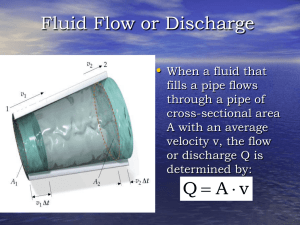
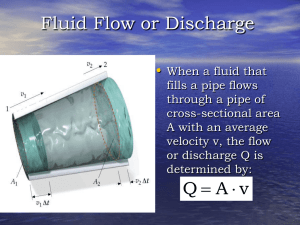
Tuesday March 18 - University of Florida
... constant at any point of the body A fluid is incompressible if the density does not change as a result of an applied pressure. ...
... constant at any point of the body A fluid is incompressible if the density does not change as a result of an applied pressure. ...
Fluid Dynamics
... Work Done by a Piston • Work done by a piston in forcing a volume V of fluid into a cylinder against an opposing pressure P is given by: W = P·V ...
... Work Done by a Piston • Work done by a piston in forcing a volume V of fluid into a cylinder against an opposing pressure P is given by: W = P·V ...
Physics 141 Mechanics Yongli Gao Lecture 4 Motion in 3-D
... • What should be the pressure a diver has to bare ? Why is it difficult to build deep ocean submarines? • The pressure increases as we go deeper into the water, described by the equation for hydrostatic pressure p p0 gh • The equation applies to all incompressible fluids. For gasses, we'd have ...
... • What should be the pressure a diver has to bare ? Why is it difficult to build deep ocean submarines? • The pressure increases as we go deeper into the water, described by the equation for hydrostatic pressure p p0 gh • The equation applies to all incompressible fluids. For gasses, we'd have ...
Balanced Flow
... because the Coriolis Force and PGF point in the same direction. This situation is called antibaric (a baric case is one in which the PGF and CF oppose each other, as normal). It is thought that this situation is unrealistic for larger scale flows in the atmosphere, and only applicable for small-scal ...
... because the Coriolis Force and PGF point in the same direction. This situation is called antibaric (a baric case is one in which the PGF and CF oppose each other, as normal). It is thought that this situation is unrealistic for larger scale flows in the atmosphere, and only applicable for small-scal ...
202 DragMoment
... dominate the dissipation of energy seems to have been advanced first by Lamb [1924] who showed that in some cases of wave motion the rate of dissipation can be calculated with sufficient accuracy by regarding the motion as irrotational with slipping at solidfluid boundaries. The computation of the d ...
... dominate the dissipation of energy seems to have been advanced first by Lamb [1924] who showed that in some cases of wave motion the rate of dissipation can be calculated with sufficient accuracy by regarding the motion as irrotational with slipping at solidfluid boundaries. The computation of the d ...
Waves are “disturbances”
... Here is another way to think about why waves grow at a beach: the front part of a wave crest is in slightly shallower water than the back part of the wave crest, so it is always going a little slower than the back part of the crest. As the back part of the crest catches up to the front part of the c ...
... Here is another way to think about why waves grow at a beach: the front part of a wave crest is in slightly shallower water than the back part of the wave crest, so it is always going a little slower than the back part of the crest. As the back part of the crest catches up to the front part of the c ...
THE EQUATIONS OF FLUID DYNAMICS—DRAFT
... awkward: We have evolution equations for each of the velocity component, and one expression for the relation between the velocities but really no separate equation for the pressure. This can be corrected by taking the divergence of the momentum equation and using the incompressibility conditions to ...
... awkward: We have evolution equations for each of the velocity component, and one expression for the relation between the velocities but really no separate equation for the pressure. This can be corrected by taking the divergence of the momentum equation and using the incompressibility conditions to ...
Chapter 9 - Mona Shores Blogs
... partially exposed from the fluid. So large density objects needs to displace a larger volume of water than their own volume in order to stay afloat. ...
... partially exposed from the fluid. So large density objects needs to displace a larger volume of water than their own volume in order to stay afloat. ...
901 bubblemotion10 05
... not arise. Though Plesset (1949) introduced a variable external driving pressure and surface tension, the effects of surface tension were also introduced and the effects of viscosity were first introduced by Poritsky (1951). His understanding of irrotational viscous stresses is exemplary, unique for ...
... not arise. Though Plesset (1949) introduced a variable external driving pressure and surface tension, the effects of surface tension were also introduced and the effects of viscosity were first introduced by Poritsky (1951). His understanding of irrotational viscous stresses is exemplary, unique for ...
Fluid Dynamics
... Work Done by a Piston • Work done by a piston in forcing a volume V of fluid into a cylinder against an opposing pressure P is given by: W = P·V ...
... Work Done by a Piston • Work done by a piston in forcing a volume V of fluid into a cylinder against an opposing pressure P is given by: W = P·V ...
Fluid Dynamics
... Under some circumstances the flow will not be as changeable as this. He following terms describe the states which are used to classify fluid flow: uniform flow: If the flow velocity is the same magnitude and direction at every point in the fluid it is said to be uniform. non-uniform: If at a giv ...
... Under some circumstances the flow will not be as changeable as this. He following terms describe the states which are used to classify fluid flow: uniform flow: If the flow velocity is the same magnitude and direction at every point in the fluid it is said to be uniform. non-uniform: If at a giv ...
Chapter 14 Solids and Fluids
... Bernoulli derived this equation in 1738. It applies to all points along a streamline in a nonviscous, imcompressible fluid. It is a disguised form of the work-energy theorem. ...
... Bernoulli derived this equation in 1738. It applies to all points along a streamline in a nonviscous, imcompressible fluid. It is a disguised form of the work-energy theorem. ...
Experimental study of Bernoulli`s equation with losses
... 共1兲. Again we see that this approach gives a poor description of the results. In Fig. 4 we also include the line that would be obtained from Eq. 共8兲 if we ignored the minor loss term (k ⫽0); again the agreement of this approximation with the data is poor. Therefore the results of the experiment indi ...
... 共1兲. Again we see that this approach gives a poor description of the results. In Fig. 4 we also include the line that would be obtained from Eq. 共8兲 if we ignored the minor loss term (k ⫽0); again the agreement of this approximation with the data is poor. Therefore the results of the experiment indi ...
Fluid redistribution Coupled to Deformation Around the NZ Plate
... redistribution around major strike-slip faults, focused at structural irregularities and coupled to stress and permeability cycling, and (v) topography-driven flow in the uplifted Southern Alps and other mountain ranges flanking the linking transform fault system, and around major volcanic edifices. ...
... redistribution around major strike-slip faults, focused at structural irregularities and coupled to stress and permeability cycling, and (v) topography-driven flow in the uplifted Southern Alps and other mountain ranges flanking the linking transform fault system, and around major volcanic edifices. ...
PDF - compatibile with Acrobat 4.0
... waves on the interaction between atmosphere and oceans. This interaction basically includes the cross-surface fluxes of mass, momentum and moisture. In this paper we discuss another important factor of air-sea interaction, namely, the roughness of the ocean surface. It is quite obvious that the inten ...
... waves on the interaction between atmosphere and oceans. This interaction basically includes the cross-surface fluxes of mass, momentum and moisture. In this paper we discuss another important factor of air-sea interaction, namely, the roughness of the ocean surface. It is quite obvious that the inten ...
Effect of Bed Porosity on Momentum Exchange in Gravel
... Momentum exchange between a rough, porous gravel substrate and the overlying turbulent flow is a key control of fine sediment ingress, pollutant exchange, spawning success and hyporheic flows. The surface topography and porosity of the substrate are known to be important controls on the near-bed hyd ...
... Momentum exchange between a rough, porous gravel substrate and the overlying turbulent flow is a key control of fine sediment ingress, pollutant exchange, spawning success and hyporheic flows. The surface topography and porosity of the substrate are known to be important controls on the near-bed hyd ...
Bernoulli`s Equation
... 7. If V2 is greater than V1 then the piezometric head ( ω +Z2) must be less than the P1 piezometric head ( ω +Z1). However if the two points considered lie along the same horizontal plane then Z1 = Z2, in which case the changes in velocity cause corresponding change in pressure. ...
... 7. If V2 is greater than V1 then the piezometric head ( ω +Z2) must be less than the P1 piezometric head ( ω +Z1). However if the two points considered lie along the same horizontal plane then Z1 = Z2, in which case the changes in velocity cause corresponding change in pressure. ...
V - ME304
... When a point by point (local) description is desired, fundamental laws are applied to an infinitesimal control volume. The result will be a set of differential equations with the fluid velocity and pressure as dependent variables and the location (x, y, z) and time as independent variables. Solution ...
... When a point by point (local) description is desired, fundamental laws are applied to an infinitesimal control volume. The result will be a set of differential equations with the fluid velocity and pressure as dependent variables and the location (x, y, z) and time as independent variables. Solution ...
Lecture Notes
... magnitude. This shearing stress (force/unit area) is created whenever a tangential force acts on a surface. When metals such as steel are acted on by a shearing stress, they will initially deform, but they will not continuously deform. However common fluids such as water, oil and air satisfy the def ...
... magnitude. This shearing stress (force/unit area) is created whenever a tangential force acts on a surface. When metals such as steel are acted on by a shearing stress, they will initially deform, but they will not continuously deform. However common fluids such as water, oil and air satisfy the def ...
Hydrostatics and Bernoulli`s Principle Slide Notes
... solid objects create a lot of turbulence cannot be satisfied with Bernoulli’s equation. Another example is something where wakes play a major roll such as an airplane wing or fish swimming. A lot of situations with sudden expansion or contractions require extra terms to make Bernoulli’s equation ...
... solid objects create a lot of turbulence cannot be satisfied with Bernoulli’s equation. Another example is something where wakes play a major roll such as an airplane wing or fish swimming. A lot of situations with sudden expansion or contractions require extra terms to make Bernoulli’s equation ...
Ocean Wave - South Eastern University of Sri Lanka
... develop techniques for harnessing wave energy, field measurements have been performed and numerical modeling as well as estimation of potential energy are under progress in Kuala Terengganu coastline. The main wave characteristics are commonly given in terms wave height, period, direction of propaga ...
... develop techniques for harnessing wave energy, field measurements have been performed and numerical modeling as well as estimation of potential energy are under progress in Kuala Terengganu coastline. The main wave characteristics are commonly given in terms wave height, period, direction of propaga ...
Fluid Mechanics
... develop when an object moves through a fluid medium. • Two fluids of interest – Water – Air ...
... develop when an object moves through a fluid medium. • Two fluids of interest – Water – Air ...
Introduction to Fluid Mechanics
... ). Specific gravity of gases is density / (density of air at the same T and P). 6. Viscosity is a measure of a fluid’s resistance to flow. Most simple fluids are represented well by Newton’s law of viscosity. The exceptions (non-Newtonian fluids) are generally complex mixtures, some of which are of ...
... ). Specific gravity of gases is density / (density of air at the same T and P). 6. Viscosity is a measure of a fluid’s resistance to flow. Most simple fluids are represented well by Newton’s law of viscosity. The exceptions (non-Newtonian fluids) are generally complex mixtures, some of which are of ...
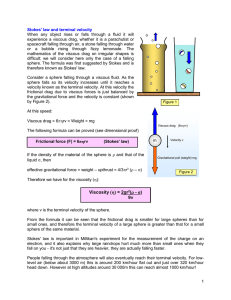
Stokes` law - schoolphysics
... electron, and it also explains why large raindrops hurt much more than small ones when they fall on you - it's not just that they are heavier, they are actually falling faster. People falling through the atmosphere will also eventually reach their terminal velocity. For lowlevel air (below about 300 ...
... electron, and it also explains why large raindrops hurt much more than small ones when they fall on you - it's not just that they are heavier, they are actually falling faster. People falling through the atmosphere will also eventually reach their terminal velocity. For lowlevel air (below about 300 ...
Airy wave theory
In fluid dynamics, Airy wave theory (often referred to as linear wave theory) gives a linearised description of the propagation of gravity waves on the surface of a homogeneous fluid layer. The theory assumes that the fluid layer has a uniform mean depth, and that the fluid flow is inviscid, incompressible and irrotational. This theory was first published, in correct form, by George Biddell Airy in the 19th century.Airy wave theory is often applied in ocean engineering and coastal engineering for the modelling of random sea states – giving a description of the wave kinematics and dynamics of high-enough accuracy for many purposes. Further, several second-order nonlinear properties of surface gravity waves, and their propagation, can be estimated from its results. Airy wave theory is also a good approximation for tsunami waves in the ocean, before they steepen near the coast.This linear theory is often used to get a quick and rough estimate of wave characteristics and their effects. This approximation is accurate for small ratios of the wave height to water depth (for waves in shallow water), and wave height to wavelength (for waves in deep water).