Coastal Processes: WAVES - Organization of American States
... x,y are Cartesian co-ordinates with y = 0 at the still water level (positive upwards) η(x,t) = the free water surface; t = time u,v, = velocity components in the x,y directions, respectively φ(x,y,t) = the two-dimensional velocity potential ρ = the fluid density; g = gravitational acceleration a = w ...
... x,y are Cartesian co-ordinates with y = 0 at the still water level (positive upwards) η(x,t) = the free water surface; t = time u,v, = velocity components in the x,y directions, respectively φ(x,y,t) = the two-dimensional velocity potential ρ = the fluid density; g = gravitational acceleration a = w ...
Chapter 2
... For Newtonian fluids (most common fluids, such as water and air), experiments have found that the shear stress as applied is directly proportional to the rate of deformation: ...
... For Newtonian fluids (most common fluids, such as water and air), experiments have found that the shear stress as applied is directly proportional to the rate of deformation: ...
Cyclostrophic Balance in Surface Gravity Waves: Essay on Coriolis
... where f is the Coriolis parameter (twice the angular velocity of the Earth times the sine of the latitude) and ω is the wave frequency. For swell with periods of order 10 sec the ratio of the two forces at mid-latitudes has the order of magnitude of 10,000, because f itself is order 10–4 sec–1. The ...
... where f is the Coriolis parameter (twice the angular velocity of the Earth times the sine of the latitude) and ω is the wave frequency. For swell with periods of order 10 sec the ratio of the two forces at mid-latitudes has the order of magnitude of 10,000, because f itself is order 10–4 sec–1. The ...
TRANSPORT PHENOMENA, FLOW OF FLUIDS A transport
... In these transport phenomena particles can move collectively, in a synchronized way (e.g. flow of fluids), or individually (e.g. diffusion). In spite of the obvious differences in the details, there are many similarities in the description of different transport processes, and in the general princip ...
... In these transport phenomena particles can move collectively, in a synchronized way (e.g. flow of fluids), or individually (e.g. diffusion). In spite of the obvious differences in the details, there are many similarities in the description of different transport processes, and in the general princip ...
Dimensional Analysis
... the kinematic viscosity v of the liquid. 23) Derive on the basis of dimensional analysis suitable parameters to present the thrust developed by a propeller Assume that the thrust P depends upon the angular velocity w, speed of advance V. diameter D. dynamic viscosity µ , mass density p. elasticity o ...
... the kinematic viscosity v of the liquid. 23) Derive on the basis of dimensional analysis suitable parameters to present the thrust developed by a propeller Assume that the thrust P depends upon the angular velocity w, speed of advance V. diameter D. dynamic viscosity µ , mass density p. elasticity o ...
The harmonic hydro-mechanical movement of the
... [1] Tieso S. Fisiologia auditiva. Corrales ediciones médicas, Buenos Aires (Argentina) 2006. [2] Geisler D. From sound to synapse, Oxford University Press, USA (1998). ...
... [1] Tieso S. Fisiologia auditiva. Corrales ediciones médicas, Buenos Aires (Argentina) 2006. [2] Geisler D. From sound to synapse, Oxford University Press, USA (1998). ...
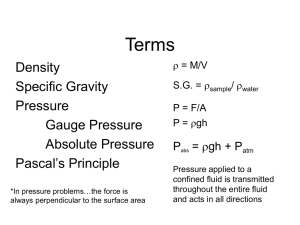
Fluid Terms
... The buoyant force is equal to the weight of the liquid displaced by the object… …the buoyant force is equal to the weight of the body of fluid whose volume equals the volume of the original submerged object Objects appear to weigh less when submerged in a fluid ...
... The buoyant force is equal to the weight of the liquid displaced by the object… …the buoyant force is equal to the weight of the body of fluid whose volume equals the volume of the original submerged object Objects appear to weigh less when submerged in a fluid ...
Lab 7: Fluids - Physics Department, Princeton University
... For fluids, things are different. Any part of the material, whether it be the entire sample or a mathematically described small portion of it, can move, and can also change shape. But each portion has mass and inertia, and can change its momentum only in response to forces. Understanding how the for ...
... For fluids, things are different. Any part of the material, whether it be the entire sample or a mathematically described small portion of it, can move, and can also change shape. But each portion has mass and inertia, and can change its momentum only in response to forces. Understanding how the for ...
16-6 The Equation of Continuity
... the use of instructors in teaching their courses and assessing student learning. Dissemination or sale of any part of this work (including on the World Wide Web) will destroy the integrity of the work and is not permitted. The work and materials from it should never be made available to students exc ...
... the use of instructors in teaching their courses and assessing student learning. Dissemination or sale of any part of this work (including on the World Wide Web) will destroy the integrity of the work and is not permitted. The work and materials from it should never be made available to students exc ...
Review Notes 2
... • Combining Newton’s second law with the equations describing the relationships between stresses and viscosity allows to derive the velocity profile for the flow system. One may also need the fluid equation of state (P = f(ρ,T)) and the density dependence of viscosity (µ = f(ρ))along Boundary and I ...
... • Combining Newton’s second law with the equations describing the relationships between stresses and viscosity allows to derive the velocity profile for the flow system. One may also need the fluid equation of state (P = f(ρ,T)) and the density dependence of viscosity (µ = f(ρ))along Boundary and I ...
Newtonian, Non-Newtonian Fluids and Viscosity
... Ideal Fluids Q.10) Ideal fluids satisfy which of the following properties; a. b. c. d. e. ...
... Ideal Fluids Q.10) Ideal fluids satisfy which of the following properties; a. b. c. d. e. ...
Continuity equation and Bernoulli`s equation
... Suppose we have a propeller, blowing air from left to right. Let’s call point 0 a point infinitely far to the left (undisturbed flow), point 1 just to the left of the propeller (infinitely close to it), point 2 identical to point 1, but then on the right, and point 3 identical to point 0, but also o ...
... Suppose we have a propeller, blowing air from left to right. Let’s call point 0 a point infinitely far to the left (undisturbed flow), point 1 just to the left of the propeller (infinitely close to it), point 2 identical to point 1, but then on the right, and point 3 identical to point 0, but also o ...
ME33: Fluid Flow Lecture 1: Information and Introduction
... These slides were developed1 during the spring semester 2005, as a teaching aid for the undergraduate Fluid Mechanics course (ME33: Fluid Flow) in the Department of Mechanical and Nuclear Engineering at Penn State University. This course had two sections, one taught by myself and one taught by Prof. ...
... These slides were developed1 during the spring semester 2005, as a teaching aid for the undergraduate Fluid Mechanics course (ME33: Fluid Flow) in the Department of Mechanical and Nuclear Engineering at Penn State University. This course had two sections, one taught by myself and one taught by Prof. ...
Presentation
... • Expansion waves are created by the interaction of multiple shock waves and convex corners • They cause a continuous change in the supersonic flow of the air. • Density, pressure and temperature ratios decrease through the expansion wave while the Mach number increases • Act like gradient index len ...
... • Expansion waves are created by the interaction of multiple shock waves and convex corners • They cause a continuous change in the supersonic flow of the air. • Density, pressure and temperature ratios decrease through the expansion wave while the Mach number increases • Act like gradient index len ...
Fully Developed Couette Flow - Pharos University in Alexandria
... Parallel flow, V=0 Incompressible, Newtonian, laminar, constant properties No pressure gradient 2D, W=0, /z = 0 Gravity acts in the -z direction, ...
... Parallel flow, V=0 Incompressible, Newtonian, laminar, constant properties No pressure gradient 2D, W=0, /z = 0 Gravity acts in the -z direction, ...
flowing fluids and pressure variation!
... e.g., pressure is low at the center of a hurricane.! For your culture : The force balance for hurricanes is the pressure force vs. the Coriolis force. That s why hurricanes in the northern hemisphere always spin counter-clockwise. In a tornado, the balance is between pressure force and centrifugal a ...
... e.g., pressure is low at the center of a hurricane.! For your culture : The force balance for hurricanes is the pressure force vs. the Coriolis force. That s why hurricanes in the northern hemisphere always spin counter-clockwise. In a tornado, the balance is between pressure force and centrifugal a ...
Analysis of wave heights and wind speeds in the Adriatic Sea
... reviewed literature. From the wind polar plot it can be noticed that the strongest winds are recorded from the direction of bura wind (N-NE). Wind forces of bura are even more emphasized due to the fact that it blows very strong for relatively short periods of time which increases its mean values. O ...
... reviewed literature. From the wind polar plot it can be noticed that the strongest winds are recorded from the direction of bura wind (N-NE). Wind forces of bura are even more emphasized due to the fact that it blows very strong for relatively short periods of time which increases its mean values. O ...
Fluids Models
... It is also considered positive if it acts in a negative direction on a surface with negative outward normal. Note: Fluid at rest experiences only pressure which is a normal force that acts opposite to the outward normal. ...
... It is also considered positive if it acts in a negative direction on a surface with negative outward normal. Note: Fluid at rest experiences only pressure which is a normal force that acts opposite to the outward normal. ...
A Brief History of Planetary Science
... Fast moving fluids exert less pressure than slow moving fluids This is known as Bernoulli’s principle Based on conservation of energy Energy that goes into velocity cannot go into pressure Note that Bernoulli holds for moving fluids ...
... Fast moving fluids exert less pressure than slow moving fluids This is known as Bernoulli’s principle Based on conservation of energy Energy that goes into velocity cannot go into pressure Note that Bernoulli holds for moving fluids ...
Document
... amplitude of the second harmonic (which is proportional to the acoustic pressure produced by this receiver. The oscilloscope screen then showed, as usual, a series of pulses decreasing exponenharmonic ) on the distance from a radiator for the tially in amplitude (Fig. 3). magnesium-aluminum alloy MA ...
... amplitude of the second harmonic (which is proportional to the acoustic pressure produced by this receiver. The oscilloscope screen then showed, as usual, a series of pulses decreasing exponenharmonic ) on the distance from a radiator for the tially in amplitude (Fig. 3). magnesium-aluminum alloy MA ...
THEORY AND PRACTICE OF AEROSOL SCIENCE
... thermodynamic properties of small clusters for use in nucleation theories. The simplest approaches, the squared gradient approximation (SGA) and mean field theory, seem to give the correct qualitative behaviour for simple fluids, although their quantitative accuracy is unclear. Early work indicated ...
... thermodynamic properties of small clusters for use in nucleation theories. The simplest approaches, the squared gradient approximation (SGA) and mean field theory, seem to give the correct qualitative behaviour for simple fluids, although their quantitative accuracy is unclear. Early work indicated ...
Airy wave theory
In fluid dynamics, Airy wave theory (often referred to as linear wave theory) gives a linearised description of the propagation of gravity waves on the surface of a homogeneous fluid layer. The theory assumes that the fluid layer has a uniform mean depth, and that the fluid flow is inviscid, incompressible and irrotational. This theory was first published, in correct form, by George Biddell Airy in the 19th century.Airy wave theory is often applied in ocean engineering and coastal engineering for the modelling of random sea states – giving a description of the wave kinematics and dynamics of high-enough accuracy for many purposes. Further, several second-order nonlinear properties of surface gravity waves, and their propagation, can be estimated from its results. Airy wave theory is also a good approximation for tsunami waves in the ocean, before they steepen near the coast.This linear theory is often used to get a quick and rough estimate of wave characteristics and their effects. This approximation is accurate for small ratios of the wave height to water depth (for waves in shallow water), and wave height to wavelength (for waves in deep water).