 13) and (–6, 13). www.imlem.org Category 5 Algebra Meet #5, March/April 2005 You may use a calculator 1. A number plus six times its reciprocal is equal to five. What is the sum of the two possible numbers this could be? 2. How many units are in the length of the shorter leg in the right triangle below? 4x + 5 x 4x + 4 3. The graph of the equation y = x 2 − 3x − 8 crosses the line y = 100 at two different points. What is the average of the x-coordinates of these points? Express your answer as a decimal to the nearest tenth. Answers 1. _______________ 2. _______________ 3. _______________ www.Imlem.org Solutions to Category 5 Average team got 11.88 points, or 1.0 questions correct Algebra Meet #5, March/April 2005 Average number of correct answers: 0.99 out of 3 Answers 1. Translating the English to algebra, we get the following equation: 1. 5 x+ 2. 9 3. 1.5 6 =5 x x 2 + 6 = 5x x2 − 5x + 6 = 0 (x − 2)(x − 3) = 0 This product will be zero when x = 2 and when x = 3, so the sum of the two possible numbers is 2 + 3 = 5. 2. Using the Pythagorean Theorem, we can write the following equation and solve for x. x 2 + (4 x + 4 ) = (4 x + 5) 2 2 x 2 + 16x 2 + 32x + 16 = 16x 2 + 40x + 25 x 2 + 32x + 16 = 40x + 25 x 2 − 8x − 9 = 0 (x − 9)(x + 1) = 0 The solutions are x = 9 or x = -1, but only the positive value makes sense for the side length of the triangle. The length of the shorter leg is thus 9 units. 3. Where the graph of the equation y = x 2 − 3x − 8 crosses y = 100, we will have 100 = x 2 − 3x − 8 . Solving this new equation for x, we get: x 2 − 3x −108 = 0 (x + 9)(x −12) = 0 The two points in question are (-9, 100) and (12, 100). The average of the x-coordinates of these points is (-9 + 12)/2 = 3/2 = 1.5. www.Imlem.org Category 5 Algebra Meet #5, April 2003 You may use a calculator today! 1. The following equation has two solutions. What are they? x 2 84 8 x 2. The graph of the function y x 2 3 x 4 crosses the x-axis at two different points. What is the average of the x-coordinates of these two x-intercepts? Express your answer as a mixed number in lowest terms. y x 3. The longer leg of a right triangle is nine centimeters shorter than the hypotenuse. The shorter leg is one centimeters less than half the length of the longer leg. How many centimeters are in the perimeter of the right triangle? Answers 1. _______________ 2. _______________ 3. _______________ Solutions to Category 5 Algebra Meet #5, April 2003 Answers 1. To factor the quadratic equation x 2 84 x we first set it equal to zero as follows: 2 1. ±14 and 6 2. 1 1 x 2 2 x 84 8 x 8 x 8 x 8 x 84 8 x , 0 We now seek to factor this trinomial into the product of two binomials of the form x r x r . We are 3. 208 looking for a pair of numbers whose product is -84 and whose difference is 8. (We look for a difference of 8 since the numbers must have the opposite sign.) 84 and 1 have a difference of 83 42 and 2 have a difference of 40 21 and 4 have a difference of 17 14 and 6 have a difference of 8 12 and 7 have a difference of 5 The pair we want is 14 and 6 and we now have the following product of two binomials equal to zero: x 14 x 6 0 For a product to equal zero, it must be true that one or the other (or both) is equal to zero. This means we can solve the two separate equations as follows: x 14 x 6 0 14 14 x 14 2 Thus the two solutions to the equation x 84 0 6 6 x 8 x 6 are -14 and 6. 2. The two points at which the graph of the function y x 2 3 x 4 cross the xaxis are known as the roots of the equation. We could determine them graphically if we create a table of well-chosen values and plot some points. It is easier to compute the roots algebraically, however, especially if we recall that the value of just need to the y-coordinate for any point on the x-axis is zero. This means we factor the equation 0 x 2 3 x 4 as we did in the previous problem. Since the only factor pairs for 4 are 1 u 4 and 2 u 2 , we should quickly find Category 5 Algebra Meet #5, April 2001 You may use a calculator today! 1. There are two solutions to the equation x 2 + 6 x = 91 . If these two solutions were plotted on the real number line, what would the distance between them be? 2. A rectangular room has a perimeter of 60 feet and an area of 216 square feet. How many feet longer is this rectangle than it is wide? 3. A rational number greater than one and its reciprocal have a sum of 2 16 . What is this number? Express your answer as an improper fraction in lowest terms. Answers 1. _____________ 2. _____________ 3. _____________ Solutions to Category 5 Algebra Meet #5, April 2001 Answers 1. 20 2. 6 3. 3 2 1. The equation x 2 + 6 x = 91 can be set equal to zero and factored as follows: x 2 + 6 x − 91 = 0 ( x − 7)( x + 13) = 0, x = 7 or − 13 Plotting these two solutions on a number line, we find them to be 20 units apart. -13 0 7 2. We need two numbers whose product is 216 and whose sum is 30 (half the perimeter). Trial and error, using factors of 216, is the best way to solve this problem. We might try 8 × 27 = 216 , but 8 + 27 = 35 ; or 9 × 24 = 216 , but 9 + 24 = 33 . By combining the prime factors in different ways, eventually we find 12 × 18 = 216 and 12 + 18 = 30 . The room is 18 feet by 12 feet, which is 6 feet longer than it is wide. Notice that algebra is no help for this problem. We can write the equations lw = 216 and l + w = 30 , substitute l = 30 − w into the first equation, and get (30 − w)w = 216 . Rearranging things, we end up looking at the equation w 2 − 30 w + 216 = 0 . We could use the quadratic formula, but it’s often quicker to factor this into the form (w − )(l − ) =0. To fill in those blanks, we need two numbers whose product is 216 and whose sum is 30. We’re back where we started and trial and error is the best way! 3. A number and its reciprocal with a sum of 2 16 may be represented algebraically as follows: x + 1x = 2 16 or x + 1x = 136 . Multiplying through by 6x, we get: 6 x 2 + 6 = 13x . Setting this equal to zero, gives: 6 x 2 − 13 x + 6 = 0 , which factors to: (2 x − 3)(3 x − 2 ) = 0 , so x = 23 or 32 . We want the solution that is greater than 1 or 23 . This may also be solved by trial and error.