Lecture 6 Locomotion • Early 20th century experiments showed that
... Hb9-‐ positive = express a particular transcription factor • Excitatory interneurons in medial lamina VIII of lower thoracic and upper lumbar segments ...
... Hb9-‐ positive = express a particular transcription factor • Excitatory interneurons in medial lamina VIII of lower thoracic and upper lumbar segments ...
Anatomical Terminology
... 5. Dorsal root ganglion a. Cell bodies of sensory neurons b. Axons project to cord via dorsal root i. Some enter white matter tracks and ascend ii. Some synapse with interneuron located in posterior horn 6. Spinal nerves a. Lateral fusion of ventral and dorsal roots b. Part of PNS (see below) C. Spi ...
... 5. Dorsal root ganglion a. Cell bodies of sensory neurons b. Axons project to cord via dorsal root i. Some enter white matter tracks and ascend ii. Some synapse with interneuron located in posterior horn 6. Spinal nerves a. Lateral fusion of ventral and dorsal roots b. Part of PNS (see below) C. Spi ...
Nervous System - Emery
... How do electrical signals pass through cells? Membrane Potential glial cells provide insulation for electrical ...
... How do electrical signals pass through cells? Membrane Potential glial cells provide insulation for electrical ...
Lecture 4: Development of nervous system. Neural plate. Brain
... − the vertebral column and the dural sac lengthen more rapidly than the neural tube → disproportionate growth → spinal nerves run obliquely − the dura remains attached to the vertebral column → the dural sac − the spinal cord in newborns extends to the body of the L3 vertebra − extension of the pia ...
... − the vertebral column and the dural sac lengthen more rapidly than the neural tube → disproportionate growth → spinal nerves run obliquely − the dura remains attached to the vertebral column → the dural sac − the spinal cord in newborns extends to the body of the L3 vertebra − extension of the pia ...
The nervous tissue is made up of
... Each spinal nerve is made up of: • A Dorsal (Sensory) root, which contains incoming fibres whose cell bodies are located in the Dorsal root ganglion and • A Ventral (Motor) root which contain outgoing fibres whose cell bodies are located in the ventral aspect (Ventral horn) of the gray matter of the ...
... Each spinal nerve is made up of: • A Dorsal (Sensory) root, which contains incoming fibres whose cell bodies are located in the Dorsal root ganglion and • A Ventral (Motor) root which contain outgoing fibres whose cell bodies are located in the ventral aspect (Ventral horn) of the gray matter of the ...
Spontaneous plasticity in the injured spinal cord
... chronic reductions in nigral inputs.3 In Alzheimer’s disease, chronic degeneration of entorhinal cortical inputs to the hippocampus results in compensatory sprouting of cholinergic and kainate inputs.4 The denervation hypersensitivity in Parkinson’s disease is likely to be functionally beneficial, f ...
... chronic reductions in nigral inputs.3 In Alzheimer’s disease, chronic degeneration of entorhinal cortical inputs to the hippocampus results in compensatory sprouting of cholinergic and kainate inputs.4 The denervation hypersensitivity in Parkinson’s disease is likely to be functionally beneficial, f ...
Five Essential Components to the Reflex Arc
... neurons, the muscle contracts, and you take your hand off the stove before your brain even knows it. This is an example of a withdrawal reflex. • Simple reflex behavior involves three neurons, and no brain involvement. Reflexes are automatic events. They involve both motor and sensory neurons, they ...
... neurons, the muscle contracts, and you take your hand off the stove before your brain even knows it. This is an example of a withdrawal reflex. • Simple reflex behavior involves three neurons, and no brain involvement. Reflexes are automatic events. They involve both motor and sensory neurons, they ...
Five Essential Components to the Reflex Arc
... neurons, the muscle contracts, and you take your hand off the stove before your brain even knows it. This is an example of a withdrawal reflex. • Simple reflex behavior involves three neurons, and no brain involvement. Reflexes are automatic events. They involve both motor and sensory neurons, they ...
... neurons, the muscle contracts, and you take your hand off the stove before your brain even knows it. This is an example of a withdrawal reflex. • Simple reflex behavior involves three neurons, and no brain involvement. Reflexes are automatic events. They involve both motor and sensory neurons, they ...
anterior spinothalamic tract.
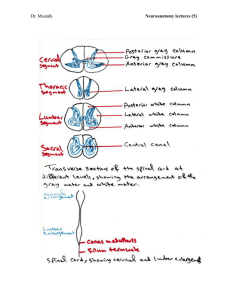
... The gray matter of the spinal cord is similar to butter fly, has two dorsal or posterior horns, intermediate horn and two anterior or ventral horns. Anterior horn: It has a motor function and it is composed of two groups of cell bodies or neurons: 1- Alpha motor neurons (the highest number). 2- Gamm ...
... The gray matter of the spinal cord is similar to butter fly, has two dorsal or posterior horns, intermediate horn and two anterior or ventral horns. Anterior horn: It has a motor function and it is composed of two groups of cell bodies or neurons: 1- Alpha motor neurons (the highest number). 2- Gamm ...
Human Anatomy, First Edition McKinley&O'Loughlin
... that houses it. The tapering inferior end of the spinal cord is called the conus medullaris and it marks the official “end” of the spinal cord proper. Inferior to this point, nerve roots (groups of axons collectively called the cauda equina) project inferiorly from the spinal cord. Within the cauda ...
... that houses it. The tapering inferior end of the spinal cord is called the conus medullaris and it marks the official “end” of the spinal cord proper. Inferior to this point, nerve roots (groups of axons collectively called the cauda equina) project inferiorly from the spinal cord. Within the cauda ...
The Brain and the Senses
... • Thick rope of interneurons • Main communication line to brain • 31 pairs of spinal nerves • Herniated disc – swelling of ...
... • Thick rope of interneurons • Main communication line to brain • 31 pairs of spinal nerves • Herniated disc – swelling of ...
Airgas template
... Neurons directly innervating muscles are affected Irritated neurons Spontaneous muscle contractions: fasciculations Death of neurons Spinal reflexes are lost ...
... Neurons directly innervating muscles are affected Irritated neurons Spontaneous muscle contractions: fasciculations Death of neurons Spinal reflexes are lost ...
11.4: The Peripheral Nervous System
... division, such as rapid heartbeat and elevated blood pressure, are reduced, and “housekeeping” (maintenance) activities such as digestion can take place. 2. At every level from the bottom to the top of the spinal cord, one ventral and one dorsal root enter from each side of the body to form a spinal ...
... division, such as rapid heartbeat and elevated blood pressure, are reduced, and “housekeeping” (maintenance) activities such as digestion can take place. 2. At every level from the bottom to the top of the spinal cord, one ventral and one dorsal root enter from each side of the body to form a spinal ...
12 - FacultyWeb
... • CSF in subarachnoid space • Denticulate ligaments: extensions of pia mater that secure cord to dura mater ...
... • CSF in subarachnoid space • Denticulate ligaments: extensions of pia mater that secure cord to dura mater ...
FUNCTIONAL NEUROANATOMY OF SPINAL CORD LEARNING
... Begins superiorly at foramen magnum Ends at lower border of first lumber vertebrae Occupy upper two thirds of vertebral canal ...
... Begins superiorly at foramen magnum Ends at lower border of first lumber vertebrae Occupy upper two thirds of vertebral canal ...
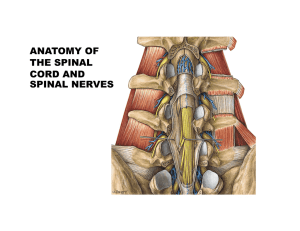
ANATOMY OF THE SPINAL CORD AND SPINAL NERVES
... DIVIDES INTO THE ULNAR NERVE AND MEDIAL HALF OF THE MEDIAN NERVE ULNAR NERVE PASSES POSTERIOR TO THE MEDIAL EPICONDYLE OF THE HUMERUS, SUPPLIES 1/1/2 MUSCLES OF THE ANTERIOR FOREARM AND THE MEDIAL AND DEEP MUSCLES OF THE HAND MEDIAN NERVE SUPPLIES MOST OF THE ANTERIOR FOREARM MUSCLES AND THE LATERAL ...
... DIVIDES INTO THE ULNAR NERVE AND MEDIAL HALF OF THE MEDIAN NERVE ULNAR NERVE PASSES POSTERIOR TO THE MEDIAL EPICONDYLE OF THE HUMERUS, SUPPLIES 1/1/2 MUSCLES OF THE ANTERIOR FOREARM AND THE MEDIAL AND DEEP MUSCLES OF THE HAND MEDIAN NERVE SUPPLIES MOST OF THE ANTERIOR FOREARM MUSCLES AND THE LATERAL ...
2.1.2. The Purpose: Acquaint the student by subject to neurologies
... periosteum of the surrounding bone (i.e., the vertebral canal) but is separated from it by the epidural space, which contains fat, loose connective tissue, and valveless venous plexuses. The root filaments (rootlets) that come together to form the ventral and dorsal spinal nerve roots are arranged i ...
... periosteum of the surrounding bone (i.e., the vertebral canal) but is separated from it by the epidural space, which contains fat, loose connective tissue, and valveless venous plexuses. The root filaments (rootlets) that come together to form the ventral and dorsal spinal nerve roots are arranged i ...
Chapter 39 Neural Signaling and Chapter 40 Neural Regulation
... – R and L hemispheres – Mostly white matter (mainly myelinated axons that connect various parts of brain) – Surface convolutions = numerous folds • Expands surface • Sulci – furrows between convolutions if shallow • Fissures if deep ...
... – R and L hemispheres – Mostly white matter (mainly myelinated axons that connect various parts of brain) – Surface convolutions = numerous folds • Expands surface • Sulci – furrows between convolutions if shallow • Fissures if deep ...
File
... • Zoloft is part of a class of drugs called selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, or • SSRIs for short. SSRIs act on a specific chemical within the brain known as serotonin. This is one of several chemicals used to send messages from one nerve cell to another. ...
... • Zoloft is part of a class of drugs called selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, or • SSRIs for short. SSRIs act on a specific chemical within the brain known as serotonin. This is one of several chemicals used to send messages from one nerve cell to another. ...
L1 Nervous System Neurons File
... Generally only 1 axon per cell Can have myelin Branch further from the cell body ...
... Generally only 1 axon per cell Can have myelin Branch further from the cell body ...
NERVOUS SYSTEM AND REFLEXES Introduction:
... interneuron within the spinal cord. Motor neuron cell bodies lie within the spinal cord and their axons extend from the spinal cord as the ventral root. Both the dorsal and ventral roots merge, to form a mixed nerve, carrying both sensory and motor information between the body and the spinal cord. W ...
... interneuron within the spinal cord. Motor neuron cell bodies lie within the spinal cord and their axons extend from the spinal cord as the ventral root. Both the dorsal and ventral roots merge, to form a mixed nerve, carrying both sensory and motor information between the body and the spinal cord. W ...
BIo 218 Lecture Outline Tortora Ch18
... a. the gray matter consists primarily of cell bodies of neurons, neuroglia, unmyelinated axons, and dendrites of interneurons and motor neurons b. the white matter consists of bundles of myelinated and unmyelinated axons of motor neurons, interneurons, and sensory neurons The gray commissure is a re ...
... a. the gray matter consists primarily of cell bodies of neurons, neuroglia, unmyelinated axons, and dendrites of interneurons and motor neurons b. the white matter consists of bundles of myelinated and unmyelinated axons of motor neurons, interneurons, and sensory neurons The gray commissure is a re ...
Spinal cord
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular bundle of nervous tissue and support cells that extends from the medulla oblongata in the brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column. The brain and spinal cord together make up the central nervous system (CNS). The spinal cord begins at the occipital bone and extends down to the space between the first and second lumbar vertebrae; it does not extend the entire length of the vertebral column. It is around 45 cm (18 in) in men and around 43 cm (17 in) long in women. Also, the spinal cord has a varying width, ranging from 13 mm (1⁄2 in) thick in the cervical and lumbar regions to 6.4 mm (1⁄4 in) thick in the thoracic area. The enclosing bony vertebral column protects the relatively shorter spinal cord. The spinal cord functions primarily in the transmission of neural signals between the brain and the rest of the body but also contains neural circuits that can independently control numerous reflexes and central pattern generators.The spinal cord has three major functions:as a conduit for motor information, which travels down the spinal cord, as a conduit for sensory information in the reverse direction, and finally as a center for coordinating certain reflexes.