Celestron Manual
... only one threaded hole. Hold the optical tube with one hand while threading the screw clockwise until tight with the other hand. Now the assembly will look like Figure 2-11. Lastly, loosen the knob for the tripod platform and lower the platform down to the level position and then ...
... only one threaded hole. Hold the optical tube with one hand while threading the screw clockwise until tight with the other hand. Now the assembly will look like Figure 2-11. Lastly, loosen the knob for the tripod platform and lower the platform down to the level position and then ...
o - Salem State University
... night we move to a location on Earth that is some significant distance from our first location. There will now be a different star at or on: a. the celestial north pole b. the zenith c. the celestial equator d. the celestial south pole e. all of the above 2. A very odd friend of yours (living in Sal ...
... night we move to a location on Earth that is some significant distance from our first location. There will now be a different star at or on: a. the celestial north pole b. the zenith c. the celestial equator d. the celestial south pole e. all of the above 2. A very odd friend of yours (living in Sal ...
fred`s 2017 astronomy challenge
... astronomers. It is found just below the first star (Alkaid) in the handle of the saucepan shaped Plough. It is bright enough that the smallest binoculars will pick it up as a blurry fuzz ...
... astronomers. It is found just below the first star (Alkaid) in the handle of the saucepan shaped Plough. It is bright enough that the smallest binoculars will pick it up as a blurry fuzz ...
Celestial Navigation in 60 min
... In this second case, to say that the True Position is the cocked hat centre, you need to correct 2 LOPs by moving them backwards and 1 LOP by moving it forward. This is impossible because the systematic error is a constant of the same sign. We have here an 'outside' fix: the True Position is outsid ...
... In this second case, to say that the True Position is the cocked hat centre, you need to correct 2 LOPs by moving them backwards and 1 LOP by moving it forward. This is impossible because the systematic error is a constant of the same sign. We have here an 'outside' fix: the True Position is outsid ...
September - Rose City Astronomers
... The 600 power telescope, due to its popularity, was remarketed by a number of different companies with their own model numbers. Meade ran continual ads for the small refractor during the 1970s, and labeled it their Model #300 (or #305 for 1 ¼" accessories—they changed the color of the dewcap to whit ...
... The 600 power telescope, due to its popularity, was remarketed by a number of different companies with their own model numbers. Meade ran continual ads for the small refractor during the 1970s, and labeled it their Model #300 (or #305 for 1 ¼" accessories—they changed the color of the dewcap to whit ...
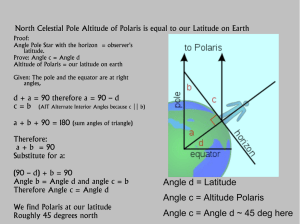
Angle d = Latitude Angle c = Altitude Polaris Angle c
... Remember Declination is always measured from the celestial equator to the object. Note: If the star is north of the zenith (i.e. the angle measured from the celestial equator to the zenith > latitude, say 50 deg, then Alt = 90 + (Phi + Dec) rather than (90 – Phi) + Dec Alt = 90 + Our Observing Latit ...
... Remember Declination is always measured from the celestial equator to the object. Note: If the star is north of the zenith (i.e. the angle measured from the celestial equator to the zenith > latitude, say 50 deg, then Alt = 90 + (Phi + Dec) rather than (90 – Phi) + Dec Alt = 90 + Our Observing Latit ...
OBJXlab-JCU_Alt
... (Figure 9) looks very much like the optical telescope window. However it controls a large radio dish antenna which can collect radio waves and send them to a radio receiver. Like the optical telescope, the antenna can track objects as they move across the sky. It can also be left stationary, picking ...
... (Figure 9) looks very much like the optical telescope window. However it controls a large radio dish antenna which can collect radio waves and send them to a radio receiver. Like the optical telescope, the antenna can track objects as they move across the sky. It can also be left stationary, picking ...
To Measure the Sky: An Introduction to Observational Astronomy.
... Instead of the altitude, astronomers sometimes use its complement, z, the zenith distance (:TOP in the figure). The (a, e) coordinates of an object clearly describe where it is located in an observer’s sky. You can readily imagine an instrument that would measure these coordinates: a telescope or oth ...
... Instead of the altitude, astronomers sometimes use its complement, z, the zenith distance (:TOP in the figure). The (a, e) coordinates of an object clearly describe where it is located in an observer’s sky. You can readily imagine an instrument that would measure these coordinates: a telescope or oth ...
Schmidt-Cassegrain Optical Tube Assembly
... the opposite direction until the image is sharp. Once an image is in focus, turn the knob clockwise to focus on a closer object and counterclockwise for a more distant object. A single turn of the focusing knob moves the primary mirror only slightly. Therefore, it will take many turns (about 30) to ...
... the opposite direction until the image is sharp. Once an image is in focus, turn the knob clockwise to focus on a closer object and counterclockwise for a more distant object. A single turn of the focusing knob moves the primary mirror only slightly. Therefore, it will take many turns (about 30) to ...
Color-Magnitude Diagram Lab Manual
... 1. One technique that is useful for locating objects is called star hopping. This involves using the locations of known bright objects to find fainter ones. Although this virtual telescope can perfectly slew to an object by its right ascension and declination, real telescopes are not so precise. In ...
... 1. One technique that is useful for locating objects is called star hopping. This involves using the locations of known bright objects to find fainter ones. Although this virtual telescope can perfectly slew to an object by its right ascension and declination, real telescopes are not so precise. In ...
2 Coordinate systems
... When viewed from the surface of the Earth the sky above forms a hemisphere, astronomical objects are seen to be projected onto this hemisphere. and their locations are convenient to describe their location with two angular coordinates in the same manner as latitude and longitude are decided on the s ...
... When viewed from the surface of the Earth the sky above forms a hemisphere, astronomical objects are seen to be projected onto this hemisphere. and their locations are convenient to describe their location with two angular coordinates in the same manner as latitude and longitude are decided on the s ...
Orion StarBlast 4.5” Telescope STAR Program
... The collage on page 16 shows some of what you can view in this telescope at different times of the year. Deep sky objects, also referred to as dim-fuzzies, are often hard to find. They are worth the effort, being some of most wonderful sights in the night sky. To find a deep sky object, look at the ...
... The collage on page 16 shows some of what you can view in this telescope at different times of the year. Deep sky objects, also referred to as dim-fuzzies, are often hard to find. They are worth the effort, being some of most wonderful sights in the night sky. To find a deep sky object, look at the ...
Autoguiding - Thrush Observatory
... capable of getting some great photos without having to deal with the flexure problems that are sometimes inherent when one uses a separate guide scope. ...
... capable of getting some great photos without having to deal with the flexure problems that are sometimes inherent when one uses a separate guide scope. ...
Spokane Public Library The Spokane Astronomical
... see the dot without difficulty. When the EZ Finder is properly aligned with the telescope, an object that is centered on the EZ Finder’s red dot should also appear in the center of the telescope’s eyepiece. Checking the alignment of the EZ Finder is easiest during daylight. Aim the telescope at a di ...
... see the dot without difficulty. When the EZ Finder is properly aligned with the telescope, an object that is centered on the EZ Finder’s red dot should also appear in the center of the telescope’s eyepiece. Checking the alignment of the EZ Finder is easiest during daylight. Aim the telescope at a di ...
Tips on taking Astro sights
... two position lines are obtained from shore objects, her position is called a 'fix.' If they are obtained from heavenly bodies, it is called an 'observed position.' The distinction is made because a position ...
... two position lines are obtained from shore objects, her position is called a 'fix.' If they are obtained from heavenly bodies, it is called an 'observed position.' The distinction is made because a position ...
telescope field of view
... The Sun, stars, and any object seen in the sky rise somewhere near east and set somewhere near west (with a few exceptions – circumpolar stars). Exact locations of rising/setting depend on the object’s declination. During the time between rising and setting, the object must move from east to west, a ...
... The Sun, stars, and any object seen in the sky rise somewhere near east and set somewhere near west (with a few exceptions – circumpolar stars). Exact locations of rising/setting depend on the object’s declination. During the time between rising and setting, the object must move from east to west, a ...
Basic principles of celestial navigation
... Imagine that a terrestrial observer is located at a fixed point P of unknown latitude % and longitude &. The celestial sphere rotates westward from the observer’s point of view at an angular rate such that the vernal equinox transits !passes through" the observer’s meridian from east to west at inte ...
... Imagine that a terrestrial observer is located at a fixed point P of unknown latitude % and longitude &. The celestial sphere rotates westward from the observer’s point of view at an angular rate such that the vernal equinox transits !passes through" the observer’s meridian from east to west at inte ...
Basic principles of celestial navigation
... Imagine that a terrestrial observer is located at a fixed point P of unknown latitude % and longitude &. The celestial sphere rotates westward from the observer’s point of view at an angular rate such that the vernal equinox transits !passes through" the observer’s meridian from east to west at inte ...
... Imagine that a terrestrial observer is located at a fixed point P of unknown latitude % and longitude &. The celestial sphere rotates westward from the observer’s point of view at an angular rate such that the vernal equinox transits !passes through" the observer’s meridian from east to west at inte ...
SylTerNav\4Curr\emet
... 7.3.2 define Greenwhich Hour Angle (GHA), Local Hour Angle (LHA) and longitude and explain their relationships; 7.3.3 state the rate of change of GHA of the sun and Aries; 7.3.4 estimate the geographical position of a body for any given GMT. ...
... 7.3.2 define Greenwhich Hour Angle (GHA), Local Hour Angle (LHA) and longitude and explain their relationships; 7.3.3 state the rate of change of GHA of the sun and Aries; 7.3.4 estimate the geographical position of a body for any given GMT. ...
The Cook Memorial Library
... them. If it happens, let the Librarian know and she or he will have it cleaned. It is very easy to scratch the coatings on the lenses! Aligning the Mirrors: Again, please don’t. That is what the three screws at the base of the scope do, and it is pretty easy to mess them up. If it seems that the te ...
... them. If it happens, let the Librarian know and she or he will have it cleaned. It is very easy to scratch the coatings on the lenses! Aligning the Mirrors: Again, please don’t. That is what the three screws at the base of the scope do, and it is pretty easy to mess them up. If it seems that the te ...
Astronomy 15 - Problem Set Number 4 1) Suppose one were to
... These electrons are accelerated to strike yet another piece of metal, the process is repeated until the original photoelectron has been multiplied by a million times or more. This results in an easily detectable pulse of electric current corresponding to the original photon. Photomultipliers therefo ...
... These electrons are accelerated to strike yet another piece of metal, the process is repeated until the original photoelectron has been multiplied by a million times or more. This results in an easily detectable pulse of electric current corresponding to the original photon. Photomultipliers therefo ...
Lecture 1 - Simon P Driver
... – The Sun’s posi/on in the Celes/al Sphere changes because of the Earth’s orbit not its rota/on. – The chunk of sky overhead changes because of the Earth’s rota/on. ...
... – The Sun’s posi/on in the Celes/al Sphere changes because of the Earth’s orbit not its rota/on. – The chunk of sky overhead changes because of the Earth’s rota/on. ...
Visual Double Star Measurements with Equatorial - Alt
... telescope is moved so that the primary star accurately drifts through the central division mark. In practice, the primary is situated about 5-8 division marks away from the central mark and allowed to drift. If the star drifts through the central mark, the drift sequence is allowed to continue until ...
... telescope is moved so that the primary star accurately drifts through the central division mark. In practice, the primary is situated about 5-8 division marks away from the central mark and allowed to drift. If the star drifts through the central mark, the drift sequence is allowed to continue until ...
1B11 Foundations of Astronomy Star names and magnitudes
... • Meridian – the plane passing north-south through the observer and the zenith (draws a great circle on the sky) ...
... • Meridian – the plane passing north-south through the observer and the zenith (draws a great circle on the sky) ...
Preparing astronomical observations and observing with OHP facilities
... 14 arcseconds divided by the aperture in cm, wich means an image of 0.15 arcsecond for 1 m-class telescopes). Because of air movements, the image never reaches this accuracy. The seeing at OHP is limited to a maximum of 2 arcseconds. The seeing is linked to the instrument’s resolution: a binary syst ...
... 14 arcseconds divided by the aperture in cm, wich means an image of 0.15 arcsecond for 1 m-class telescopes). Because of air movements, the image never reaches this accuracy. The seeing at OHP is limited to a maximum of 2 arcseconds. The seeing is linked to the instrument’s resolution: a binary syst ...
Meridian circle

The meridian circle is an instrument for timing of the passage of stars across the local meridian, an event known as a transit, while at the same time measuring their angular distance from the nadir. These are special purpose telescopes mounted so as to allow pointing only in the meridian, the great circle through the north point of the horizon, the zenith, the south point of the horizon, and the nadir. Meridian telescopes rely on the rotation of the Earth to bring objects into their field of view and are mounted on a fixed, horizontal, east-west axis.The similar transit instrument, transit circle or transit telescope is likewise mounted on a horizontal axis, but the axis need not be fixed in the east-west direction. For instance, a surveyor's theodolite can function as a transit instrument if its telescope is capable of a full revolution about the horizontal axis. Meridian circles are often called by these names, although they are less specific.For many years, transit timings were the most accurate method of measuring the positions of heavenly bodies, and meridian instruments were relied upon to perform this painstaking work. Before spectroscopy, photography, and the perfection of reflecting telescopes, the measuring of positions (and the deriving of orbits and astronomical constants) was the major work of observatories.