BASICS OF NEUROBIOLOGY Zsolt Liposits and Imre Kalló 2016
... SPINAL CORD INTERNAL STRUCTURE OF SPINAL CORD ...
... SPINAL CORD INTERNAL STRUCTURE OF SPINAL CORD ...
Nervous System - Fuller Anatomy
... Adult spinal cord is 18 inches long and 14 mm wide Spinal cord does not continue in length with the vertebrae; stops at L1 and L2 Entire spinal cord can be divided into 31 segments on the basis of the origins of the spinal nerves ...
... Adult spinal cord is 18 inches long and 14 mm wide Spinal cord does not continue in length with the vertebrae; stops at L1 and L2 Entire spinal cord can be divided into 31 segments on the basis of the origins of the spinal nerves ...
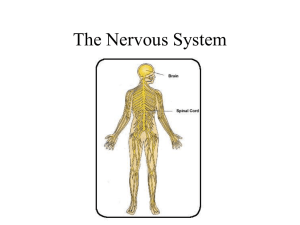
The Nervous System
... • Impulse goes from neuronal axon to another neuron or a receptor – This junction called ---synapse – neurotransmitters ...
... • Impulse goes from neuronal axon to another neuron or a receptor – This junction called ---synapse – neurotransmitters ...
Brain/Sc Notes
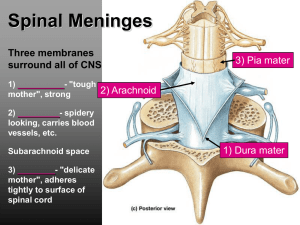
... If I only had a brain……… Meninges –membranes between bone and tissue protecting brain and spinal cord 3 layers of meninges: Dura mater-white fibrous CT, blood vessels and nerves, attaches to inside of cranial cavity, forms periosteum Arachnoid mater-middle, weblike, no blood vessels Pia mater-innerm ...
... If I only had a brain……… Meninges –membranes between bone and tissue protecting brain and spinal cord 3 layers of meninges: Dura mater-white fibrous CT, blood vessels and nerves, attaches to inside of cranial cavity, forms periosteum Arachnoid mater-middle, weblike, no blood vessels Pia mater-innerm ...
The Anterolateral System
... • The Anterolateral System is an ascending pathway conveying pain and temperature sensation. • Cell bodies of the primary sensory neurons reside in the dorsal root ganglia and the trigeminal complex. • This pathway receives input from thermoreceptors, nociceptors, and mechanoreceptors. ...
... • The Anterolateral System is an ascending pathway conveying pain and temperature sensation. • Cell bodies of the primary sensory neurons reside in the dorsal root ganglia and the trigeminal complex. • This pathway receives input from thermoreceptors, nociceptors, and mechanoreceptors. ...
Ch 14: Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves
... gray commissures - axons carrying information from side to side ...
... gray commissures - axons carrying information from side to side ...
Spinal Cord Worksheet - District 196 e
... ! ! Which of the four plexuses controls the diaphragmatic muscles? ! ! Damage to this region of the spinal cord would require a mechanical respirator to ! ! keep the victim alive (try to be specific): ! ! ! The largest and longest nerve in the body belongs to this plexuses: ! ! When somebody says “I ...
... ! ! Which of the four plexuses controls the diaphragmatic muscles? ! ! Damage to this region of the spinal cord would require a mechanical respirator to ! ! keep the victim alive (try to be specific): ! ! ! The largest and longest nerve in the body belongs to this plexuses: ! ! When somebody says “I ...
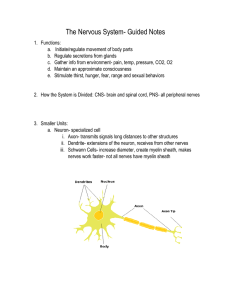
Nervous System Guided Notes
... c. Brain Stem - controls functions to maintain life (blood pressure, HR, RR) ...
... c. Brain Stem - controls functions to maintain life (blood pressure, HR, RR) ...
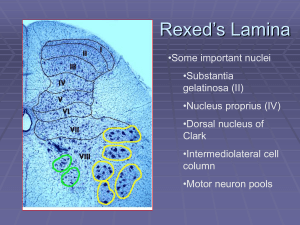
Rexed`s Lamina
... Spinocerebellar Pathway Proprioceptive signals from limbs and trunk travel up to the cerebellum Second order nerves ascend in ipsilateral lateral column ...
... Spinocerebellar Pathway Proprioceptive signals from limbs and trunk travel up to the cerebellum Second order nerves ascend in ipsilateral lateral column ...
The Neurological System
... Synapses • Needed, a chemical, an electrical stimulus, a chemical and electrical stimulus • Nerve impulses have to jump from one area to the other because the neurons are not continuous. ...
... Synapses • Needed, a chemical, an electrical stimulus, a chemical and electrical stimulus • Nerve impulses have to jump from one area to the other because the neurons are not continuous. ...
Document
... • carries messages from sensory nerves to the brain and motor nerve messages from the brain to organs, muscles and glands. • it contains two types of tissue: • grey matter - non-myelinated interneurons • white matter - myelinated neurons (motor and sensory) • the interneurons are arranged in tracts ...
... • carries messages from sensory nerves to the brain and motor nerve messages from the brain to organs, muscles and glands. • it contains two types of tissue: • grey matter - non-myelinated interneurons • white matter - myelinated neurons (motor and sensory) • the interneurons are arranged in tracts ...
CNS
... • carries messages from sensory nerves to the brain and motor nerve messages from the brain to organs, muscles and glands. • it contains two types of tissue: • grey matter - non-myelinated interneurons • white matter - myelinated neurons (motor and sensory) • the interneurons are arranged in tracts ...
... • carries messages from sensory nerves to the brain and motor nerve messages from the brain to organs, muscles and glands. • it contains two types of tissue: • grey matter - non-myelinated interneurons • white matter - myelinated neurons (motor and sensory) • the interneurons are arranged in tracts ...
Nervous System - Biology Junction
... Types of Neurons • Sensory – incoming signals • Motor - movement • Interneurons – in brain and spinal cord only (processors/relay terminals) ...
... Types of Neurons • Sensory – incoming signals • Motor - movement • Interneurons – in brain and spinal cord only (processors/relay terminals) ...
7-1_SegmOrgSpinCord_BogdanyP
... carry commands from the brain and spinal cord to other parts of the body, particularly to skeletal muscles. The sensory roots carry information to the brain from other parts of the body. The butterfly-shape part of the cord is the grey matter, which contains cell bodies of neurons. The outer part is ...
... carry commands from the brain and spinal cord to other parts of the body, particularly to skeletal muscles. The sensory roots carry information to the brain from other parts of the body. The butterfly-shape part of the cord is the grey matter, which contains cell bodies of neurons. The outer part is ...
1 Chapter 12 Central Nervous System Spinal Cord
... Gray matter of spinal cord • Dorsal horns – associated with afferent, sensory nerve impulses from receptors, C1-L5 neuron cell bodies bundled in dorsal root ganglion • Ventral horns – associated with efferent, motor nerve impulses to effectors, C1-L5 neuron cell bodies are in gray matter of ventral ...
... Gray matter of spinal cord • Dorsal horns – associated with afferent, sensory nerve impulses from receptors, C1-L5 neuron cell bodies bundled in dorsal root ganglion • Ventral horns – associated with efferent, motor nerve impulses to effectors, C1-L5 neuron cell bodies are in gray matter of ventral ...
Axial vs. Appendicular Skeleton
... the skeletal muscles of the arms and legs. Neural signals follow specific pathways. In the case of the descending tracts axons from the brain synapse with cell bodies in the spinal cord which then send impulses out to the rest of the body. ...
... the skeletal muscles of the arms and legs. Neural signals follow specific pathways. In the case of the descending tracts axons from the brain synapse with cell bodies in the spinal cord which then send impulses out to the rest of the body. ...
Lies outside the central nervous system
... -Lies between the spinal cord and the PONS -Regulates heartbeat, breathing, and blood pressure -Reflex center for vomiting, sneezing, swallowing, and coughing ...
... -Lies between the spinal cord and the PONS -Regulates heartbeat, breathing, and blood pressure -Reflex center for vomiting, sneezing, swallowing, and coughing ...
spinal cord - (canvas.brown.edu).
... Single spinal nerve on each side Each nerve defines spinal segment Cervical (8 segments; supply neck, upper trunk, arm) Thoracic (12 segments; thorax, abdomen) Lumbar (5 segments; lower abdomen, legs) Sacral, coccygeal (5 and 2-3 segments; pelvic) Cauda equina Differential growth of vertebral column ...
... Single spinal nerve on each side Each nerve defines spinal segment Cervical (8 segments; supply neck, upper trunk, arm) Thoracic (12 segments; thorax, abdomen) Lumbar (5 segments; lower abdomen, legs) Sacral, coccygeal (5 and 2-3 segments; pelvic) Cauda equina Differential growth of vertebral column ...
Sp.CBSTH functions
... The peripheral regions of the spinal cord contains neuronal white matter tracts containing sensory and motor neurons. The central region is gray matter that contains nerve cell bodies. ...
... The peripheral regions of the spinal cord contains neuronal white matter tracts containing sensory and motor neurons. The central region is gray matter that contains nerve cell bodies. ...
Study Guide for The Spinal Cord – Chapter 8, Part B Be familiar with
... Be familiar with the following terms and their biological importance (structure and function): arachnoid membrane, central canal, central nervous system, cerebrospinal fluid, cervical enlargement, conus medullaris, dorsal (posterior) gray horn, dorsal root (sensory fibers), dorsal root ganglion, dur ...
... Be familiar with the following terms and their biological importance (structure and function): arachnoid membrane, central canal, central nervous system, cerebrospinal fluid, cervical enlargement, conus medullaris, dorsal (posterior) gray horn, dorsal root (sensory fibers), dorsal root ganglion, dur ...
The Nervous System
... • Pia mater The pia is on the surface of the CNS and forms the filum terminale which anchors the spinal cord onto the sacrum/coccyx ...
... • Pia mater The pia is on the surface of the CNS and forms the filum terminale which anchors the spinal cord onto the sacrum/coccyx ...
Chapter 14 - WordPress.com
... Posterior median sulcus- shallow groove on the dorsal surface Anterior median fissure- deep crease on the ventral surface Each region of the spinal cord contains tracts involved with that particular segment and those inferior to it Enlargements areas of coordination of incoming and outgoing ...
... Posterior median sulcus- shallow groove on the dorsal surface Anterior median fissure- deep crease on the ventral surface Each region of the spinal cord contains tracts involved with that particular segment and those inferior to it Enlargements areas of coordination of incoming and outgoing ...
Spinal cord
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular bundle of nervous tissue and support cells that extends from the medulla oblongata in the brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column. The brain and spinal cord together make up the central nervous system (CNS). The spinal cord begins at the occipital bone and extends down to the space between the first and second lumbar vertebrae; it does not extend the entire length of the vertebral column. It is around 45 cm (18 in) in men and around 43 cm (17 in) long in women. Also, the spinal cord has a varying width, ranging from 13 mm (1⁄2 in) thick in the cervical and lumbar regions to 6.4 mm (1⁄4 in) thick in the thoracic area. The enclosing bony vertebral column protects the relatively shorter spinal cord. The spinal cord functions primarily in the transmission of neural signals between the brain and the rest of the body but also contains neural circuits that can independently control numerous reflexes and central pattern generators.The spinal cord has three major functions:as a conduit for motor information, which travels down the spinal cord, as a conduit for sensory information in the reverse direction, and finally as a center for coordinating certain reflexes.