Min-218 Fundamentals of Fluid Flow
... Imagine a circular cross-section of pipe containing a fluid such as water. For flow to occur without slippage, the various layers must move at different velocities. The fluid layer adjacent to the pipe wall is virtually stationary, while the layers further out move at increasingly higher velocities ...
... Imagine a circular cross-section of pipe containing a fluid such as water. For flow to occur without slippage, the various layers must move at different velocities. The fluid layer adjacent to the pipe wall is virtually stationary, while the layers further out move at increasingly higher velocities ...
Core Ag Engineering Principles – Session 1
... F for milk at 20.2 C flowing at 0.075 m3/min in sanitary tubing with a 4 cm ID through 20 m of pipe, with one type A elbow and one type A entrance. The milk flows from one reservoir into another. ...
... F for milk at 20.2 C flowing at 0.075 m3/min in sanitary tubing with a 4 cm ID through 20 m of pipe, with one type A elbow and one type A entrance. The milk flows from one reservoir into another. ...
Fluid Mechanics
... with a liquid of density ρ as shown in the diagram. A block of density D (D < ρ) and dimensions x, y, and z is attached to the bottom of the tank by a string so that its top surface is a distance h from the surface of the liquid. a) What is the total force due to pressure on the block? b) What is th ...
... with a liquid of density ρ as shown in the diagram. A block of density D (D < ρ) and dimensions x, y, and z is attached to the bottom of the tank by a string so that its top surface is a distance h from the surface of the liquid. a) What is the total force due to pressure on the block? b) What is th ...
Fluid Mechanics
... with a liquid of density ρ as shown in the diagram. A block of density D (D < ρ) and dimensions x, y, and z is attached to the bottom of the tank by a string so that its top surface is a distance h from the surface of the liquid. a) What is the total force due to pressure on the block? b) What is th ...
... with a liquid of density ρ as shown in the diagram. A block of density D (D < ρ) and dimensions x, y, and z is attached to the bottom of the tank by a string so that its top surface is a distance h from the surface of the liquid. a) What is the total force due to pressure on the block? b) What is th ...
Using Dimensions
... the dimensions of flow, that is, L3T −1 , otherwise the above equation must be invalid. The first thing to notice is that there is no M term in flow, and none in a either, so ΔP / L and η must appear in the equation in such a way that their M terms cancel, that is, one divides the other. We know of ...
... the dimensions of flow, that is, L3T −1 , otherwise the above equation must be invalid. The first thing to notice is that there is no M term in flow, and none in a either, so ΔP / L and η must appear in the equation in such a way that their M terms cancel, that is, one divides the other. We know of ...
Document
... of this sediment in suspension requires a balancing upward Reynolds flux, further dictating that mean suspended sediment concentration should decrease upward. Since higher concentration implies larger density, the implication is that sediment suspension generates its own stable stratification. In th ...
... of this sediment in suspension requires a balancing upward Reynolds flux, further dictating that mean suspended sediment concentration should decrease upward. Since higher concentration implies larger density, the implication is that sediment suspension generates its own stable stratification. In th ...
contributed papers - Department of Mathematical Sciences
... Rossby Wave Interaction Connecting the Tropics and Midlatitudes: A New Asymptotic Theory and Solitary Waves Equatorial baroclinic Rossby waves are equatorially trapped and can respond to equatorial diabatic heating. Equatorial barotropic Rossby waves also have a significant midlatitude projection. B ...
... Rossby Wave Interaction Connecting the Tropics and Midlatitudes: A New Asymptotic Theory and Solitary Waves Equatorial baroclinic Rossby waves are equatorially trapped and can respond to equatorial diabatic heating. Equatorial barotropic Rossby waves also have a significant midlatitude projection. B ...
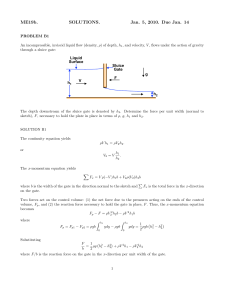
ME19b. SOLUTIONS. Jan. 5, 2010. Due Jan. 14
... The pressure in the cavity is simply given by the vapor pressure, pv , of the water at the operating water temperature (po > pv ). It is to be assumed that the effect of friction, the effect of gravity, the density of the vapor and the amount of water vaporized at the free surface are all negligible ...
... The pressure in the cavity is simply given by the vapor pressure, pv , of the water at the operating water temperature (po > pv ). It is to be assumed that the effect of friction, the effect of gravity, the density of the vapor and the amount of water vaporized at the free surface are all negligible ...
Flow velocity and volumetric flow rates are important quantities in
... decomposition of the flow velocity vector, making an angle θ with respect to the normal of the surface plane in order to calculate volumetric flow rate through that surface. Thus, volumetric flow rate for a given fluid velocity and cross-sectional surface area increases as θ decreases, and is maximi ...
... decomposition of the flow velocity vector, making an angle θ with respect to the normal of the surface plane in order to calculate volumetric flow rate through that surface. Thus, volumetric flow rate for a given fluid velocity and cross-sectional surface area increases as θ decreases, and is maximi ...
Bernoulli`s equation
... The flow is clearly fore-aft symmetric (symmetry about z = 0); the front (S1 ) and the back (S2 ) of the sphere are stagnation points at equal pressure, PS1 = PS2 = p∞ + 12 ρU 2 . At the side, ur = 0 and u2θ > 0, so from Bernoulli’s theorem, the pressure there is lower than at the stagnation points ...
... The flow is clearly fore-aft symmetric (symmetry about z = 0); the front (S1 ) and the back (S2 ) of the sphere are stagnation points at equal pressure, PS1 = PS2 = p∞ + 12 ρU 2 . At the side, ur = 0 and u2θ > 0, so from Bernoulli’s theorem, the pressure there is lower than at the stagnation points ...
Document
... the losses resulting from viscous friction in a flow. • The Moody Chart can be used to estimate the frictional losses in pipe and duct flows. • The SFEE can be used to determine the performance of a pump needed in a pipe system. ...
... the losses resulting from viscous friction in a flow. • The Moody Chart can be used to estimate the frictional losses in pipe and duct flows. • The SFEE can be used to determine the performance of a pump needed in a pipe system. ...
Mathematical Analysis of Problems in the Natural Sciences
... The possibility of such a transition from the general relation (1.4) to the simpler relations (1.5) and (1.6) forms the content of the so-called ΠTheorem,1 which is the fundamental theorem of the theory of dimensions of physical quantities (which we have just proved). ...
... The possibility of such a transition from the general relation (1.4) to the simpler relations (1.5) and (1.6) forms the content of the so-called ΠTheorem,1 which is the fundamental theorem of the theory of dimensions of physical quantities (which we have just proved). ...
Instantaneous velocity field measurement in densely
... Two-phase flow phenomena play a key role in many processes in both industry and nature. Despite their importance, the understanding of their underlying physics - a necessity for proper modelling - is somewhat limited. This can be attributed to the fact that the current de facto standard methods used ...
... Two-phase flow phenomena play a key role in many processes in both industry and nature. Despite their importance, the understanding of their underlying physics - a necessity for proper modelling - is somewhat limited. This can be attributed to the fact that the current de facto standard methods used ...
Lecture 14c - TTU Physics
... • Viscosity is a measure of the amount of internal friction in the fluid. • This internal friction or VISCOUS FORCE, comes from the resistance that two adjacent layers of fluid have to moving relative to each other. ...
... • Viscosity is a measure of the amount of internal friction in the fluid. • This internal friction or VISCOUS FORCE, comes from the resistance that two adjacent layers of fluid have to moving relative to each other. ...
Department of Mechanical Eng.
... point only. This point is called the minimum pressure point or the point of maximum suction. Evaluation the lower critical Mach number for airfoil with Cpimin=-0.7 . The characteristic Mach number at point of maximum suction when the airfoil is traveling at M cr1 is equal 1.0 i.e λ c = 1.0, from Cr ...
... point only. This point is called the minimum pressure point or the point of maximum suction. Evaluation the lower critical Mach number for airfoil with Cpimin=-0.7 . The characteristic Mach number at point of maximum suction when the airfoil is traveling at M cr1 is equal 1.0 i.e λ c = 1.0, from Cr ...
Wave Energy
... The methodology, which is followed, consists of two parts. In first part, it is examined the technical characteristics of the device and if it’s efficient in the place, we have chosen. It’s taken into consideration the wave height, depth of water, wind velocity and the annual output. If the device i ...
... The methodology, which is followed, consists of two parts. In first part, it is examined the technical characteristics of the device and if it’s efficient in the place, we have chosen. It’s taken into consideration the wave height, depth of water, wind velocity and the annual output. If the device i ...
drag
... In some cases, fluid forces have little effect on an object’s motion (e.g., shotput) In other cases, fluid forces are significant ...
... In some cases, fluid forces have little effect on an object’s motion (e.g., shotput) In other cases, fluid forces are significant ...
CVE 240 – Fluid Mechanics
... The SI system consists of six primary units, from which all quantities may be described but in fluid mechanics we are generally only interested in the top four units from this table. ...
... The SI system consists of six primary units, from which all quantities may be described but in fluid mechanics we are generally only interested in the top four units from this table. ...
Chapter 13: Fluids Mechanics
... This photograph was taken in a water tunnel using hydrogen bubbles to visualize the flow pattern around a cylinder. The flow was started from rest, and at this instant the pattern shows the development of a complex wake structure on the downstream side of the cylinder. Four characteristics of an id ...
... This photograph was taken in a water tunnel using hydrogen bubbles to visualize the flow pattern around a cylinder. The flow was started from rest, and at this instant the pattern shows the development of a complex wake structure on the downstream side of the cylinder. Four characteristics of an id ...
The Use of the Primitive Equations of Motion in Numerical Prediction
... Initial conditions were prescribed for the flow of an atmosphere consisting of two homogeneous incompressible layers of different density bounded above and below by rigid surfaces. The lower layer was assumed to be so deep that its motion could be ignored. The upper layer would then move as though i ...
... Initial conditions were prescribed for the flow of an atmosphere consisting of two homogeneous incompressible layers of different density bounded above and below by rigid surfaces. The lower layer was assumed to be so deep that its motion could be ignored. The upper layer would then move as though i ...
chapter (ii) characteristics of fluids
... The cross section for the fuel tank of an experimental vehicle is shown in Fig. The rectangular tank is vented to the atmosphere, and a pressure transducer is located in its side as illustrated. During testing of the vehicle, the tank is subjected to a constant linear acceleration, ay. (a) Determine ...
... The cross section for the fuel tank of an experimental vehicle is shown in Fig. The rectangular tank is vented to the atmosphere, and a pressure transducer is located in its side as illustrated. During testing of the vehicle, the tank is subjected to a constant linear acceleration, ay. (a) Determine ...
Laminar and Turbulent Flow in Pipes
... smooth walls such as glass, copper, brass and polyethylene have only a small effect on the frictional resistance. Pipes with less smooth walls such as concrete, cast iron and steel will create larger eddy currents which will sometimes have a significant effect on the frictional resistance. The veloc ...
... smooth walls such as glass, copper, brass and polyethylene have only a small effect on the frictional resistance. Pipes with less smooth walls such as concrete, cast iron and steel will create larger eddy currents which will sometimes have a significant effect on the frictional resistance. The veloc ...
Three-dimensional numerical analysis to predict behavior of driftage carried by tsunami
... cylindrical driftage was modeled as an octagonal pillar with cross-sectional area and volume equal to that of the actual cylinder (driftage). Figure 8 shows the results of a comparison between the vertical 2D trajectory of the driftage obtained by the computation and that obtained in the experiment. ...
... cylindrical driftage was modeled as an octagonal pillar with cross-sectional area and volume equal to that of the actual cylinder (driftage). Figure 8 shows the results of a comparison between the vertical 2D trajectory of the driftage obtained by the computation and that obtained in the experiment. ...
ME 101
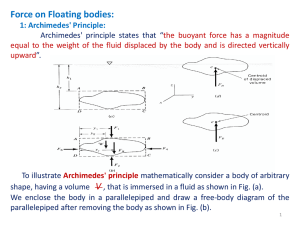
... What happens when fluids interact with solids? The forces created are known as buoyancy, drag, and lift – Buoyancy is the force developed when a solid object is immersed in a fluid (no relative motion) – Lift and Drag forces arise when fluids interact with a solid object ...
... What happens when fluids interact with solids? The forces created are known as buoyancy, drag, and lift – Buoyancy is the force developed when a solid object is immersed in a fluid (no relative motion) – Lift and Drag forces arise when fluids interact with a solid object ...
Fluid Mechanics - GTU e
... The SI system consists of six primary units, from which all quantities may be described but in fluid mechanics we are generally only interested in the top four units from this table. ...
... The SI system consists of six primary units, from which all quantities may be described but in fluid mechanics we are generally only interested in the top four units from this table. ...
Airy wave theory
In fluid dynamics, Airy wave theory (often referred to as linear wave theory) gives a linearised description of the propagation of gravity waves on the surface of a homogeneous fluid layer. The theory assumes that the fluid layer has a uniform mean depth, and that the fluid flow is inviscid, incompressible and irrotational. This theory was first published, in correct form, by George Biddell Airy in the 19th century.Airy wave theory is often applied in ocean engineering and coastal engineering for the modelling of random sea states – giving a description of the wave kinematics and dynamics of high-enough accuracy for many purposes. Further, several second-order nonlinear properties of surface gravity waves, and their propagation, can be estimated from its results. Airy wave theory is also a good approximation for tsunami waves in the ocean, before they steepen near the coast.This linear theory is often used to get a quick and rough estimate of wave characteristics and their effects. This approximation is accurate for small ratios of the wave height to water depth (for waves in shallow water), and wave height to wavelength (for waves in deep water).