File
... so as to form equal alternate interior angles or corresponding angles, then the lines are parallel with a common perpendicular. Theorem 1-9: If two lines have a common perpendicular, there exists transversals, other than the perpendicular, which cut the lines so as to form equal alternate interior ...
... so as to form equal alternate interior angles or corresponding angles, then the lines are parallel with a common perpendicular. Theorem 1-9: If two lines have a common perpendicular, there exists transversals, other than the perpendicular, which cut the lines so as to form equal alternate interior ...
TEKS Snapshot – Geometry
... G.12(A) apply theorems about circles, including relationships among angles, radii, chords, tangents, and secants, to solve non-contextual problems G.12(B) apply the proportional relationship between the measure of an arc length of a circle and the circumference of the circle to solve problems G.12(C ...
... G.12(A) apply theorems about circles, including relationships among angles, radii, chords, tangents, and secants, to solve non-contextual problems G.12(B) apply the proportional relationship between the measure of an arc length of a circle and the circumference of the circle to solve problems G.12(C ...
SLV RT3 - Within and Around - Integrated Math III Unit 2
... Critical Language: includes the Academic and Technical vocabulary, semantics, and discourse which are particular to and necessary for accessing a given discipline. EXAMPLE: A student in Language Arts can demonstrate the ability to apply and comprehend critical language through the following statemen ...
... Critical Language: includes the Academic and Technical vocabulary, semantics, and discourse which are particular to and necessary for accessing a given discipline. EXAMPLE: A student in Language Arts can demonstrate the ability to apply and comprehend critical language through the following statemen ...
Unit 7 - Geometry 2D and 3D Spheres
... Students should have had experiences with problems involving areas and volumes extend previous work and provide a context for developing and using equations. Students’ competencies in shape composition and decomposition should be highly developed. These competencies form the foundation for understan ...
... Students should have had experiences with problems involving areas and volumes extend previous work and provide a context for developing and using equations. Students’ competencies in shape composition and decomposition should be highly developed. These competencies form the foundation for understan ...
Geometry Quiz Ch 7
... a) with side length 8 cm b) with apothem 4in c) with radius of inscribed circle 6 in d) with radius of circumscribed circle 6 in ...
... a) with side length 8 cm b) with apothem 4in c) with radius of inscribed circle 6 in d) with radius of circumscribed circle 6 in ...
IM7 - Unit 7 Geometric Figures.docx
... Draw, construct, and describe geometrical figures and describe the relationship between them. (7.G.1) Solve problems involving scale drawings of geometric figures, including computing actual lengths and areas from a scale drawing and reproducing a scale drawing at a different scale. (7.G.2) Draw (fr ...
... Draw, construct, and describe geometrical figures and describe the relationship between them. (7.G.1) Solve problems involving scale drawings of geometric figures, including computing actual lengths and areas from a scale drawing and reproducing a scale drawing at a different scale. (7.G.2) Draw (fr ...
Strange Geometries
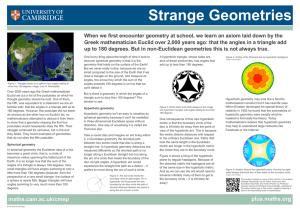
... familiar with: that the angles in a triangle add up to 180 degrees. However, this postulate did not seem as obvious as the other four on Euclid’s list, so mathematicians attempted to deduce it from them: to show that a geometry obeying the first four postulates would necessarily obey the fifth. Thei ...
... familiar with: that the angles in a triangle add up to 180 degrees. However, this postulate did not seem as obvious as the other four on Euclid’s list, so mathematicians attempted to deduce it from them: to show that a geometry obeying the first four postulates would necessarily obey the fifth. Thei ...
2010 SOL Geometry Released Test
... If a cube with side length 6 inches has its dimensions divided in half, what will be the volume of the new cube? A B C D ...
... If a cube with side length 6 inches has its dimensions divided in half, what will be the volume of the new cube? A B C D ...
M04CG1.1.3a Recognize a line of symmetry in a two
... CC.2.3.4.A.1 Draw lines and angles and identify these in two‐dimensional figures. CC.2.3.4.A.2 Classify two‐dimensional figures by properties of their lines and angles. CC.2.3.4.A.3 Recognize symmetric shapes and draw lines of symmetry. Assessment Anchor: M04.C-G.1 Draw and identify lines and ...
... CC.2.3.4.A.1 Draw lines and angles and identify these in two‐dimensional figures. CC.2.3.4.A.2 Classify two‐dimensional figures by properties of their lines and angles. CC.2.3.4.A.3 Recognize symmetric shapes and draw lines of symmetry. Assessment Anchor: M04.C-G.1 Draw and identify lines and ...
M04CG1.1.3a Recognize a line of symmetry in a two
... • CC.2.3.4.A.1 Draw lines and angles and identify these in two‐dimensional figures. • CC.2.3.4.A.2 Classify two‐dimensional figures by properties of their lines and angles. • CC.2.3.4.A.3 Recognize symmetric shapes and draw lines of symmetry. Assessment Anchor: M04.C-G.1 Draw and identify lines and ...
... • CC.2.3.4.A.1 Draw lines and angles and identify these in two‐dimensional figures. • CC.2.3.4.A.2 Classify two‐dimensional figures by properties of their lines and angles. • CC.2.3.4.A.3 Recognize symmetric shapes and draw lines of symmetry. Assessment Anchor: M04.C-G.1 Draw and identify lines and ...
Geometry Shapes and Formulas Triangle
... Trapezoid – 4 sides, only one pair of parallel sides. Other two sides are not the same length. Area = ½ x h (b1 + b2) Perimeter = add up all of the sides ...
... Trapezoid – 4 sides, only one pair of parallel sides. Other two sides are not the same length. Area = ½ x h (b1 + b2) Perimeter = add up all of the sides ...
Four-dimensional space

In mathematics, four-dimensional space (""4D"") is a geometric space with four dimensions. It typically is more specifically four-dimensional Euclidean space, generalizing the rules of three-dimensional Euclidean space. It has been studied by mathematicians and philosophers for over two centuries, both for its own interest and for the insights it offered into mathematics and related fields.Algebraically, it is generated by applying the rules of vectors and coordinate geometry to a space with four dimensions. In particular a vector with four elements (a 4-tuple) can be used to represent a position in four-dimensional space. The space is a Euclidean space, so has a metric and norm, and so all directions are treated as the same: the additional dimension is indistinguishable from the other three.In modern physics, space and time are unified in a four-dimensional Minkowski continuum called spacetime, whose metric treats the time dimension differently from the three spatial dimensions (see below for the definition of the Minkowski metric/pairing). Spacetime is not a Euclidean space.