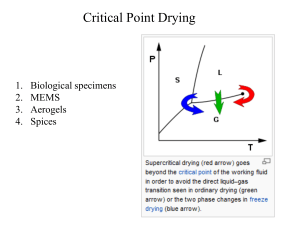
Chapter 1: Introductory Concepts, Units, and Definitions
... (2) - Saturated Liquid). As more heat is added the water progressively changes phase from liquid to water vapor (steam) while maintaining the temperature at 100°C (Saturation Temperature - Tsat) until there is no liquid remaining in the cylinder (State (4) - Saturated Vapor). If heating continues th ...
... (2) - Saturated Liquid). As more heat is added the water progressively changes phase from liquid to water vapor (steam) while maintaining the temperature at 100°C (Saturation Temperature - Tsat) until there is no liquid remaining in the cylinder (State (4) - Saturated Vapor). If heating continues th ...
PHYS140 - Ch15.pptx
... A state variable describes the state of a system at time t, but it does not reveal how the system was put into that state. Examples of state variables: pressure, temperature, volume, number of moles, and internal energy. A PV diagram can be used to r ...
... A state variable describes the state of a system at time t, but it does not reveal how the system was put into that state. Examples of state variables: pressure, temperature, volume, number of moles, and internal energy. A PV diagram can be used to r ...
Chapter 4
... ►The closed gas turbine operates as follows: ►A gas circulates through four components: turbine, compressor, and two heat exchangers at higher and lower operating temperatures, respectively. ►The turbine and compressor play the same roles as in the open gas turbine. ►As the gas passes through the hi ...
... ►The closed gas turbine operates as follows: ►A gas circulates through four components: turbine, compressor, and two heat exchangers at higher and lower operating temperatures, respectively. ►The turbine and compressor play the same roles as in the open gas turbine. ►As the gas passes through the hi ...
Chapter 28 - UF Physics
... It is the temperature of a body alone that determines whether heat will flow to or from a body, “Heat energy is transferred across the boundary of a system as a result of a temperature difference only.” •However, this does not necessarily imply that the transfer of heat to a body will increase its t ...
... It is the temperature of a body alone that determines whether heat will flow to or from a body, “Heat energy is transferred across the boundary of a system as a result of a temperature difference only.” •However, this does not necessarily imply that the transfer of heat to a body will increase its t ...
Sample pages 2 PDF
... solids. DH is the enthalpy of vaporization if the substance is a liquid or the enthalpy of sublimation if it is a solid. The enthalpy of vaporization (or sublimation) is assumed to be constant over the temperature range of interest. This is not true, but actual changes in DH values are negligible at ...
... solids. DH is the enthalpy of vaporization if the substance is a liquid or the enthalpy of sublimation if it is a solid. The enthalpy of vaporization (or sublimation) is assumed to be constant over the temperature range of interest. This is not true, but actual changes in DH values are negligible at ...
CHEM 2: Exam 3
... Imagine you are a scuba diver at a depth of 20 meters below the water surface where the pressure is 3 atm. If you fill your lungs to a total capacity of 6 Liters at this depth and hold your breath, then rise to the surface where the pressure is 1 atm, what would be the final volume of the air in you ...
... Imagine you are a scuba diver at a depth of 20 meters below the water surface where the pressure is 3 atm. If you fill your lungs to a total capacity of 6 Liters at this depth and hold your breath, then rise to the surface where the pressure is 1 atm, what would be the final volume of the air in you ...
CHEM 2: Exam 3
... Imagine you are a scuba diver at a depth of 20 meters below the water surface where the pressure is 3 atm. If you fill your lungs to a total capacity of 6 Liters at this depth and hold your breath, then rise to the surface where the pressure is 1 atm, what would be the final volume of the air in you ...
... Imagine you are a scuba diver at a depth of 20 meters below the water surface where the pressure is 3 atm. If you fill your lungs to a total capacity of 6 Liters at this depth and hold your breath, then rise to the surface where the pressure is 1 atm, what would be the final volume of the air in you ...
Air purification in industrial plants producing automotive
... heat recovery exchangers in just a few days. In the plant in which the research was conducted, tar contamination causes blockage of ventilation ducts. The effect of this phenomenon was that every half year channels had to be replaced with new ones, since the economic analysis has shown that cleaning ...
... heat recovery exchangers in just a few days. In the plant in which the research was conducted, tar contamination causes blockage of ventilation ducts. The effect of this phenomenon was that every half year channels had to be replaced with new ones, since the economic analysis has shown that cleaning ...
Type Of Chemical Reaction
... What is the molar ratio of Oxygen to Water? What is the molar ratio of carbon dioxide to C2H2? 23. Identify the diatomic molecule : F2 or MgO ...
... What is the molar ratio of Oxygen to Water? What is the molar ratio of carbon dioxide to C2H2? 23. Identify the diatomic molecule : F2 or MgO ...
matterLessonPlan
... The smallest unit of matter An atom is does have smaller components (electrons, protons, neutrons, etc). An atom, however, is the smallest particle of an element that still has the chemical properties of that element. Scientists have found 115 types of atoms so far, and new ones are still bein ...
... The smallest unit of matter An atom is does have smaller components (electrons, protons, neutrons, etc). An atom, however, is the smallest particle of an element that still has the chemical properties of that element. Scientists have found 115 types of atoms so far, and new ones are still bein ...
Control of Liquid Cooling Unit
... The electronics and the manned compartment in the two mobile ground-based radar systems, Arthur and Giraffe, at Saab Electronic Defence Systems are cooled by a Liquid Cooling Unit (LCU). This LCU is today controlled by means of relay logic and is robust, but not flexible for changes. Furthermore, th ...
... The electronics and the manned compartment in the two mobile ground-based radar systems, Arthur and Giraffe, at Saab Electronic Defence Systems are cooled by a Liquid Cooling Unit (LCU). This LCU is today controlled by means of relay logic and is robust, but not flexible for changes. Furthermore, th ...
Name - cloudfront.net
... If heat is released by a chemical system, an equal amount of heat will be ____. By what quantity must the heat capacity (J/oC) of an object be divided to obtain the specific heat (J/goC) of that material? 64. When energy is changed from one form to another, ____. 65. What happens to the energy produ ...
... If heat is released by a chemical system, an equal amount of heat will be ____. By what quantity must the heat capacity (J/oC) of an object be divided to obtain the specific heat (J/goC) of that material? 64. When energy is changed from one form to another, ____. 65. What happens to the energy produ ...
Process Heat Transfer Lab - University of Engineering and Technology
... two modes. The fact that radiant energy transfer occurs across a vacuum is often disturbing to students unless the theory relating to properties of electromagnetic waves has been presented. The engineer is not directly concerned with the mechanism by which heat transfer occurs, but a sound knowledge ...
... two modes. The fact that radiant energy transfer occurs across a vacuum is often disturbing to students unless the theory relating to properties of electromagnetic waves has been presented. The engineer is not directly concerned with the mechanism by which heat transfer occurs, but a sound knowledge ...
Thermodynamics Exam 1 Info/Problems
... Crosse winter day, it will probably become much colder than 0 C. Ice may be able to exist at temperatures above that, but certainly not at atmospheric pressure (and probably not much warmer, in any event). 25. The air in the middle of the two panes acts as an insulator, adding to your overall “R” v ...
... Crosse winter day, it will probably become much colder than 0 C. Ice may be able to exist at temperatures above that, but certainly not at atmospheric pressure (and probably not much warmer, in any event). 25. The air in the middle of the two panes acts as an insulator, adding to your overall “R” v ...
9/21 properties of matter ppt
... heat) or vaporizing (change from liquid to gas with adding heat) ...
... heat) or vaporizing (change from liquid to gas with adding heat) ...
Ch. 15 - UCSB Physics
... • will find new ‘laws’ • key concepts: temperature, heat internal energy thermal equilibrium ...
... • will find new ‘laws’ • key concepts: temperature, heat internal energy thermal equilibrium ...
Transient Exergy Destruction Analysis of a Vapor Compression
... design and operational parameters in many thermal systems from a static point of view. For example, design parameters such as heat exchanger geometry have been optimized using EDM (Nag & De, 1997) (Vargas & Bejan, 2001). As can be seen from Eq. (1), minimizing the exergy destroyed in a system will m ...
... design and operational parameters in many thermal systems from a static point of view. For example, design parameters such as heat exchanger geometry have been optimized using EDM (Nag & De, 1997) (Vargas & Bejan, 2001). As can be seen from Eq. (1), minimizing the exergy destroyed in a system will m ...
ert254-chapter 4
... In cold climates their efficiency drops considerably when temperatures are below the freezing point. In such cases, geothermal (ground-source) HP that use the ground as the heat source can be used. Such heat pumps are more expensive to install, but they are also more efficient. Air conditioners are ...
... In cold climates their efficiency drops considerably when temperatures are below the freezing point. In such cases, geothermal (ground-source) HP that use the ground as the heat source can be used. Such heat pumps are more expensive to install, but they are also more efficient. Air conditioners are ...
AP Chem Mr. Dehne Name: ___________ Date: Per#: ___ AP
... 1.00atm from the tank? Assume that there is no temperature change and that the tank cannot be emptied below 1.00atm pressure. 4. A 2.00L sample of O2(g) was collected over water at a total pressure of 785torr and 25 oC . When the O2(g) was dried (water vapor removed), the gas had a volume of 1.94L a ...
... 1.00atm from the tank? Assume that there is no temperature change and that the tank cannot be emptied below 1.00atm pressure. 4. A 2.00L sample of O2(g) was collected over water at a total pressure of 785torr and 25 oC . When the O2(g) was dried (water vapor removed), the gas had a volume of 1.94L a ...
Intermolecular forces
... The hydrogen bond is a special dipole-dipole interaction between they hydrogen atom in a polar N-H, O-H, or F-H bond and an electronegative O, N, or F atom. ...
... The hydrogen bond is a special dipole-dipole interaction between they hydrogen atom in a polar N-H, O-H, or F-H bond and an electronegative O, N, or F atom. ...
Metathesis Problems (and Some Solutions) Identified Through
... • Most gases are less soluble in water at higher temperatures (bubbles that appear when heating water) • Most ionic solids are more soluble in water at higher temperatures – Some have very little change, like NaCl – Some are less soluble in higher temperatures • Heat of solution: heat absorbed or re ...
... • Most gases are less soluble in water at higher temperatures (bubbles that appear when heating water) • Most ionic solids are more soluble in water at higher temperatures – Some have very little change, like NaCl – Some are less soluble in higher temperatures • Heat of solution: heat absorbed or re ...
Document
... Heat pipes exhibits the highest efficiency of heat transport. They are based on phasechanging between liquid and vapor. This changing is repeatable. Composition of used liquid can change a boiling temperature. Water is used for 100°C (standard 101 kPa); alcohol-based liquids for range 60-80°C; lique ...
... Heat pipes exhibits the highest efficiency of heat transport. They are based on phasechanging between liquid and vapor. This changing is repeatable. Composition of used liquid can change a boiling temperature. Water is used for 100°C (standard 101 kPa); alcohol-based liquids for range 60-80°C; lique ...
Cooling, thermal resistance, modeling of heat transfer as an electric
... It is based on a reversed Siebeck’s effect. Temperature changes (cooling effects) are caused by current flowing through a contact between two different metals. This is not a typical „cooling system“, because one side of cells is cool, but the second one is hot! It is just a „transmitting of the temp ...
... It is based on a reversed Siebeck’s effect. Temperature changes (cooling effects) are caused by current flowing through a contact between two different metals. This is not a typical „cooling system“, because one side of cells is cool, but the second one is hot! It is just a „transmitting of the temp ...
From control-mass systems to control
... The momentum balance is the key to understand engine thrust in propulsive systems, where FA is the force exerted by the outside on the impermeable wall of the engine (the drag of the medium and the reaction in the supports. For instance, for a jet engine in steady horizontal flight with horizontal t ...
... The momentum balance is the key to understand engine thrust in propulsive systems, where FA is the force exerted by the outside on the impermeable wall of the engine (the drag of the medium and the reaction in the supports. For instance, for a jet engine in steady horizontal flight with horizontal t ...
Chapter 5: Control Volume
... The momentum balance is the key to understand engine thrust in propulsive systems, where FA is the force exerted by the outside on the impermeable wall of the engine (the drag of the medium and the reaction in the supports. For instance, for a jet engine in steady horizontal flight with horizontal t ...
... The momentum balance is the key to understand engine thrust in propulsive systems, where FA is the force exerted by the outside on the impermeable wall of the engine (the drag of the medium and the reaction in the supports. For instance, for a jet engine in steady horizontal flight with horizontal t ...
Vapor-compression refrigeration

Vapor-compression refrigeration, in which the refrigerant undergoes phase changes, is one of the many refrigeration cycles and is the most widely used method for air-conditioning of buildings and automobiles. It is also used in domestic and commercial refrigerators, large-scale warehouses for chilled or frozen storage of foods and meats, refrigerated trucks and railroad cars, and a host of other commercial and industrial services. Oil refineries, petrochemical and chemical processing plants, and natural gas processing plants are among the many types of industrial plants that often utilize large vapor-compression refrigeration systems.Refrigeration may be defined as lowering the temperature of an enclosed space by removing heat from that space and transferring it elsewhere. A device that performs this function may also be called an air conditioner, refrigerator, air source heat pump, geothermal heat pump or chiller (heat pump).