Thermodynamics and Kinetics of Solids 21 ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
... to the Langmuir method may be performed at considerably lower pressures. The Langmuir Method is often applied in order to increase the rate of the weight loss (especially suitable for substances with high sublimation energies). Examples: Fig. 3.5.: shows the resulting activities of Cu - Ge alloys. ...
... to the Langmuir method may be performed at considerably lower pressures. The Langmuir Method is often applied in order to increase the rate of the weight loss (especially suitable for substances with high sublimation energies). Examples: Fig. 3.5.: shows the resulting activities of Cu - Ge alloys. ...
Chapter 10 Cycles
... There are other classes of Brayton cycle plants. Schematics are shown next. • Turbojet. In the turbojet, the kinetic energy of the fluid becomes important at two points in the cycle. In the compression, the freestream fluid, entering the compressor at the flight speed, has its pressure increased by ...
... There are other classes of Brayton cycle plants. Schematics are shown next. • Turbojet. In the turbojet, the kinetic energy of the fluid becomes important at two points in the cycle. In the compression, the freestream fluid, entering the compressor at the flight speed, has its pressure increased by ...
• Work
... and work W, may be transferred between the system and its surroundings. (c) Adiabatic process (Q = 0): ∆U = Q - W = - W (d) Isothermal process (T = cte.): An example of an isothermal process is a phase change. (i) Free expansion of an ideal gas: Take a container with two compartments, one of which h ...
... and work W, may be transferred between the system and its surroundings. (c) Adiabatic process (Q = 0): ∆U = Q - W = - W (d) Isothermal process (T = cte.): An example of an isothermal process is a phase change. (i) Free expansion of an ideal gas: Take a container with two compartments, one of which h ...
Thermoelectric Cooling A Closer Look.indd
... compared to a refrigerant based cooler or a simple heat exchanger. However, the reduced need for maintenance and replacement parts must be considered as part of the value added to using the technology. Under normal conditions, a thermoelectric air conditioner may last 7 years (or much longer in some ...
... compared to a refrigerant based cooler or a simple heat exchanger. However, the reduced need for maintenance and replacement parts must be considered as part of the value added to using the technology. Under normal conditions, a thermoelectric air conditioner may last 7 years (or much longer in some ...
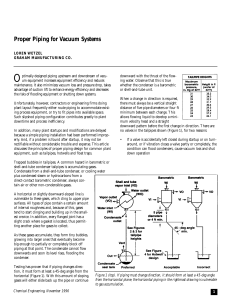
Proper Piping for Vacuum Systems
... Suction lift is a function of vacuum systems that can be used to advantage in piping (Figure 2). For example, it can enhance a pumping system by reducing the load on an existing motor. Imagine, for instance, pumping a liquid from one level up 80 ft to a vessel operating under vacuum. The vacuum or s ...
... Suction lift is a function of vacuum systems that can be used to advantage in piping (Figure 2). For example, it can enhance a pumping system by reducing the load on an existing motor. Imagine, for instance, pumping a liquid from one level up 80 ft to a vessel operating under vacuum. The vacuum or s ...
P3_U8doc - Port Fest Baltimore
... train (line shaft losses: 2-5%) some of the torque delivered to the reduction gears by the engine is used to overcome friction in the drive train; thus the difference in BHP, SHP and DHP BHP-SHP = Line Losses numerically, HP = Torque (ft-lbs) x RPM ...
... train (line shaft losses: 2-5%) some of the torque delivered to the reduction gears by the engine is used to overcome friction in the drive train; thus the difference in BHP, SHP and DHP BHP-SHP = Line Losses numerically, HP = Torque (ft-lbs) x RPM ...
Liquids and Solids
... • Evaporation and condensation – In an open container/beaker, all the water that is present will eventually escape into the gaseous phase (Figure 1310). – What if the beaker is sealed? What will happen? After molecules enter the gas phase they may be recaptured by the liquid by collisions. This proc ...
... • Evaporation and condensation – In an open container/beaker, all the water that is present will eventually escape into the gaseous phase (Figure 1310). – What if the beaker is sealed? What will happen? After molecules enter the gas phase they may be recaptured by the liquid by collisions. This proc ...
110 EXAM IV MATERIAL Tro Spr 2015
... 4. Smelling salts contain ammonium carbonate, which can decompose to form ammonia, a mild heart stimulant. The ammonium carbonate decomposes according to the following reaction: (NH4)2CO3(s) 2NH3(g) + CO2(g) + H2O(l) ...
... 4. Smelling salts contain ammonium carbonate, which can decompose to form ammonia, a mild heart stimulant. The ammonium carbonate decomposes according to the following reaction: (NH4)2CO3(s) 2NH3(g) + CO2(g) + H2O(l) ...
Phase Changes
... 0 q is measure in Joules, (J) or kilojoules (kJ). 0 The heat of a reaction is based on the mass of the substance, the temperature change it undergoes and specific heat. ...
... 0 q is measure in Joules, (J) or kilojoules (kJ). 0 The heat of a reaction is based on the mass of the substance, the temperature change it undergoes and specific heat. ...
Chapter 11: Thermochemistry
... Heating and Cooling Curve Some Notes and Practice Problems: Exothermic and Endothermic Processes System is your point of focus. Surroundings means the region in the immediate vicinity of the system. We are studying the flow of energy from the system to the surroundings and vice-versa. Heat flowi ...
... Heating and Cooling Curve Some Notes and Practice Problems: Exothermic and Endothermic Processes System is your point of focus. Surroundings means the region in the immediate vicinity of the system. We are studying the flow of energy from the system to the surroundings and vice-versa. Heat flowi ...
Heat Pumps for Space Heating
... that there will come a time when all fuel sources would be exhausted and thus motive power would no longer be available. Therefore, he designed a machine, which he called “Heat Multiplier”. It comprised a compressor and two water tanks serving as a hot reservoir and a cold reservoir. This arrangemen ...
... that there will come a time when all fuel sources would be exhausted and thus motive power would no longer be available. Therefore, he designed a machine, which he called “Heat Multiplier”. It comprised a compressor and two water tanks serving as a hot reservoir and a cold reservoir. This arrangemen ...
The general performance characteristics of a Stirling refrigerator with
... of finite-rate heat transfer. In the present paper we establish a new cycle model of the Stirling refrigerator using an ideal or Van der Waals gas as the working substance. Then, the cycle model is used to investigate the general performance characteristics of the Stirling refrigeration cycle affect ...
... of finite-rate heat transfer. In the present paper we establish a new cycle model of the Stirling refrigerator using an ideal or Van der Waals gas as the working substance. Then, the cycle model is used to investigate the general performance characteristics of the Stirling refrigeration cycle affect ...
Document
... Imagine two systems A and B, separated by an adiabatic wall, while each is in contact with a third system C, via a conducting wall ]. The states of the systems change until both A and B come to thermal equilibrium with C. After this has happened if the adiabatic wall between A and B is replaced by a ...
... Imagine two systems A and B, separated by an adiabatic wall, while each is in contact with a third system C, via a conducting wall ]. The states of the systems change until both A and B come to thermal equilibrium with C. After this has happened if the adiabatic wall between A and B is replaced by a ...
Temperature Differences in the Beam Screen
... • In the LHC the Beam Screen between the dipoles aren’t cooled • BUT: the PSR of the FCC is two magnitudes higher • Due to the low heat conductivity of steel in the given temperature range, the temperature differences in the interconnections with necessary distances are to high • To keep the tempera ...
... • In the LHC the Beam Screen between the dipoles aren’t cooled • BUT: the PSR of the FCC is two magnitudes higher • Due to the low heat conductivity of steel in the given temperature range, the temperature differences in the interconnections with necessary distances are to high • To keep the tempera ...
Student AP PHYSICS 2 Date ______ Thermodynamics FR #13
... c. Plot the data on the graph below, labeling the axes with appropriate numbers to indicate the ...
... c. Plot the data on the graph below, labeling the axes with appropriate numbers to indicate the ...
Exam 1
... 12. The lid is tightly sealed on a rigid flask containing 3.50 L H2 at 17 °C and 0.913 atm. If the flask is heated to 71 °C, what is the pressure in the flask? 13. A 0.225-L flask contains CH4 at 27 °C and 318 mm Hg. What is the pressure of the CH4 if the volume is increased to 0.500 L and the tempe ...
... 12. The lid is tightly sealed on a rigid flask containing 3.50 L H2 at 17 °C and 0.913 atm. If the flask is heated to 71 °C, what is the pressure in the flask? 13. A 0.225-L flask contains CH4 at 27 °C and 318 mm Hg. What is the pressure of the CH4 if the volume is increased to 0.500 L and the tempe ...
Basic Concepts of the Gas Phase
... combination of temperature and pressure. (It is also possible to select other state variables to define the state of the system, e.g. its values for density ρ and viscosity μ, which – in that case – would fix p and T). Two phases can only co-exist at equilibrium for specific combinations of temperat ...
... combination of temperature and pressure. (It is also possible to select other state variables to define the state of the system, e.g. its values for density ρ and viscosity μ, which – in that case – would fix p and T). Two phases can only co-exist at equilibrium for specific combinations of temperat ...
Validation of Molecular Dynamics simulations of evaporation and
... heat flux of 500 kW/m2 [5]. The heat removal is increased by flow boiling, because the heat of evaporation can be used: experiments have shown a critical heat flux of 3183 kW/m2 , at the cost of less stability [6]. To be able to use flow boiling in micro channels for practical applications, the oper ...
... heat flux of 500 kW/m2 [5]. The heat removal is increased by flow boiling, because the heat of evaporation can be used: experiments have shown a critical heat flux of 3183 kW/m2 , at the cost of less stability [6]. To be able to use flow boiling in micro channels for practical applications, the oper ...
Flash Calculations - Rowan University
... On your own: Use the Peng Robinson Equation of State and the simulator to solve Example 8.4-4 in Felder & Rousseau on page 383. An equimolar mixture of Benzene and Toluene 10°C and 34.8 mm Hg are fed to a heated separator. The liquid product is 40 mol% Benzene at 50°C and the vapor product is 68.4mo ...
... On your own: Use the Peng Robinson Equation of State and the simulator to solve Example 8.4-4 in Felder & Rousseau on page 383. An equimolar mixture of Benzene and Toluene 10°C and 34.8 mm Hg are fed to a heated separator. The liquid product is 40 mol% Benzene at 50°C and the vapor product is 68.4mo ...
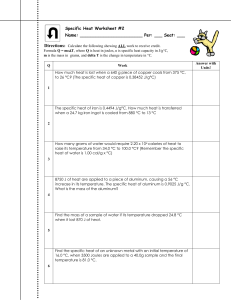
Specific Heat WS #2 - My Chemistry Class
... Formula Q = mcT, where Q is heat in joules, c is specific heat capacity in J/gC, m is the mass in grams, and delta T is the change in temperature in C. ...
... Formula Q = mcT, where Q is heat in joules, c is specific heat capacity in J/gC, m is the mass in grams, and delta T is the change in temperature in C. ...
Earth – The Water Planet
... The saturation vapor pressure of water over ice is higher than that over liquid water. This leads to small, but measurable change is the relative humidity. ...
... The saturation vapor pressure of water over ice is higher than that over liquid water. This leads to small, but measurable change is the relative humidity. ...
Lecture 36.Thermodyn..
... Yes, it is indeed possible for the temperature to stay the same. This is precisely what occurs during a phase change – the added heat goes into changing the state of the substance (from solid to liquid or from liquid to gas) and does not go into changing the temperature! Once the phase change has be ...
... Yes, it is indeed possible for the temperature to stay the same. This is precisely what occurs during a phase change – the added heat goes into changing the state of the substance (from solid to liquid or from liquid to gas) and does not go into changing the temperature! Once the phase change has be ...
Basic Thermodynamics Goals The ideal gas Entropy, Heat and Work
... 8. Two thermally insulated cylinders, A and B, of equal volume, both equipped with pistons, are connected by a valve. When open, the valve allows unrestricted flow. Initially A has its piston fully withdrawn and contains a perfect monatomic gas at temperature Ti , and B has its piston fully inserted ...
... 8. Two thermally insulated cylinders, A and B, of equal volume, both equipped with pistons, are connected by a valve. When open, the valve allows unrestricted flow. Initially A has its piston fully withdrawn and contains a perfect monatomic gas at temperature Ti , and B has its piston fully inserted ...
Section 16.3 ppt - Mrs. Graves Science
... If you ever shop for a new washing machine, you’ll notice the bright yellow Energy Guide sticker on each machine. The sticker gives the machine’s operating cost per year as estimated by the U.S. Department of Energy. The largest part of the cost for cleaning clothes is heating the water that goes in ...
... If you ever shop for a new washing machine, you’ll notice the bright yellow Energy Guide sticker on each machine. The sticker gives the machine’s operating cost per year as estimated by the U.S. Department of Energy. The largest part of the cost for cleaning clothes is heating the water that goes in ...
Vapor-compression refrigeration

Vapor-compression refrigeration, in which the refrigerant undergoes phase changes, is one of the many refrigeration cycles and is the most widely used method for air-conditioning of buildings and automobiles. It is also used in domestic and commercial refrigerators, large-scale warehouses for chilled or frozen storage of foods and meats, refrigerated trucks and railroad cars, and a host of other commercial and industrial services. Oil refineries, petrochemical and chemical processing plants, and natural gas processing plants are among the many types of industrial plants that often utilize large vapor-compression refrigeration systems.Refrigeration may be defined as lowering the temperature of an enclosed space by removing heat from that space and transferring it elsewhere. A device that performs this function may also be called an air conditioner, refrigerator, air source heat pump, geothermal heat pump or chiller (heat pump).