Biome - Terrestrial
... A collection of ecosystems that share similar climatic conditions, vegetation and animals. In relation to ecosystems • Most changes in ecosystems are caused by climate change, species movement in and out of the ecosystem and ecological succession. • Species basic physical conditions for survival als ...
... A collection of ecosystems that share similar climatic conditions, vegetation and animals. In relation to ecosystems • Most changes in ecosystems are caused by climate change, species movement in and out of the ecosystem and ecological succession. • Species basic physical conditions for survival als ...
slides - UBC Botany
... – Red Queen works best for short-term, ecosystem-scale processes, but these local patterns may be overwhelmed at larger scales where ‘random geological events’ have large effects Benton 2009 ...
... – Red Queen works best for short-term, ecosystem-scale processes, but these local patterns may be overwhelmed at larger scales where ‘random geological events’ have large effects Benton 2009 ...
Linking Top-down Forces to the Pleistocene Megafaunal Extinctions
... herbivore populations irrupt and these dense herbivore populations most likely become limited by resources or human hunting (Beschta and Ripple 2009). An exception to the above pattern is that some migrating ungulates are not limited by predation and can cycle over a wide range of abundance. Migrati ...
... herbivore populations irrupt and these dense herbivore populations most likely become limited by resources or human hunting (Beschta and Ripple 2009). An exception to the above pattern is that some migrating ungulates are not limited by predation and can cycle over a wide range of abundance. Migrati ...
Linking Top-down Forces to the Pleistocene
... herbivore populations irrupt and these dense herbivore populations most likely become limited by resources or human hunting (Beschta and Ripple 2009). An exception to the above pattern is that some migrating ungulates are not limited by predation and can cycle over a wide range of abundance. Migrati ...
... herbivore populations irrupt and these dense herbivore populations most likely become limited by resources or human hunting (Beschta and Ripple 2009). An exception to the above pattern is that some migrating ungulates are not limited by predation and can cycle over a wide range of abundance. Migrati ...
Ecology Review Packet
... 3. Water can enter the atmosphere by evaporating from the leaves of plants in the process of ___________________. 4. Circle the letter of each process involved in the water ...
... 3. Water can enter the atmosphere by evaporating from the leaves of plants in the process of ___________________. 4. Circle the letter of each process involved in the water ...
THE ADAPTIVE EVOLUTION OF EXTINCTION Guest editors
... Biology Letters. After a long illness, Niclas passed away during the preparation of this symposium. Even as a youth, Niclas took pleasure in natural history and field biology. He was especially interested in birds and in understanding how global climate change was likely to affect their breeding, mo ...
... Biology Letters. After a long illness, Niclas passed away during the preparation of this symposium. Even as a youth, Niclas took pleasure in natural history and field biology. He was especially interested in birds and in understanding how global climate change was likely to affect their breeding, mo ...
2.6.1-.4, 2.1.7 Population Dynamics - DAVIS-DAIS
... The population size of a species in a given space at a given time is determined by the interplay between BIOTIC POTENTIAL and ENVIRONMENTAL RESISTANCE. Biotic potential = growth rate with unlimited resources. Environmental resistance = all the factors acting jointly to limit population growth. ...
... The population size of a species in a given space at a given time is determined by the interplay between BIOTIC POTENTIAL and ENVIRONMENTAL RESISTANCE. Biotic potential = growth rate with unlimited resources. Environmental resistance = all the factors acting jointly to limit population growth. ...
Inducing Evolution in Bean Beetles
... and individuals differ in their survival and reproductive success as a consequence of the particular character of a trait. For example, if adult body mass varied in a population and the risk of predation were greater among the smallest individuals in the population, then the larger individuals would ...
... and individuals differ in their survival and reproductive success as a consequence of the particular character of a trait. For example, if adult body mass varied in a population and the risk of predation were greater among the smallest individuals in the population, then the larger individuals would ...
Precambrian - Cambrian Eukaryotes
... – Extinctions must not be instantaneous – Expect to see pulses of extinction as disaster intensifies ...
... – Extinctions must not be instantaneous – Expect to see pulses of extinction as disaster intensifies ...
Clicker Review
... Global warming is affecting polar bear populations by all of the following EXCEPT? A. Arctic ice is melting more rapidly. B. The polar bear’s hunting season is getting longer. C. Floating sea ice is breaking up earlier in the year. [Default] D. The amount of arctic ice available in the [MC Any] [MC ...
... Global warming is affecting polar bear populations by all of the following EXCEPT? A. Arctic ice is melting more rapidly. B. The polar bear’s hunting season is getting longer. C. Floating sea ice is breaking up earlier in the year. [Default] D. The amount of arctic ice available in the [MC Any] [MC ...
Mary
... reduction of the grinding component of mastication in favor of the shearing component, which overall reduces the wearing of teeth to a slower rate • Important because the growth of new teeth is what they depend on for survival. • Otherwise they starve to death. ...
... reduction of the grinding component of mastication in favor of the shearing component, which overall reduces the wearing of teeth to a slower rate • Important because the growth of new teeth is what they depend on for survival. • Otherwise they starve to death. ...
Dinosaurs - ScienceTIPs
... Dinosaurs Dinosaurs were the dominant vertebrate animals of terrestrial ecosystems for over 160 million years, from the late Triassic period until the end of the Cretaceous period ...
... Dinosaurs Dinosaurs were the dominant vertebrate animals of terrestrial ecosystems for over 160 million years, from the late Triassic period until the end of the Cretaceous period ...
Chapter 10 The Triploblastic, Acoelomate Body Plan
... thousand species of parasitic flatworms in the class Trematoda are collectively called flukes, which describes their wide, flat shape. A large oval holdfast organ called the ...
... thousand species of parasitic flatworms in the class Trematoda are collectively called flukes, which describes their wide, flat shape. A large oval holdfast organ called the ...
An Introduction to Trilobites
... Trilobites were marine organisms that lived on Earth for over 270 million years and are considered known to be one of the most successful early animal groups ...
... Trilobites were marine organisms that lived on Earth for over 270 million years and are considered known to be one of the most successful early animal groups ...
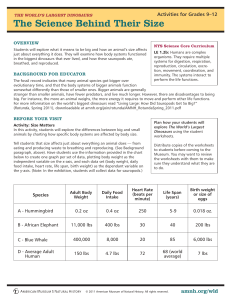
The World`s Largest Dinosaurs: Activities for Grades 9-12
... natural selection favoring large size. An exception is the hummingbird, the smallest bird and living dinosaur.) • Are the individual cells in the body of a big animal the same size as those in a small animal? (Answer: Yes, it’s just that big animals have many more cells. The amount of energy require ...
... natural selection favoring large size. An exception is the hummingbird, the smallest bird and living dinosaur.) • Are the individual cells in the body of a big animal the same size as those in a small animal? (Answer: Yes, it’s just that big animals have many more cells. The amount of energy require ...
Modelling the extinction of Steller`s sea cow
... 1741 and extinct by 1768, is one of the few megafaunal mammal species to have died out during the historical period. The species is traditionally considered to have been exterminated by ‘blitzkrieg’-style direct overharvesting for food, but it has also been proposed that its extinction resulted from ...
... 1741 and extinct by 1768, is one of the few megafaunal mammal species to have died out during the historical period. The species is traditionally considered to have been exterminated by ‘blitzkrieg’-style direct overharvesting for food, but it has also been proposed that its extinction resulted from ...
One elephant at a time
... One objection is that too much time has passed since the Pleistocene for the concept of ecologically analogous species to be valid. Both the species and the environment have undoubtedly ...
... One objection is that too much time has passed since the Pleistocene for the concept of ecologically analogous species to be valid. Both the species and the environment have undoubtedly ...
Genetic Variation
... • Giant eruptions coincide with mass extinctions more so than any other factor • The best known series of eruptions occurred throughout 1 million years, between 66.5-64.5 million years ago, when over one million cubic kilometers of basaltic lava was poured out from under the Earth’s surface. • Havin ...
... • Giant eruptions coincide with mass extinctions more so than any other factor • The best known series of eruptions occurred throughout 1 million years, between 66.5-64.5 million years ago, when over one million cubic kilometers of basaltic lava was poured out from under the Earth’s surface. • Havin ...
Spa-o-‐temporal trends in diversity of the demersal fish communi
... Biodiversity is changing at an unprecedented rate on a global scale (Pimm et al., 1995), as a complex response to several anthropogenic changes in the global environment (Vitousek, ...
... Biodiversity is changing at an unprecedented rate on a global scale (Pimm et al., 1995), as a complex response to several anthropogenic changes in the global environment (Vitousek, ...
Does the positive body size-trophic level - Archimer
... with increasing body size; Similar positive trends were found within some demersal species. The change in feeding resources with body size is sometimes accompanied by a habitat effect: the increase of trophic level with body size is larger in some habitats than in others probably due to differences ...
... with increasing body size; Similar positive trends were found within some demersal species. The change in feeding resources with body size is sometimes accompanied by a habitat effect: the increase of trophic level with body size is larger in some habitats than in others probably due to differences ...
Ch 11: Wolves
... Changes at the top of the “food chain” (apex predator) has had “cascading” impact on all other species on the island., including both other carnivores, herbivores as well as all sorts of various plant life/forest type/ etc., Well known ecological “maxim”: “everything in an ecosystem is connected or ...
... Changes at the top of the “food chain” (apex predator) has had “cascading” impact on all other species on the island., including both other carnivores, herbivores as well as all sorts of various plant life/forest type/ etc., Well known ecological “maxim”: “everything in an ecosystem is connected or ...
Lecture 051
... filling similar ecological roles in similar environments, so similar adaptations were selected ...
... filling similar ecological roles in similar environments, so similar adaptations were selected ...
Megafauna

In terrestrial zoology, megafauna (Ancient Greek megas ""large"" + New Latin fauna ""animal"") are large or giant animals. The most common thresholds used are 45 kilograms (100 lb) or 100 kilograms (220 lb). This thus includes many species not popularly thought of as overly large, such as white-tailed deer, red kangaroo, and humans.In practice, the most common usage encountered in academic and popular writing describes land animals roughly larger than a human that are not (solely) domesticated. The term is especially associated with the Pleistocene megafauna – the land animals often larger than modern counterparts considered archetypical of the last ice age, such as mammoths, the majority of which in northern Eurasia, the Americas and Australia became extinct as recently as 10,000–40,000 years ago. It is also commonly used for the largest extant wild land animals, especially elephants, giraffes, hippopotamuses, rhinoceroses, and large bovines. Megafauna may be subcategorized by their trophic position into megaherbivores (e.g., elk), megacarnivores (e.g., lions), and, more rarely, megaomnivores (e.g., bears).Other common uses are for giant aquatic species, especially whales, any larger wild or domesticated land animals such as larger antelope and cattle, as well as numerous dinosaurs and other extinct giant reptilians.The term is also sometimes applied to animals (usually extinct) of great size relative to a more common or surviving type of the animal, for example the 1 m (3 ft) dragonflies of the Carboniferous period.