Pressure
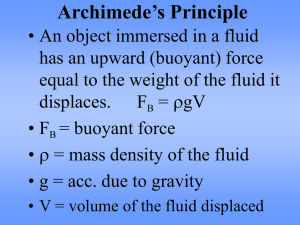
... = 0 so Wobj = FB = Wfd • Volume of the fluid displaced = volume of the submerged part of the ...
... = 0 so Wobj = FB = Wfd • Volume of the fluid displaced = volume of the submerged part of the ...
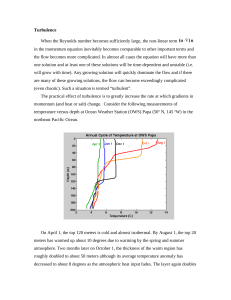
Turbulence When the Reynolds number becomes sufficiently large
... all these correlations as a function of separation gives you information about the spatial spectrum of the eddy sizes and their magnitudes. The Reynolds stress is a real shear stress and can be measured. So we have made progress, because we now understand that the main consequence of the velocity fl ...
... all these correlations as a function of separation gives you information about the spatial spectrum of the eddy sizes and their magnitudes. The Reynolds stress is a real shear stress and can be measured. So we have made progress, because we now understand that the main consequence of the velocity fl ...
No Slide Title - Cobb Learning
... that as each particle in the fluid passes a certain point it follows the same path as the particles that preceded it. There is no loss of energy due to internal friction (viscosity) in the fluid. In reality, particles in a fluid exhibit turbulent flow, which is the irregular movement of particles in ...
... that as each particle in the fluid passes a certain point it follows the same path as the particles that preceded it. There is no loss of energy due to internal friction (viscosity) in the fluid. In reality, particles in a fluid exhibit turbulent flow, which is the irregular movement of particles in ...
On fluid flow induced by a rotating magnetic field
... in the laboratory) is that the magnetic field distribution is unaffected by the motion of the fluid, and may be calculated as though thejuid were a solid conductor (It is of course far from uniform being zero in the core of the conductor; the distortion of the field is associated with the condition ...
... in the laboratory) is that the magnetic field distribution is unaffected by the motion of the fluid, and may be calculated as though thejuid were a solid conductor (It is of course far from uniform being zero in the core of the conductor; the distortion of the field is associated with the condition ...
Coast Terminology
... Storm Surge: a rapid rise in sea level caused by storms forcing water into a narrowing sea area. Low air pressure at the centre of the storm also causes sea levels to rise. Stump: formed by continuing wave action attacking a stack until it collapses. Swash: forward movement of a wave up a beach. Tom ...
... Storm Surge: a rapid rise in sea level caused by storms forcing water into a narrowing sea area. Low air pressure at the centre of the storm also causes sea levels to rise. Stump: formed by continuing wave action attacking a stack until it collapses. Swash: forward movement of a wave up a beach. Tom ...
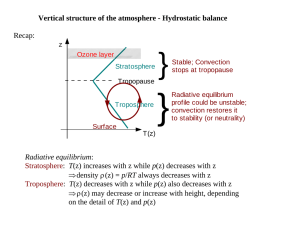
Vertical structure of the atmosphere
... The atmosphere is very close to hydrostatic balance most of the time, except at isolated locations when the vertical profile becomes statically unstable. In that situation, convection will happen to restore stability. This takes place on a very short time scale (~ a few hours), therefore after some ...
... The atmosphere is very close to hydrostatic balance most of the time, except at isolated locations when the vertical profile becomes statically unstable. In that situation, convection will happen to restore stability. This takes place on a very short time scale (~ a few hours), therefore after some ...
Observation and Modeling of High Individual Ocean Waves and
... the spectral energy density is estimated, integral wave properties can be obtained, such as significant wave height, mean and peak period and direction. The input information for the wave modeling are the surface wind at a height of 10m and water depth. The real wind is variable over short distances ...
... the spectral energy density is estimated, integral wave properties can be obtained, such as significant wave height, mean and peak period and direction. The input information for the wave modeling are the surface wind at a height of 10m and water depth. The real wind is variable over short distances ...
Determination of viscosity with Ostwald viscometer
... 2. Measure 20 cm3 distilled water to the lower reservoir and put the viscometer to the thermostat (even the h1 level should be under the level of the water in the thermostat)! 3. Measure the weight of the empty, dry(!) pycnometer! 4. Fill the pycnometer with 2x distilled water and put the pycnometer ...
... 2. Measure 20 cm3 distilled water to the lower reservoir and put the viscometer to the thermostat (even the h1 level should be under the level of the water in the thermostat)! 3. Measure the weight of the empty, dry(!) pycnometer! 4. Fill the pycnometer with 2x distilled water and put the pycnometer ...
View the PowerPoint
... Conservation of mass in tube of flow means mass of fluid entering A1 in time t = mass of fluid leaving A2 in time t For incompressible fluid this means volume is also conserved. Volume entering and leaving in time t is V V = A1 v1 t =A2 v2 t ...
... Conservation of mass in tube of flow means mass of fluid entering A1 in time t = mass of fluid leaving A2 in time t For incompressible fluid this means volume is also conserved. Volume entering and leaving in time t is V V = A1 v1 t =A2 v2 t ...
View the PowerPoint
... Conservation of mass in tube of flow means mass of fluid entering A1 in time t = mass of fluid leaving A2 in time t For incompressible fluid this means volume is also conserved. Volume entering and leaving in time t is V V = A1 v1 t =A2 v2 t ...
... Conservation of mass in tube of flow means mass of fluid entering A1 in time t = mass of fluid leaving A2 in time t For incompressible fluid this means volume is also conserved. Volume entering and leaving in time t is V V = A1 v1 t =A2 v2 t ...
Chapter Four Fluid Dynamic
... between two points and is constrained by the pipe walls. The direction of the flow is always from a point of high pressure to a point of low pressure. - If the fluid does not completely fill the pipe, such as in a concrete sewer, the existence of any gas phase generates an almost constant pressure a ...
... between two points and is constrained by the pipe walls. The direction of the flow is always from a point of high pressure to a point of low pressure. - If the fluid does not completely fill the pipe, such as in a concrete sewer, the existence of any gas phase generates an almost constant pressure a ...
Critical flow in rockbed streams with estimated values for Manning`s
... 1995a,b,Montes and Chanson, 1998. and they result from the interactions between the sidewall boundary layers and the bed boundary layer. In natural channels, the photographs of undular flows Žpresented by Tinkler. show identical flow patterns as those observed in laboratory and it is believed that t ...
... 1995a,b,Montes and Chanson, 1998. and they result from the interactions between the sidewall boundary layers and the bed boundary layer. In natural channels, the photographs of undular flows Žpresented by Tinkler. show identical flow patterns as those observed in laboratory and it is believed that t ...
Xie-EGM-RPI-2011.pdf
... • The COMSOL results predict the expected flattening of velocity profiles as well as the vortex elimination in the backward facing step flow. ...
... • The COMSOL results predict the expected flattening of velocity profiles as well as the vortex elimination in the backward facing step flow. ...
ООО НПП «Электротех»
... • cement squeeze. System SKCS-01 may be used for various processes where fluids of different density are pumped. ...
... • cement squeeze. System SKCS-01 may be used for various processes where fluids of different density are pumped. ...
Types of Flow
... the liquid at rest. Now we will study the motion on liquids without any reference to the force causing motion. This lecture deals with the study of velocity and acceleration of the liquid particles without taking into consideration any force or energy. ...
... the liquid at rest. Now we will study the motion on liquids without any reference to the force causing motion. This lecture deals with the study of velocity and acceleration of the liquid particles without taking into consideration any force or energy. ...
Document
... • Given the necessary information, the force components can be calculated. The analysis of a moving deflector is more complicated. Is it a single deflector (a water scoop to slow a high-speed train), or is it a series of deflectors as in a turbine? First, let us consider a single deflector moving wi ...
... • Given the necessary information, the force components can be calculated. The analysis of a moving deflector is more complicated. Is it a single deflector (a water scoop to slow a high-speed train), or is it a series of deflectors as in a turbine? First, let us consider a single deflector moving wi ...
pr04Tsol
... lower viscosity is used, as viscosity increases when oil cools. In hot climates a more viscous oil is used. b. Rowing would not be possible, just as walking would not be possible if there were no friction. You would have a very limited reaction force, and not get very far. Like rowing, flying would ...
... lower viscosity is used, as viscosity increases when oil cools. In hot climates a more viscous oil is used. b. Rowing would not be possible, just as walking would not be possible if there were no friction. You would have a very limited reaction force, and not get very far. Like rowing, flying would ...
Experimental demonstration of the supersonic
... When increasing the external fluid height H , care must be taken not to destabilize the type I jump (or drown it altogether). We have verified that H can indeed be increased beyond htrans within the limits of the white hole analogy. The outer region can therefore be tuned to be in a super- or in a s ...
... When increasing the external fluid height H , care must be taken not to destabilize the type I jump (or drown it altogether). We have verified that H can indeed be increased beyond htrans within the limits of the white hole analogy. The outer region can therefore be tuned to be in a super- or in a s ...
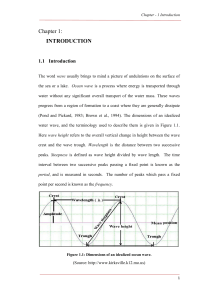
Chapter 1: INTRODUCTION
... energy proportional to the time. Once the waves exit, they may modify the air flow so that the growth rate becomes proportional to the wave amplitude and hence exponential in time. ...
... energy proportional to the time. Once the waves exit, they may modify the air flow so that the growth rate becomes proportional to the wave amplitude and hence exponential in time. ...
afmflow2 - Royal Society of Chemistry
... The novel design of flow cell, which allows AFM to be carried out under known flow conditions, was described in references [1 - 4]. This cell was developed from the Topometrix liquid immersion cell, by the addition of a new inlet tube which enabled a jet of fluid to be applied directly to the sample ...
... The novel design of flow cell, which allows AFM to be carried out under known flow conditions, was described in references [1 - 4]. This cell was developed from the Topometrix liquid immersion cell, by the addition of a new inlet tube which enabled a jet of fluid to be applied directly to the sample ...
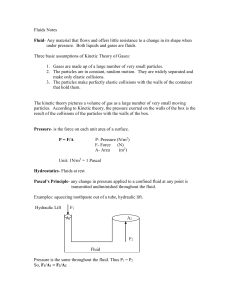
Fluids Notes - Net Start Class
... Bernoulli’s Principle- As the velocity of a fluid increases, the pressure exerted by the fluid decreases. Equation of Continuity -the volume of fluid passing two points per second is equal A1 v1 = A2 v2 Where A-area (m2) and v-velocity (m/s) In a narrow tube, the velocity of the liquid is high; in a ...
... Bernoulli’s Principle- As the velocity of a fluid increases, the pressure exerted by the fluid decreases. Equation of Continuity -the volume of fluid passing two points per second is equal A1 v1 = A2 v2 Where A-area (m2) and v-velocity (m/s) In a narrow tube, the velocity of the liquid is high; in a ...
In the late 1700s, Swiss physicist Daniel Bernoulli and his father
... the velocity of a fluid increases its kinetic energy while decreasing its static energy. It is for this reason that any flow restriction causes an increase in the flowing velocity and also causes a drop in the static pressure of the flowing fluid. For noncompressible fluids, such as liquids, the equ ...
... the velocity of a fluid increases its kinetic energy while decreasing its static energy. It is for this reason that any flow restriction causes an increase in the flowing velocity and also causes a drop in the static pressure of the flowing fluid. For noncompressible fluids, such as liquids, the equ ...
On rotational water waves with surface tension
... current, over a flat, impermeable bed. A current here means a water flow with a flat surface and it is specified by vorticity. For example, a current which is uniform with depth is described by zero vorticity, while constant non-zero vorticity describes a linearly sheared current and so on. Ignoring vis ...
... current, over a flat, impermeable bed. A current here means a water flow with a flat surface and it is specified by vorticity. For example, a current which is uniform with depth is described by zero vorticity, while constant non-zero vorticity describes a linearly sheared current and so on. Ignoring vis ...
Airy wave theory
In fluid dynamics, Airy wave theory (often referred to as linear wave theory) gives a linearised description of the propagation of gravity waves on the surface of a homogeneous fluid layer. The theory assumes that the fluid layer has a uniform mean depth, and that the fluid flow is inviscid, incompressible and irrotational. This theory was first published, in correct form, by George Biddell Airy in the 19th century.Airy wave theory is often applied in ocean engineering and coastal engineering for the modelling of random sea states – giving a description of the wave kinematics and dynamics of high-enough accuracy for many purposes. Further, several second-order nonlinear properties of surface gravity waves, and their propagation, can be estimated from its results. Airy wave theory is also a good approximation for tsunami waves in the ocean, before they steepen near the coast.This linear theory is often used to get a quick and rough estimate of wave characteristics and their effects. This approximation is accurate for small ratios of the wave height to water depth (for waves in shallow water), and wave height to wavelength (for waves in deep water).