Nervous System Part Three Name: Sec 1: Peripheral NS Sec 2
... o Ganglia Contain neuron cell bodies associated with nerves Dorsal root ganglia (sensory, somatic) Autonomic ganglia (motor, visceral) o Regeneration of nerve fibers Mature neurons are ______________ If the soma of a damaged nerve is intact, ___________ will regenerate Involves coordinat ...
... o Ganglia Contain neuron cell bodies associated with nerves Dorsal root ganglia (sensory, somatic) Autonomic ganglia (motor, visceral) o Regeneration of nerve fibers Mature neurons are ______________ If the soma of a damaged nerve is intact, ___________ will regenerate Involves coordinat ...
Unit Three
... cerebral hemispheres & brain stem, are continuous with the central canal of the spinal cord, & are filled with cerebrospinal fluid *choroid plexuses (red cauliflowerlike) in the walls of ventricle secrete cerebrospinal fluid *ependymal cells of the choroid plexus regulate the composition of cerebros ...
... cerebral hemispheres & brain stem, are continuous with the central canal of the spinal cord, & are filled with cerebrospinal fluid *choroid plexuses (red cauliflowerlike) in the walls of ventricle secrete cerebrospinal fluid *ependymal cells of the choroid plexus regulate the composition of cerebros ...
lecture 14 neurophysiology review
... arm” with sensory neurons centered in the dorsal root ganglion of spinal nerves. There is also a “motor arm” with neuron cell bodies in the anterior horns of the gray matter of the spinal cord. These sensory and motor arms are integrated by means of an interneuron within the gray matter of the cord. ...
... arm” with sensory neurons centered in the dorsal root ganglion of spinal nerves. There is also a “motor arm” with neuron cell bodies in the anterior horns of the gray matter of the spinal cord. These sensory and motor arms are integrated by means of an interneuron within the gray matter of the cord. ...
Divisions of the Nervous System
... – Medulla oblongata involuntary activities (breathing, heart rate, blood pressure) ...
... – Medulla oblongata involuntary activities (breathing, heart rate, blood pressure) ...
SPINAL ANATOMY - Circle of Docs
... C. abducens D. optic E. trochlear 20. The origin and termination of the filum terminale are the A. atlas of coccyx B. cervical enlargement and lumbar enlargement C. cervical enlargement and first lumbar D. atlas and axis E. apex of conus medullaris and first segment of coccyx 21. All of the followin ...
... C. abducens D. optic E. trochlear 20. The origin and termination of the filum terminale are the A. atlas of coccyx B. cervical enlargement and lumbar enlargement C. cervical enlargement and first lumbar D. atlas and axis E. apex of conus medullaris and first segment of coccyx 21. All of the followin ...
BIO 218 F 2012 Ch 14 Martini Lecture Outline
... Sectional Anatomy of the Spinal Cord Organization of gray matter Posterior gray horns: somatic sensory and visceral nuclei Lateral gray horns: visceral motor nuclei Anterior gray horns: somatic motor nuclei Gray commissure Consists of axons crossing from one side to the other ...
... Sectional Anatomy of the Spinal Cord Organization of gray matter Posterior gray horns: somatic sensory and visceral nuclei Lateral gray horns: visceral motor nuclei Anterior gray horns: somatic motor nuclei Gray commissure Consists of axons crossing from one side to the other ...
BIO 218 F 2012 Ch 14 Martini Lecture Outline
... Sectional Anatomy of the Spinal Cord Organization of gray matter Posterior gray horns: somatic sensory and visceral nuclei Lateral gray horns: visceral motor nuclei Anterior gray horns: somatic motor nuclei Gray commissure Consists of axons crossing from one side to the other ...
... Sectional Anatomy of the Spinal Cord Organization of gray matter Posterior gray horns: somatic sensory and visceral nuclei Lateral gray horns: visceral motor nuclei Anterior gray horns: somatic motor nuclei Gray commissure Consists of axons crossing from one side to the other ...
TRIGEMINAL NUCLEUS - eCurriculum
... Transmits pain and temperature sensation from the body. Located laterally in the spinal cord and remains relatively lateral through the brainstem and midbrain – (you will need to know the exact location – shown to you in video). Crosses in the spinal cord. Called the Lateral Spinothalamic Tr ...
... Transmits pain and temperature sensation from the body. Located laterally in the spinal cord and remains relatively lateral through the brainstem and midbrain – (you will need to know the exact location – shown to you in video). Crosses in the spinal cord. Called the Lateral Spinothalamic Tr ...
Document
... behavior. Although we know how the sensory-motor system generally works, the main issue lies in identifying all neurons involved and understanding their interrelationships. Many interneurons contribute to sensory-motor circuits and have been well studied. For example, Renshaw cells (RC) are inhibito ...
... behavior. Although we know how the sensory-motor system generally works, the main issue lies in identifying all neurons involved and understanding their interrelationships. Many interneurons contribute to sensory-motor circuits and have been well studied. For example, Renshaw cells (RC) are inhibito ...
General anatomy [edit]
... In the medial part of the medulla is the anterior median fissure. Moving laterally on each side are the pyramids. The pyramids contain the fibers of the corticospinal tract (also called the pyramidal tract), or the upper motor neuronal axons as they head inferiorly to synapse on lower motor neuronal ...
... In the medial part of the medulla is the anterior median fissure. Moving laterally on each side are the pyramids. The pyramids contain the fibers of the corticospinal tract (also called the pyramidal tract), or the upper motor neuronal axons as they head inferiorly to synapse on lower motor neuronal ...
Ch. 27 notes - The Nervous System
... muscles under emergency conditions, often called the “fight or flight” response (e.g. increased breathing rate, suspension of digestive system processing) 3. The nerves of the body are bundles of axons of neurons in the PNS. These bundles are both sensory neuron axons carrying information from senso ...
... muscles under emergency conditions, often called the “fight or flight” response (e.g. increased breathing rate, suspension of digestive system processing) 3. The nerves of the body are bundles of axons of neurons in the PNS. These bundles are both sensory neuron axons carrying information from senso ...
MSI - NERVOUS SYSTEM
... • Pathway for ascending and descending tracts • Pons – in front of cerebellum, between midbrain and medulla – contains center that controls respiration • Midbrain – vision and hearing • Medulla oblongata – bulb-shaped structure between pons and spinal cord, inside the cranium above foramen magnum. R ...
... • Pathway for ascending and descending tracts • Pons – in front of cerebellum, between midbrain and medulla – contains center that controls respiration • Midbrain – vision and hearing • Medulla oblongata – bulb-shaped structure between pons and spinal cord, inside the cranium above foramen magnum. R ...
chapter29_Neural Control(9
... • Three membranes that cover and protect the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) • cerebrospinal fluid • Fills the space between the meninges, the central canal of the spinal cord, and ventricles within the brain ...
... • Three membranes that cover and protect the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) • cerebrospinal fluid • Fills the space between the meninges, the central canal of the spinal cord, and ventricles within the brain ...
Document
... •epithalamus – consists of the pineal gland and habenular nuclei -pineal gland – part of the endocrine system -secretes the hormone melatonin -increased secretion in dark -promote sleepiness and helps set the circadian rhythms of the body (awake/sleep period) ...
... •epithalamus – consists of the pineal gland and habenular nuclei -pineal gland – part of the endocrine system -secretes the hormone melatonin -increased secretion in dark -promote sleepiness and helps set the circadian rhythms of the body (awake/sleep period) ...
Lecture
... •epithalamus – consists of the pineal gland and habenular nuclei -pineal gland – part of the endocrine system -secretes the hormone melatonin -increased secretion in dark -promote sleepiness and helps set the circadian rhythms of the body (awake/sleep period) ...
... •epithalamus – consists of the pineal gland and habenular nuclei -pineal gland – part of the endocrine system -secretes the hormone melatonin -increased secretion in dark -promote sleepiness and helps set the circadian rhythms of the body (awake/sleep period) ...
Central Nervous System
... • Pair of dorsal or posterior horns • dorsal root of spinal nerve is totally sensory fibers • Pair of ventral or anterior horns • ventral root of spinal nerve is totally motor fibers • Connected by gray commissure punctured by a central canal continuous above with 4th ventricle ...
... • Pair of dorsal or posterior horns • dorsal root of spinal nerve is totally sensory fibers • Pair of ventral or anterior horns • ventral root of spinal nerve is totally motor fibers • Connected by gray commissure punctured by a central canal continuous above with 4th ventricle ...
Slide 1 - AccessMedicine
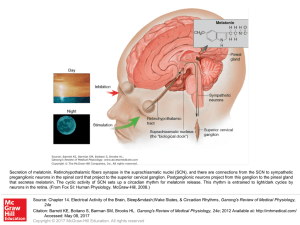
... Secretion of melatonin. Retinohypothalamic fibers synapse in the suprachiasmatic nuclei (SCN), and there are connections from the SCN to sympathetic preganglionic neurons in the spinal cord that project to the superior cervical ganglion. Postganglionic neurons project from this ganglion to the pinea ...
... Secretion of melatonin. Retinohypothalamic fibers synapse in the suprachiasmatic nuclei (SCN), and there are connections from the SCN to sympathetic preganglionic neurons in the spinal cord that project to the superior cervical ganglion. Postganglionic neurons project from this ganglion to the pinea ...
Central Nervous System I. Brain - Function A. Hindbrain 1. Medulla
... bundles of nerves that serve specific region of the body. Each of the nerves in turn sends branches to specific structures they innervate. Advantage of the Plexus Within the plexus the neurons from different ventral rami become redistributed so that each branch of the plexus contains neurons from se ...
... bundles of nerves that serve specific region of the body. Each of the nerves in turn sends branches to specific structures they innervate. Advantage of the Plexus Within the plexus the neurons from different ventral rami become redistributed so that each branch of the plexus contains neurons from se ...
Disorders of the Spinal Cord
... • the ventral and the dorsal roots join together and form the spinal nerve • spinal nerves get out of the spinal canal through the intervertebral foramina • the end of the spinal cord is under which vertebra (vertebral body)? (L2) • anatomical relationships of spinal cord segments and bony spine: sp ...
... • the ventral and the dorsal roots join together and form the spinal nerve • spinal nerves get out of the spinal canal through the intervertebral foramina • the end of the spinal cord is under which vertebra (vertebral body)? (L2) • anatomical relationships of spinal cord segments and bony spine: sp ...
introduction to peripheral nervous system 26. 02. 2014
... The anterior rami form plexuses (network). All major somatic plexuses (cervical, brachial, lumbar, and sacral) are formed by anterior rami (ramus=branch, rami=branches). The spinal cord is a long tubular structure that is divided into a peripheral white matter (composed of myelinated axons) and a ce ...
... The anterior rami form plexuses (network). All major somatic plexuses (cervical, brachial, lumbar, and sacral) are formed by anterior rami (ramus=branch, rami=branches). The spinal cord is a long tubular structure that is divided into a peripheral white matter (composed of myelinated axons) and a ce ...
Emergency Management of Spinal Cord Lesions
... The propriospinal (or fasciculus proprius) tract is located around the gray matter deep within the cord at segments T2 to L3. Inhibition and coordination of the frontlimbs occurs with respect to movement of the rearlimbs through this tract. With severe, deep, diffuse spinal cord compression between ...
... The propriospinal (or fasciculus proprius) tract is located around the gray matter deep within the cord at segments T2 to L3. Inhibition and coordination of the frontlimbs occurs with respect to movement of the rearlimbs through this tract. With severe, deep, diffuse spinal cord compression between ...
Central Nervous System Sensory neurons transmit impulses from the
... a) from the central nervous system to a muscle a gland b) from the brain to the spinal cord c) from the environment to the spinal cord or brain d) within the brain e) All of the above are true. ...
... a) from the central nervous system to a muscle a gland b) from the brain to the spinal cord c) from the environment to the spinal cord or brain d) within the brain e) All of the above are true. ...
THE SPINAL CORD
... perception of form, and modality termed proprioception, which gives a sense of where the- body parts are (position sense) and of tension of joints and muscles. They divide into ascending and descending branches and terminate in lamina III-VI (A-Beta) and L VI-VII, IX (A-alfa fibers). Impulses from c ...
... perception of form, and modality termed proprioception, which gives a sense of where the- body parts are (position sense) and of tension of joints and muscles. They divide into ascending and descending branches and terminate in lamina III-VI (A-Beta) and L VI-VII, IX (A-alfa fibers). Impulses from c ...
Spinal cord
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular bundle of nervous tissue and support cells that extends from the medulla oblongata in the brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column. The brain and spinal cord together make up the central nervous system (CNS). The spinal cord begins at the occipital bone and extends down to the space between the first and second lumbar vertebrae; it does not extend the entire length of the vertebral column. It is around 45 cm (18 in) in men and around 43 cm (17 in) long in women. Also, the spinal cord has a varying width, ranging from 13 mm (1⁄2 in) thick in the cervical and lumbar regions to 6.4 mm (1⁄4 in) thick in the thoracic area. The enclosing bony vertebral column protects the relatively shorter spinal cord. The spinal cord functions primarily in the transmission of neural signals between the brain and the rest of the body but also contains neural circuits that can independently control numerous reflexes and central pattern generators.The spinal cord has three major functions:as a conduit for motor information, which travels down the spinal cord, as a conduit for sensory information in the reverse direction, and finally as a center for coordinating certain reflexes.










![General anatomy [edit]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000712414_1-9f164978a5775158fafd921c8e3d4cef-300x300.png)