experimental investigation of different ejector geometries
... (2008) and ZHA et al. (2007). Pressure energy recovery is particularly interesting for R744 refrigeration and heat pump technologies, as a relatively large fraction of the cycle losses are related to throttling losses. Some of the Japanese heat pump water heaters do apply ejectors in transcritical u ...
... (2008) and ZHA et al. (2007). Pressure energy recovery is particularly interesting for R744 refrigeration and heat pump technologies, as a relatively large fraction of the cycle losses are related to throttling losses. Some of the Japanese heat pump water heaters do apply ejectors in transcritical u ...
Radiant Cooling: Thermally Active Floors
... a high space, of minimizing thermal stratification. The maximum temperature of stratified air is limited by the maximum surface temperature within the space. Small surface area, high temperature convectors, while nominally of adequate capacity for a given heat loss, will generate significant buoyant ...
... a high space, of minimizing thermal stratification. The maximum temperature of stratified air is limited by the maximum surface temperature within the space. Small surface area, high temperature convectors, while nominally of adequate capacity for a given heat loss, will generate significant buoyant ...
CHE 1401 - Spring 2015 - Chapter 5 Homework 5 (Chapter 5
... A) The system gains heat and does work on the surroundings. B) The system gains heat and has work done on it by the surroundings. C) The system loses heat and does work on the surroundings. D) The system loses heat and has work done on it by the surroundings. E) None of the above is correct. ...
... A) The system gains heat and does work on the surroundings. B) The system gains heat and has work done on it by the surroundings. C) The system loses heat and does work on the surroundings. D) The system loses heat and has work done on it by the surroundings. E) None of the above is correct. ...
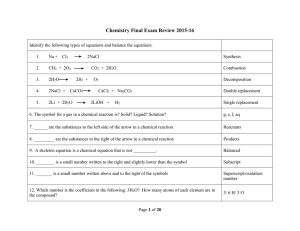
Type Of Chemical Reaction
... What is the molar ratio of Oxygen to Water? What is the molar ratio of carbon dioxide to C2H2? 23. Identify the diatomic molecule : F2 or MgO ...
... What is the molar ratio of Oxygen to Water? What is the molar ratio of carbon dioxide to C2H2? 23. Identify the diatomic molecule : F2 or MgO ...
CHE 1401 - Summer 2012 - Chapter 5 Homework 5 (Chapter 5
... 9) The British thermal unit (Btu) is commonly used in engineering applications. A Btu is defined as the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 lb of water by 1°F. There are __________ joules in one Btu. 1 lb = 453.59 g; °C = (5/9)(°F - 32°); specific heat of H2O (l) = 4.18 J/g-K. A) 1 ...
... 9) The British thermal unit (Btu) is commonly used in engineering applications. A Btu is defined as the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 lb of water by 1°F. There are __________ joules in one Btu. 1 lb = 453.59 g; °C = (5/9)(°F - 32°); specific heat of H2O (l) = 4.18 J/g-K. A) 1 ...
CHE 1401 - Spring 2016 - Chapter 5 Homework 5 (Chapter 5
... 30) The combustion of titanium with oxygen produces titanium dioxide: ...
... 30) The combustion of titanium with oxygen produces titanium dioxide: ...
CHE 1401 - Fall 2016 - Chapter 5 Homework 5 (Chapter 5
... is __________, and therefore heat is __________ by the reaction. A) exothermic, absorbed B) exothermic, released C) endothermic, released D) endothermic, absorbed E) thermoneutral, neither released nor absorbed 27) Which of the following is a statement of Hess's law? A) The ΔH for a process in the f ...
... is __________, and therefore heat is __________ by the reaction. A) exothermic, absorbed B) exothermic, released C) endothermic, released D) endothermic, absorbed E) thermoneutral, neither released nor absorbed 27) Which of the following is a statement of Hess's law? A) The ΔH for a process in the f ...
CHE 1401 - Fall 2015 - Chapter 5 Homework 5 (Chapter 5
... MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The British thermal unit (Btu) is commonly used in engineering applications. A Btu is defined as the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 lb of water by 1°F. There are _________ ...
... MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The British thermal unit (Btu) is commonly used in engineering applications. A Btu is defined as the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 lb of water by 1°F. There are _________ ...
Specific Heat
... Amount of heat it takes to raise 1g of How easy or hard an object a substance by 1°C is to heat up – how fast does it absorb heat energy ...
... Amount of heat it takes to raise 1g of How easy or hard an object a substance by 1°C is to heat up – how fast does it absorb heat energy ...
chapter 4 : heat
... 4.4.5 Explain the absolute/Kelvin scale of temperature 4.4.6 Solve problems involving the pressure, temperature and volume of a fixed mass of gas Complete the table below about gas laws’ ...
... 4.4.5 Explain the absolute/Kelvin scale of temperature 4.4.6 Solve problems involving the pressure, temperature and volume of a fixed mass of gas Complete the table below about gas laws’ ...
Condensation and the Nusselt`s Film Theory
... condensation occurs in the condensate film. The following gives an explanation of the Nusselt theory at the example of condensation on a vertical wall. Condensation occurs if a vapor is cooled below its (pressure dependent) saturation temperature. The heat of evaporation which is released during con ...
... condensation occurs in the condensate film. The following gives an explanation of the Nusselt theory at the example of condensation on a vertical wall. Condensation occurs if a vapor is cooled below its (pressure dependent) saturation temperature. The heat of evaporation which is released during con ...
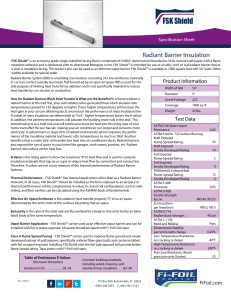
FSK Shield - Fi-Foil
... a class A insulation facing. The product also can be used as an effective vapor barrier. FSK Shield™ is available in 1000 square foot rolls 54” wide. Other widths available by special order. Radiant Barrier System (RBS) is a building construction consisting of a low emittance (normally 0.1 or less) ...
... a class A insulation facing. The product also can be used as an effective vapor barrier. FSK Shield™ is available in 1000 square foot rolls 54” wide. Other widths available by special order. Radiant Barrier System (RBS) is a building construction consisting of a low emittance (normally 0.1 or less) ...
Heat of vaporization of liquid nitrogen
... In this experiment we will measure the heat of vaporization of liquid nitrogen and calculate the entropy change per nitrogen molecule of the vaporization process. Theory The heat of vaporization of a liquid is the energy that must be supplied in order to convert a unit mass of the liquid to the gas ...
... In this experiment we will measure the heat of vaporization of liquid nitrogen and calculate the entropy change per nitrogen molecule of the vaporization process. Theory The heat of vaporization of a liquid is the energy that must be supplied in order to convert a unit mass of the liquid to the gas ...
Chapter 2: Properties of Pure Substances We now turn our attention
... Real substances that readily change phase from solid to liquid to gas such as water, refrigerant-134a, and ammonia cannot be treated as ideal gases in general. The pressure, volume, temperature relation, or equation of state for these substances is generally very complicated, and the thermodynamic ...
... Real substances that readily change phase from solid to liquid to gas such as water, refrigerant-134a, and ammonia cannot be treated as ideal gases in general. The pressure, volume, temperature relation, or equation of state for these substances is generally very complicated, and the thermodynamic ...
ChBE 11: Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics
... First Law of Thermodynamics The First Law of Thermodynamics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Reversible and Irreversible Processes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . The First Law of Thermodynamics for ...
... First Law of Thermodynamics The First Law of Thermodynamics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Reversible and Irreversible Processes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . The First Law of Thermodynamics for ...
Implimenting a Simple Heat Exchanger Unit with
... Traditional heat exchangers are complex units comprised of compressors, radiators, and phase changes involving chemical refrigerants. These systems have several points for failure and are expensive to build, making them impractical for applications requiring small amounts of cooling in a portable en ...
... Traditional heat exchangers are complex units comprised of compressors, radiators, and phase changes involving chemical refrigerants. These systems have several points for failure and are expensive to build, making them impractical for applications requiring small amounts of cooling in a portable en ...
Basic Properties of the Atmosphere
... • The Arctic Ocean has a large amount of heat (because of large mass) even though the temperature is low. • Air in an oven at 500 F has high temperature but little heat. • However, touch anything solid in the oven, and you’ll get burned. Same temperature, much larger amount of heat. 1. Heat, Tempera ...
... • The Arctic Ocean has a large amount of heat (because of large mass) even though the temperature is low. • Air in an oven at 500 F has high temperature but little heat. • However, touch anything solid in the oven, and you’ll get burned. Same temperature, much larger amount of heat. 1. Heat, Tempera ...
Basic Properties of the Atmosphere
... • The Arctic Ocean has a large amount of heat (because of large mass) even though the temperature is low. • Air in an oven at 500 F has high temperature but little heat. • However, touch anything solid in the oven, and you’ll get burned. Same temperature, much larger amount of heat. 1. Heat, Tempera ...
... • The Arctic Ocean has a large amount of heat (because of large mass) even though the temperature is low. • Air in an oven at 500 F has high temperature but little heat. • However, touch anything solid in the oven, and you’ll get burned. Same temperature, much larger amount of heat. 1. Heat, Tempera ...
Solution FRQs Practice
... ___________ (increase/decrease) the boiling point more that an equal concentration of sugar (a molecular cpd) that does not dissociate or ionize. At _______ (high/low) temperatures and ____________ (high/low) pressures, the methane molecules are slow and closer together. Under these conditions, van ...
... ___________ (increase/decrease) the boiling point more that an equal concentration of sugar (a molecular cpd) that does not dissociate or ionize. At _______ (high/low) temperatures and ____________ (high/low) pressures, the methane molecules are slow and closer together. Under these conditions, van ...
МХ, англ.яз., Лопухова В.Н - Астраханский Государственный
... William Cullen at the University of Glasgow in Scotland in 1748. Cullen used a pump to create a partial vacuum over a container of ethyl ether, which then boiled , absorbing heat from the surrounding air. The experiment even created a small amount of ice, but had no practical application at that tim ...
... William Cullen at the University of Glasgow in Scotland in 1748. Cullen used a pump to create a partial vacuum over a container of ethyl ether, which then boiled , absorbing heat from the surrounding air. The experiment even created a small amount of ice, but had no practical application at that tim ...
Physics, Chapter 17: The Phases of Matter
... containing a liquid and its saturated vapor is heated to the critical temperature, the meniscus dividing the liquid from the vapor phase disappears. At temperatures above the critical temperature the substance cannot exist as a liquid; that is, no matter how great the pressure, it cannot be put into ...
... containing a liquid and its saturated vapor is heated to the critical temperature, the meniscus dividing the liquid from the vapor phase disappears. At temperatures above the critical temperature the substance cannot exist as a liquid; that is, no matter how great the pressure, it cannot be put into ...
Objective of Project
... condenser and evaporator in a vapor compression cycle are the hot and cold gas-to-gas heat exchangers in gas cycles. The gas cycle is less efficient than the vapor compression cycle because the gas cycle works on the reverse Brayton cycle instead of the reverse Rankine cycle. As such the working flu ...
... condenser and evaporator in a vapor compression cycle are the hot and cold gas-to-gas heat exchangers in gas cycles. The gas cycle is less efficient than the vapor compression cycle because the gas cycle works on the reverse Brayton cycle instead of the reverse Rankine cycle. As such the working flu ...
File
... 58. A 160. mg sample of NaOH, (MM = 40.0 g) is dissolved to prepare an aqueous solution with a volume of 200. mL. What is the molarity of sodium hydroxide in 40. mL of this solution? A) 0.00400 M B) 0.0160 M C) 0.0200 M D) 0.0800 M E) 0.100 M 59. The ionization constant, Kb, of the base HONH2 is 1. ...
... 58. A 160. mg sample of NaOH, (MM = 40.0 g) is dissolved to prepare an aqueous solution with a volume of 200. mL. What is the molarity of sodium hydroxide in 40. mL of this solution? A) 0.00400 M B) 0.0160 M C) 0.0200 M D) 0.0800 M E) 0.100 M 59. The ionization constant, Kb, of the base HONH2 is 1. ...
Vapor-compression refrigeration

Vapor-compression refrigeration, in which the refrigerant undergoes phase changes, is one of the many refrigeration cycles and is the most widely used method for air-conditioning of buildings and automobiles. It is also used in domestic and commercial refrigerators, large-scale warehouses for chilled or frozen storage of foods and meats, refrigerated trucks and railroad cars, and a host of other commercial and industrial services. Oil refineries, petrochemical and chemical processing plants, and natural gas processing plants are among the many types of industrial plants that often utilize large vapor-compression refrigeration systems.Refrigeration may be defined as lowering the temperature of an enclosed space by removing heat from that space and transferring it elsewhere. A device that performs this function may also be called an air conditioner, refrigerator, air source heat pump, geothermal heat pump or chiller (heat pump).