A STEP - Observatoire de la Côte d`Azur
... know of more than ~200 planets or planetary systems orbiting solar type stars in our neighbourhood. The discovery of more planets, smaller planets and the ability to characterize them directly impacts our ability to understand how planets form, how the Solar System formed, and to better prepare futu ...
... know of more than ~200 planets or planetary systems orbiting solar type stars in our neighbourhood. The discovery of more planets, smaller planets and the ability to characterize them directly impacts our ability to understand how planets form, how the Solar System formed, and to better prepare futu ...
orion® starBlast™ - Spectrum Scientifics
... Tracking Celestial Objects The Earth is constantly rotating about its polar axis, completing one full rotation every 24 hours; this is what defines a “day”. We do not feel the Earth rotating, but we see it at night from the apparent movement of stars from east to west. When you observe any astronomi ...
... Tracking Celestial Objects The Earth is constantly rotating about its polar axis, completing one full rotation every 24 hours; this is what defines a “day”. We do not feel the Earth rotating, but we see it at night from the apparent movement of stars from east to west. When you observe any astronomi ...
Astronomy 518 Astrometry Lecture
... Because of the Earth's orbital motion, this is a little shorter than a solar day. (In one year, the Earth rotates 365 times relative to the Sun, but 366 times relative to the stars. So the sidereal day is about 4 minutes shorter than the solar day.) ...
... Because of the Earth's orbital motion, this is a little shorter than a solar day. (In one year, the Earth rotates 365 times relative to the Sun, but 366 times relative to the stars. So the sidereal day is about 4 minutes shorter than the solar day.) ...
Galileo`s telescope - Exhibits on-line
... which rapidly diminishes with increasing magnification. If, in fact, the field of view of a Galileian telescope with twenty magnifications is indicatively 15 minutes, that is, about half the apparent diameter of the Moon, it decreases to the order of only 5 minutes in a telescope with fifty magnific ...
... which rapidly diminishes with increasing magnification. If, in fact, the field of view of a Galileian telescope with twenty magnifications is indicatively 15 minutes, that is, about half the apparent diameter of the Moon, it decreases to the order of only 5 minutes in a telescope with fifty magnific ...
December 2011
... be a meteor shower known as the Geminid shower. The best time to watch for the meteors will be in the evening of 13 th and the morning of 14th December when the shower should be at its peak. However some should be visible all night. Unfortunately the Moon will be a waning gibbous crescent just 20° s ...
... be a meteor shower known as the Geminid shower. The best time to watch for the meteors will be in the evening of 13 th and the morning of 14th December when the shower should be at its peak. However some should be visible all night. Unfortunately the Moon will be a waning gibbous crescent just 20° s ...
Here - Astrophysics Research Institute
... Coordinates of Solar System Objects All the objects considered so far have been "fixed stars", which keep almost constant values of Right Ascension and Declination. But bodies within the Solar System move a lot within the equatorial coordinate system. The most important one to consider is the Sun. ...
... Coordinates of Solar System Objects All the objects considered so far have been "fixed stars", which keep almost constant values of Right Ascension and Declination. But bodies within the Solar System move a lot within the equatorial coordinate system. The most important one to consider is the Sun. ...
IN 175 SkyView Pro 8 EQ
... a closer view. If the object is off-center (i.e., it is near the edge of the field of view) you will lose it when you increase magnification since the field of view will be narrower with the higher-powered eyepiece. To change eyepieces, first loosen the securing thumbscrew on the focuser. Then caref ...
... a closer view. If the object is off-center (i.e., it is near the edge of the field of view) you will lose it when you increase magnification since the field of view will be narrower with the higher-powered eyepiece. To change eyepieces, first loosen the securing thumbscrew on the focuser. Then caref ...
MEADE INSTRUCTION MANUAL
... Use a compass to make a circle, or trace around the lid of a jar. Draw what you see in your eyepiece inside the circle. The best exercise for drawing is to observe the moons of Jupiter every night or so. Try to make Jupiter and the moons approximately the same size as they look in your eyepiece. You ...
... Use a compass to make a circle, or trace around the lid of a jar. Draw what you see in your eyepiece inside the circle. The best exercise for drawing is to observe the moons of Jupiter every night or so. Try to make Jupiter and the moons approximately the same size as they look in your eyepiece. You ...
Instruction Manual
... mirror is to your right, and the open end of the telescope tube is to your left. The diagonal mirror will appear centered as shown (2, Fig. D). If the diagonal appears off center, then adjust the 3 collimation screws (2, Fig. B) on the plastic diagonal mirror housing. 2. If the reflection of the pri ...
... mirror is to your right, and the open end of the telescope tube is to your left. The diagonal mirror will appear centered as shown (2, Fig. D). If the diagonal appears off center, then adjust the 3 collimation screws (2, Fig. B) on the plastic diagonal mirror housing. 2. If the reflection of the pri ...
114EQ-AR
... power you’re referring to is eyepiece magnification, yes you can! The most common mistake of the beginning observer is to “overpower” a telescope by using high magnifications which the telescope’s aperture and atmospheric conditions cannot reasonably support. Keep in mind that a smaller, but bright ...
... power you’re referring to is eyepiece magnification, yes you can! The most common mistake of the beginning observer is to “overpower” a telescope by using high magnifications which the telescope’s aperture and atmospheric conditions cannot reasonably support. Keep in mind that a smaller, but bright ...
114EQ-AR
... is necessary. Virtually all of the required telescope tracking will be in Right Ascension. For the purposes of casual visual telescopic observations, lining up the telescope's polar axis to within a degree or two of the pole is more than sufficient: with this level of pointing accuracy, the telescop ...
... is necessary. Virtually all of the required telescope tracking will be in Right Ascension. For the purposes of casual visual telescopic observations, lining up the telescope's polar axis to within a degree or two of the pole is more than sufficient: with this level of pointing accuracy, the telescop ...
telestar instruction manual
... telescope no bigger than the one you are using right now. Galileo, who is one of the first astronomers to use a telescope, discovered four of the moons of Jupiter with a telescope about the same size as yours (and his didn’t even focus very well!). OBSERVING Observe during the daytime: Try out your ...
... telescope no bigger than the one you are using right now. Galileo, who is one of the first astronomers to use a telescope, discovered four of the moons of Jupiter with a telescope about the same size as yours (and his didn’t even focus very well!). OBSERVING Observe during the daytime: Try out your ...
40-04135 8 Page Manual Template
... altitude control knobs (5). Loosening this knob allows you to move the telescope up and down. 2. Slightly loosen the horizontal lock knob (6). Loosening this lock allows the telescope to be moved from side to side. 3. Once an object is found, re-tighten the control knobs. You can then use the slow m ...
... altitude control knobs (5). Loosening this knob allows you to move the telescope up and down. 2. Slightly loosen the horizontal lock knob (6). Loosening this lock allows the telescope to be moved from side to side. 3. Once an object is found, re-tighten the control knobs. You can then use the slow m ...
telestar instruction manual
... Use a compass to make a circle, or trace around the lid of a jar. Draw what you see in your eyepiece inside the circle. The best exercise for drawing is to observe the moons of Jupiter every night or so. Try to make Jupiter and the moons approximately the same size as they look in your eyepiece. You ...
... Use a compass to make a circle, or trace around the lid of a jar. Draw what you see in your eyepiece inside the circle. The best exercise for drawing is to observe the moons of Jupiter every night or so. Try to make Jupiter and the moons approximately the same size as they look in your eyepiece. You ...
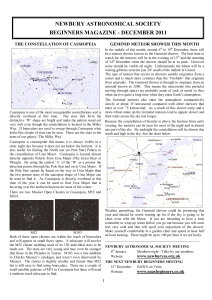
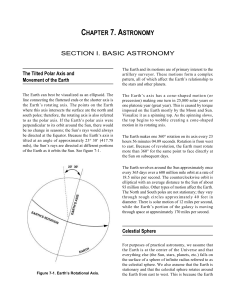
MCWP 3-16.7 Chapter 7: Astronomy
... The Earth makes one 360° rotation on its axis every 23 hours 56 minutes 04.09 seconds. Rotation is from west to east. Because of revolution, the Earth must rotate more than 360° for the same point to face directly at the Sun on subsequent days. The Earth revolves around the Sun approximately once ev ...
... The Earth makes one 360° rotation on its axis every 23 hours 56 minutes 04.09 seconds. Rotation is from west to east. Because of revolution, the Earth must rotate more than 360° for the same point to face directly at the Sun on subsequent days. The Earth revolves around the Sun approximately once ev ...
20225_TerraStar60 InstrctnMnl 042111.qxd
... than the one you are using right now. Galileo, who is one of the first astronomers to use a telescope, discovered four of the moons of Jupiter with a telescope about the same size as yours (and his didn’t even focus very well!). Observe during the daytime: Try out your telescope during the daytime a ...
... than the one you are using right now. Galileo, who is one of the first astronomers to use a telescope, discovered four of the moons of Jupiter with a telescope about the same size as yours (and his didn’t even focus very well!). Observe during the daytime: Try out your telescope during the daytime a ...
The Celestial Sphere - George Mason University
... • Meridian altitude of any object = 90 - (observer's latitude) + declination degrees. If declination is negative, then addition of declination becomes a ...
... • Meridian altitude of any object = 90 - (observer's latitude) + declination degrees. If declination is negative, then addition of declination becomes a ...
NAME: SECTION: Mon Tue Wed Thu ASTRONOMY LAB Stellarium
... directions given to a computer-driven “alt-az” telescope mount to make the telescope point at a specific spot on the sky. The Dobsonian telescopes in this lab course are alt-az telescopes. On the internet find an example of a large professional astronomical telescope that uses an alt-az mount. Such ...
... directions given to a computer-driven “alt-az” telescope mount to make the telescope point at a specific spot on the sky. The Dobsonian telescopes in this lab course are alt-az telescopes. On the internet find an example of a large professional astronomical telescope that uses an alt-az mount. Such ...
AN ATTEMPT To prove the MOTION OF THE EARTH FROM
... with their Instruments and wayes of using them, we shall find that their performances thereby ...
... with their Instruments and wayes of using them, we shall find that their performances thereby ...
Series Telescopes INSTRUCTION MANUAL
... • All models can be used terrestrially as well as astronomically with the standard accessories included. Take time to read through this manual before embarking on your journey through the Universe. It may take a few observing sessions to become familiar with your telescope, so you should keep this m ...
... • All models can be used terrestrially as well as astronomically with the standard accessories included. Take time to read through this manual before embarking on your journey through the Universe. It may take a few observing sessions to become familiar with your telescope, so you should keep this m ...
JMAPS
... Figure 9, the JMAPS instrument can be used to observe Solar system objects. By combining observations of multiple objects, the position of the instrument within the solar system can be determined. This is analogous to work currently be done in the Department of Defense which uses objects in orbit ar ...
... Figure 9, the JMAPS instrument can be used to observe Solar system objects. By combining observations of multiple objects, the position of the instrument within the solar system can be determined. This is analogous to work currently be done in the Department of Defense which uses objects in orbit ar ...
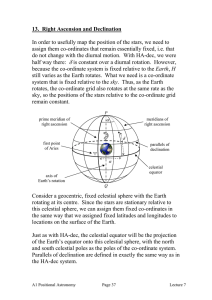
13. Right Ascension and Declination
... also need an analogue for terrestrial longitude: this is the right ascension, α. Great half-circles passing through the north and south celestial poles form the meridians of right ascension. Just as we use the Greenwich meridian as the prime meridian on the Earth, we need a prime meridian for the ce ...
... also need an analogue for terrestrial longitude: this is the right ascension, α. Great half-circles passing through the north and south celestial poles form the meridians of right ascension. Just as we use the Greenwich meridian as the prime meridian on the Earth, we need a prime meridian for the ce ...
User Guide
... All parts of the telescope will arrive in one box. Be careful unpacking it. We recommend keeping the original shipping containers. In the event that the telescope needs to be shipped to another location, having the proper shipping containers will help ensure that your telescope survives the journey ...
... All parts of the telescope will arrive in one box. Be careful unpacking it. We recommend keeping the original shipping containers. In the event that the telescope needs to be shipped to another location, having the proper shipping containers will help ensure that your telescope survives the journey ...
SU3150-Astronomy - Michigan Technological University
... Spherical or curvilinear coordinates are used for defining points on a spherical surface These coordinates are used in astronomy to indicate positions of stars and other celestial objects, and in geodesy, to indicate positions of points on earth Often, computations such as the distances (arc lengths ...
... Spherical or curvilinear coordinates are used for defining points on a spherical surface These coordinates are used in astronomy to indicate positions of stars and other celestial objects, and in geodesy, to indicate positions of points on earth Often, computations such as the distances (arc lengths ...
Meridian circle

The meridian circle is an instrument for timing of the passage of stars across the local meridian, an event known as a transit, while at the same time measuring their angular distance from the nadir. These are special purpose telescopes mounted so as to allow pointing only in the meridian, the great circle through the north point of the horizon, the zenith, the south point of the horizon, and the nadir. Meridian telescopes rely on the rotation of the Earth to bring objects into their field of view and are mounted on a fixed, horizontal, east-west axis.The similar transit instrument, transit circle or transit telescope is likewise mounted on a horizontal axis, but the axis need not be fixed in the east-west direction. For instance, a surveyor's theodolite can function as a transit instrument if its telescope is capable of a full revolution about the horizontal axis. Meridian circles are often called by these names, although they are less specific.For many years, transit timings were the most accurate method of measuring the positions of heavenly bodies, and meridian instruments were relied upon to perform this painstaking work. Before spectroscopy, photography, and the perfection of reflecting telescopes, the measuring of positions (and the deriving of orbits and astronomical constants) was the major work of observatories.