Wazzat Mean - Peterborough Astronomical Association
... Unit-Power Finder A device for aiming your telescope that shows the sky as it appears to your unaided eye, without magnification. The simplest type is a pair of notches or circles that you line up with your target. Other versions use an LED to project a red dot or circle onto a viewing ...
... Unit-Power Finder A device for aiming your telescope that shows the sky as it appears to your unaided eye, without magnification. The simplest type is a pair of notches or circles that you line up with your target. Other versions use an LED to project a red dot or circle onto a viewing ...
Ay 122a Fall 2012 – HOMEWORK #1
... 3. Thinking Big... Suppose you are put in charge of designing a 30m optical/IR telescope, and that the baseline configuration is a Ritchey-Chretien design with with a primary focal ratio of f/1.0. Suppose that the final ratio at the R-C focus is f/15 (this would probably be a Nasmyth focus for this ...
... 3. Thinking Big... Suppose you are put in charge of designing a 30m optical/IR telescope, and that the baseline configuration is a Ritchey-Chretien design with with a primary focal ratio of f/1.0. Suppose that the final ratio at the R-C focus is f/15 (this would probably be a Nasmyth focus for this ...
Low-budget satellite tracking system for highly elliptical orbits
... the failure of AO-40. But who knows, maybe there will be a successor in the near future. If that happens and if you are not one of those who can already call a full-size satellite tracking system their own, you might be interested in just getting started by taking our approach. The idea: In order to ...
... the failure of AO-40. But who knows, maybe there will be a successor in the near future. If that happens and if you are not one of those who can already call a full-size satellite tracking system their own, you might be interested in just getting started by taking our approach. The idea: In order to ...
AST 443/PHY 517 Homework 1 Solutions
... 4. Which of these 5 stars is closest to the moon? What is the angular distance? Sirius, at about 44.3 degrees 5. The sidereal time at midnight advances by 3m 56s each day. What are the best days to observe these targets? See column (3) above. 6. What is the minimum zenith distance for each star? Se ...
... 4. Which of these 5 stars is closest to the moon? What is the angular distance? Sirius, at about 44.3 degrees 5. The sidereal time at midnight advances by 3m 56s each day. What are the best days to observe these targets? See column (3) above. 6. What is the minimum zenith distance for each star? Se ...
1 - GEOCITIES.ws
... point is located. This angle is measured along the equator. It is positive if it is west of the prime meridian and negative if to the east of the prime meridian. Terrestrial Triangle- Any triangle in the face of the earth whose two sides are the meridians of two points and one angle at the pole. The ...
... point is located. This angle is measured along the equator. It is positive if it is west of the prime meridian and negative if to the east of the prime meridian. Terrestrial Triangle- Any triangle in the face of the earth whose two sides are the meridians of two points and one angle at the pole. The ...
Local Horizon View
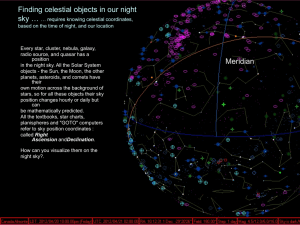
... is a useful point in the sky because it helps to define your meridian. Meridian is the important North/South line through your zenith and also through both celestial poles. We look at our celestial objects while we are oriented along our ...
... is a useful point in the sky because it helps to define your meridian. Meridian is the important North/South line through your zenith and also through both celestial poles. We look at our celestial objects while we are oriented along our ...
ADAS Simple Guide to Telescope Instrumentation and Operation
... Above is a simple telescope diagram of how the objective lens of a telescope works. The telescope objective is represented by a simple convex lens. In truth, modern refractors usually have two lenses that make up the objective, and they may be convex (curved out on both sides) or plano-convex (bulge ...
... Above is a simple telescope diagram of how the objective lens of a telescope works. The telescope objective is represented by a simple convex lens. In truth, modern refractors usually have two lenses that make up the objective, and they may be convex (curved out on both sides) or plano-convex (bulge ...
Celestial Position Lines
... It is sometimes not possible to obtain the altitude of the celestial body when it is on same observer’s meridian due to cloud, environmental factors, etc. If the altitude of the celestial body can be obtained a few minutes before or after meridian passage, the Ex-Meridian method can be used to reduc ...
... It is sometimes not possible to obtain the altitude of the celestial body when it is on same observer’s meridian due to cloud, environmental factors, etc. If the altitude of the celestial body can be obtained a few minutes before or after meridian passage, the Ex-Meridian method can be used to reduc ...
RELATION BETWEEN LONGITUDE AND TIME
... Nadir – the corresponding point in the opposite hemisphere, directly below the observer Celestial equator – is the great circle formed by the intersection of the earth’s equatorial plane with the surface of the celestial sphere Declination of any celestial body – is the angular distance of the ...
... Nadir – the corresponding point in the opposite hemisphere, directly below the observer Celestial equator – is the great circle formed by the intersection of the earth’s equatorial plane with the surface of the celestial sphere Declination of any celestial body – is the angular distance of the ...
ASTRONOMICAL SURVEYING - I - IDC
... center at the position of the observer. This imaginary sphere on which the star appear to lie or to be studded is known as the celestial sphere. The radius of the celestial sphere may be of any value – from a few thousand metres to a few thousand kilometers. Since the stars are very distant from us, ...
... center at the position of the observer. This imaginary sphere on which the star appear to lie or to be studded is known as the celestial sphere. The radius of the celestial sphere may be of any value – from a few thousand metres to a few thousand kilometers. Since the stars are very distant from us, ...
Introduction to Telescopes
... There are many different eyepiece designs – some offer a very wide FOV(field of view the area of sky visible in the eyepiece) for observing extended objects; others might offer a smaller, but highly corrected FOV for observing subtle detail on the planets. We will not concern ourselves with the diff ...
... There are many different eyepiece designs – some offer a very wide FOV(field of view the area of sky visible in the eyepiece) for observing extended objects; others might offer a smaller, but highly corrected FOV for observing subtle detail on the planets. We will not concern ourselves with the diff ...
Planets and Transits
... 2) Free-floating objects in young star clusters (which presumably formed in the same manner as stars and have not been shown to be ejected from planetary systems) with masses below the limiting mass for thermonuclear fusion of deuterium are not "planets", but are "sub-brown dwarfs" (or whatever name ...
... 2) Free-floating objects in young star clusters (which presumably formed in the same manner as stars and have not been shown to be ejected from planetary systems) with masses below the limiting mass for thermonuclear fusion of deuterium are not "planets", but are "sub-brown dwarfs" (or whatever name ...
Chapter Notes - Alpcentauri.info
... The Prime Meridian is the meridian (line of longitude) at which longitude is defined to be 0°. The Prime Meridian and the opposite 180th meridian, at 180° longitude, which the international date line generally follows, form a great circle that divides the Earth into the Eastern and Western Hemispher ...
... The Prime Meridian is the meridian (line of longitude) at which longitude is defined to be 0°. The Prime Meridian and the opposite 180th meridian, at 180° longitude, which the international date line generally follows, form a great circle that divides the Earth into the Eastern and Western Hemispher ...
N (North) Equator Latitude and Declination
... the observer’s head. The observer’s meridian is an imaginary arc in the sky which runs north-south (so passes over the poles) and through the observer’s zenith. The meridian lies directly over the observer’s great circle of longitude. The observer’s horizon is the plane tangent to the earth and pass ...
... the observer’s head. The observer’s meridian is an imaginary arc in the sky which runs north-south (so passes over the poles) and through the observer’s zenith. The meridian lies directly over the observer’s great circle of longitude. The observer’s horizon is the plane tangent to the earth and pass ...
AST 443/PHY 517 Homework 1
... Which, if any, are observable (zenith distance <60o )? Which, if any, are above the horizon? 4. Which of these 5 stars can be observed at some time on this night from Cerro Tololo? At what times? 5. Which of these 5 stars is closest to the moon? What is the angular distance? 6. The sidereal time at ...
... Which, if any, are observable (zenith distance <60o )? Which, if any, are above the horizon? 4. Which of these 5 stars can be observed at some time on this night from Cerro Tololo? At what times? 5. Which of these 5 stars is closest to the moon? What is the angular distance? 6. The sidereal time at ...
The Search for Earth-Like Planets
... Premise: If there is intelligent life “out there”, it probably is similar to life as we know it on Earth. ...
... Premise: If there is intelligent life “out there”, it probably is similar to life as we know it on Earth. ...
In your own words explain what the following terms
... 1. Describe how to hold a star chart so that is matches the sky. 2. Describe sunspots and the sunspot cycle. 3. Describe and sketch the set-up of and annotate one projection method and one filtered method for safely viewing the sun. 4. Convert 80.0 km/hr to ft/s, record your answer using significant ...
... 1. Describe how to hold a star chart so that is matches the sky. 2. Describe sunspots and the sunspot cycle. 3. Describe and sketch the set-up of and annotate one projection method and one filtered method for safely viewing the sun. 4. Convert 80.0 km/hr to ft/s, record your answer using significant ...
Physics 127 Descriptive Astronomy Homework #2
... A-4. As viewed from Provo (latitude = +40°), a star transits (crosses the celestial meridian) south of the zenith at an altitude of 63°. What is the star's declination? What is the declination of a star which passes through Provo's zenith? Since the altitude of the celestial equator, where it inters ...
... A-4. As viewed from Provo (latitude = +40°), a star transits (crosses the celestial meridian) south of the zenith at an altitude of 63°. What is the star's declination? What is the declination of a star which passes through Provo's zenith? Since the altitude of the celestial equator, where it inters ...
2 - BYU Physics and Astronomy
... A-2. An observer notes that the stars neither rise nor set but move right to left, parallel to her horizon. What is her location? ...
... A-2. An observer notes that the stars neither rise nor set but move right to left, parallel to her horizon. What is her location? ...
No Slide Title
... latitude from the CE, i.e., the declination of the zenith is your latitude. Any vertical line on your SC-1 (north-south) is a meridian. Approximately one half of the stars on the SC-1 are visible at any given time (12 hours of RA). ...
... latitude from the CE, i.e., the declination of the zenith is your latitude. Any vertical line on your SC-1 (north-south) is a meridian. Approximately one half of the stars on the SC-1 are visible at any given time (12 hours of RA). ...
PHY216_lect1_2014 - Astrophysics Research Institute
... The Euclidean cosine rule can also be recovered by the same method. ...
... The Euclidean cosine rule can also be recovered by the same method. ...
5.1-The process of Science - Homework
... • The duration of one rotation of the Earth, or occassionally another celestial body, on its axis. Its is measured by successive transits of a reference point on the celestial sphere over the meridian, and each type takes its name from the reference used… www.reson.com/Gloss-d.htm • 1. A basic time ...
... • The duration of one rotation of the Earth, or occassionally another celestial body, on its axis. Its is measured by successive transits of a reference point on the celestial sphere over the meridian, and each type takes its name from the reference used… www.reson.com/Gloss-d.htm • 1. A basic time ...
Meridian circle

The meridian circle is an instrument for timing of the passage of stars across the local meridian, an event known as a transit, while at the same time measuring their angular distance from the nadir. These are special purpose telescopes mounted so as to allow pointing only in the meridian, the great circle through the north point of the horizon, the zenith, the south point of the horizon, and the nadir. Meridian telescopes rely on the rotation of the Earth to bring objects into their field of view and are mounted on a fixed, horizontal, east-west axis.The similar transit instrument, transit circle or transit telescope is likewise mounted on a horizontal axis, but the axis need not be fixed in the east-west direction. For instance, a surveyor's theodolite can function as a transit instrument if its telescope is capable of a full revolution about the horizontal axis. Meridian circles are often called by these names, although they are less specific.For many years, transit timings were the most accurate method of measuring the positions of heavenly bodies, and meridian instruments were relied upon to perform this painstaking work. Before spectroscopy, photography, and the perfection of reflecting telescopes, the measuring of positions (and the deriving of orbits and astronomical constants) was the major work of observatories.