CIEG-306 Fluid Mechanics Laboratory 5. HYDRAULIC JUMP
... The purpose of this experiment is to observe the hydraulic jump phenomenon and to compare measured flow depths with theoretical results based on the application of continuity and momentum principles. In the laboratory flume, the flow is regulated from the upstream end by a sluice gate so that a shal ...
... The purpose of this experiment is to observe the hydraulic jump phenomenon and to compare measured flow depths with theoretical results based on the application of continuity and momentum principles. In the laboratory flume, the flow is regulated from the upstream end by a sluice gate so that a shal ...
Fluids - Duke Physics
... spatial relation to each other, i.e., are bound. This kind of system is a solid. If the particles are not bound, but still are on average close enough together to interact continuously with nearest neighbors, we have a liquid. When the particles are on average far apart and only interact occasionall ...
... spatial relation to each other, i.e., are bound. This kind of system is a solid. If the particles are not bound, but still are on average close enough together to interact continuously with nearest neighbors, we have a liquid. When the particles are on average far apart and only interact occasionall ...
Slide 1
... It is the average density that matters; a boat made of steel can float because its interior is mostly air. An object’s density may be changed; submarines fill tanks with water to submerge, and with air to rise. ...
... It is the average density that matters; a boat made of steel can float because its interior is mostly air. An object’s density may be changed; submarines fill tanks with water to submerge, and with air to rise. ...
Chapter 14 Fluids
... In the case of a liquid the tracer can be a dye. An example is given in the picture to the left. In the case of gas, smoke particles can be used as a tracer. Each visible tracer particle follows a streamline, which is a path that a fluid element would take. Three such streamlines are shown in the fi ...
... In the case of a liquid the tracer can be a dye. An example is given in the picture to the left. In the case of gas, smoke particles can be used as a tracer. Each visible tracer particle follows a streamline, which is a path that a fluid element would take. Three such streamlines are shown in the fi ...
Manual Valve Theory
... occur. This condition is held as long as possible. Station 3 represents the full diameter of the pipe. The energy equation may also be written between stations 2 and 3 as follows: ...
... occur. This condition is held as long as possible. Station 3 represents the full diameter of the pipe. The energy equation may also be written between stations 2 and 3 as follows: ...
Fluids
... A pitot-static tube (probe) is stuck into a flow in a pipe the probe would stop the flow (remember the stream lines for flow over objects). Assuming you know the velocity of the flow in the pipe and the pressure at some point downstream, what is the pressure that the probe reads? Can we use Bernoull ...
... A pitot-static tube (probe) is stuck into a flow in a pipe the probe would stop the flow (remember the stream lines for flow over objects). Assuming you know the velocity of the flow in the pipe and the pressure at some point downstream, what is the pressure that the probe reads? Can we use Bernoull ...
bubbling up keep metering problems from
... Empty-full-empty batching can pose a related measurement issue. Such batching is most common to avoid cross-contamination of products when filling large tanks such as rail cars or trucks. Therefore, the loading line is purged with air or other inert gas between loads, leaving the meter empty before ...
... Empty-full-empty batching can pose a related measurement issue. Such batching is most common to avoid cross-contamination of products when filling large tanks such as rail cars or trucks. Therefore, the loading line is purged with air or other inert gas between loads, leaving the meter empty before ...
PowerPoint Slides - University of Toronto Physics
... • It increases its velocity. This means the kinetic energy per volume of the fluid will increase. • How can this be? There must be a force which does work on the fluid to speed it up. • The force must come from a pressure difference. • Pressure must be lower in the region of increased fluid velo ...
... • It increases its velocity. This means the kinetic energy per volume of the fluid will increase. • How can this be? There must be a force which does work on the fluid to speed it up. • The force must come from a pressure difference. • Pressure must be lower in the region of increased fluid velo ...
Flow past a Groove - Scientific Research Publishing
... An elementary theoretical (analytical) model of flow past a groove appears to be out of reach at present and no such model already exists as far as I can determine. Numerical techniques may be brought into service on the problem in the future, however. Of course further observations are always welco ...
... An elementary theoretical (analytical) model of flow past a groove appears to be out of reach at present and no such model already exists as far as I can determine. Numerical techniques may be brought into service on the problem in the future, however. Of course further observations are always welco ...
Ocean Dynamics
... basic hydrodynamic equations, depending on the patterns of the observed motions. It is possible to simplify the equations of motion using the following scale analysis: For the open ocean, typical values of the distance L, horizontal velocity U, depth H, Coriolis parameter f, gravity g and density ρ ...
... basic hydrodynamic equations, depending on the patterns of the observed motions. It is possible to simplify the equations of motion using the following scale analysis: For the open ocean, typical values of the distance L, horizontal velocity U, depth H, Coriolis parameter f, gravity g and density ρ ...
Continuous and Episodic Fluid Flow in Regional Metamorphism
... subsequently, and controls the salt content of the sequence, which will influence whether or not fluid immiscibility extends significantly into the metamorphic realm. Continental shelf sequences with abundant carbonates and evaporites will experience very different fluid evolution patterns from fore ...
... subsequently, and controls the salt content of the sequence, which will influence whether or not fluid immiscibility extends significantly into the metamorphic realm. Continental shelf sequences with abundant carbonates and evaporites will experience very different fluid evolution patterns from fore ...
Slide 1 - Union College
... effects, a process through which a surface is electrowetted in such a way that it will cause a droplet to be pulled forward. Because this is a relatively new field, not much is known about the flows within droplets while they are undergoing this electrocapillary propulsion. However, much of the drop ...
... effects, a process through which a surface is electrowetted in such a way that it will cause a droplet to be pulled forward. Because this is a relatively new field, not much is known about the flows within droplets while they are undergoing this electrocapillary propulsion. However, much of the drop ...
DES601 - Hour 13
... Flow Classification by Critical Depth • Classification important in water surface profile (HGL) estimation and discharge measurement. • Water can exist at two depths except at critical depth • Critical depth important in measuring discharge • Sub- and Super-Critical classification determine if the ...
... Flow Classification by Critical Depth • Classification important in water surface profile (HGL) estimation and discharge measurement. • Water can exist at two depths except at critical depth • Critical depth important in measuring discharge • Sub- and Super-Critical classification determine if the ...
Wave energy converters, sediment transport and coastal erosion
... Waves approaching a shore with an angle of impact other than perpendicular create a longshore current which, depending on the velocity of this current, removes sediment and thus potentially reduces the sediment available to form a beach in the affected region. The same is valid for perpendicular wav ...
... Waves approaching a shore with an angle of impact other than perpendicular create a longshore current which, depending on the velocity of this current, removes sediment and thus potentially reduces the sediment available to form a beach in the affected region. The same is valid for perpendicular wav ...
Pressure and Fluid Flow_ppt_RevW10
... When you are swimming at a depth h, the pressure outside you in the water is Patm+ gh. Inside your lungs, which are directly connected to the air by the snorkel, the pressure is Patm. So your lungs have to breathe against a gauge pressure of gh. You can expand your chest against a pressure only ...
... When you are swimming at a depth h, the pressure outside you in the water is Patm+ gh. Inside your lungs, which are directly connected to the air by the snorkel, the pressure is Patm. So your lungs have to breathe against a gauge pressure of gh. You can expand your chest against a pressure only ...
The Reynolds transport Theorem
... Let a fluid particle exactly positioned at point A moving to another point A during time interval t . The velocity of the fluid particle is the same as the local velocity at that point as obtained from the Eulerian description At time t, ...
... Let a fluid particle exactly positioned at point A moving to another point A during time interval t . The velocity of the fluid particle is the same as the local velocity at that point as obtained from the Eulerian description At time t, ...
1.1 Introduction and Surface Energy Balance
... Effect on the rest of the atmosphere. Boundary-layer clouds are very important for climate. 3. Structure of ABL over a diurnal cycle During a clear day the boundary layer can be divided into several sublayers, as shown in Figure 1: 1. The roughness sublayer – this is the layer of air in which ai ...
... Effect on the rest of the atmosphere. Boundary-layer clouds are very important for climate. 3. Structure of ABL over a diurnal cycle During a clear day the boundary layer can be divided into several sublayers, as shown in Figure 1: 1. The roughness sublayer – this is the layer of air in which ai ...
E80FlowMeasurements 2014
... Osborne Reynolds (University of Manchester, 1883) discovered that, – if the same atmospheric pressure was used for experiments with wind tunnel models as a full-size airplane would encounter under actual conditions, the results would be invalid. For the results to be valid, – the air density inside ...
... Osborne Reynolds (University of Manchester, 1883) discovered that, – if the same atmospheric pressure was used for experiments with wind tunnel models as a full-size airplane would encounter under actual conditions, the results would be invalid. For the results to be valid, – the air density inside ...
Biofluids - Louisiana Tech University
... Newtonian vs. Non-Newtonian Fluids • Newtonian Fluids: Linear Viscosity Equation ...
... Newtonian vs. Non-Newtonian Fluids • Newtonian Fluids: Linear Viscosity Equation ...
File - The Physics Doctor
... liquid around the sphere is laminar As the molecules its passing through will stick to the surface as it travels, a viscous drag (F) is created This force was shown to be related to the radius of the sphere, the velocity of the sphere and the coefficient of viscosity ( η ) ...
... liquid around the sphere is laminar As the molecules its passing through will stick to the surface as it travels, a viscous drag (F) is created This force was shown to be related to the radius of the sphere, the velocity of the sphere and the coefficient of viscosity ( η ) ...
Sediment-induced stratification and density current in
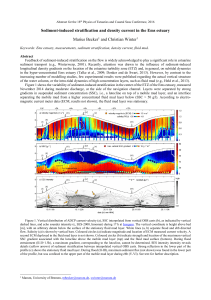
... During the first half of the flood tide (Figure 1b, II-III), the mobile mud layer was entrained. We observed the reformation of the mobile mud layer during an unexpectedly early stage of the flood phase (III). This is interpreted to result from a super-saturated situation after the flood accelerati ...
... During the first half of the flood tide (Figure 1b, II-III), the mobile mud layer was entrained. We observed the reformation of the mobile mud layer during an unexpectedly early stage of the flood phase (III). This is interpreted to result from a super-saturated situation after the flood accelerati ...
DHANALAKSHMI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, CHENNAI
... There may be a practical situation that the required length of a required diameter pipe may not be adequately available. In such a situation, one has to go in for different diameter and different lengths of pipes to form pipes in series. 14. When are pipes used in parallel? Total head loss in a pip ...
... There may be a practical situation that the required length of a required diameter pipe may not be adequately available. In such a situation, one has to go in for different diameter and different lengths of pipes to form pipes in series. 14. When are pipes used in parallel? Total head loss in a pip ...
Khusnutdinova2009-Kolmogorov.pdf
... Which feed on their velocity, And little whirls have lesser whirls, And so on to viscosity.” He took an inspiration from the Jonathan Swift’s verse: ...
... Which feed on their velocity, And little whirls have lesser whirls, And so on to viscosity.” He took an inspiration from the Jonathan Swift’s verse: ...
control volume approach and continuity principle
... the problem you want to solve. Steady flow problems are often easier than unsteady ones, so control volume b) may be preferable. ...
... the problem you want to solve. Steady flow problems are often easier than unsteady ones, so control volume b) may be preferable. ...
Airy wave theory
In fluid dynamics, Airy wave theory (often referred to as linear wave theory) gives a linearised description of the propagation of gravity waves on the surface of a homogeneous fluid layer. The theory assumes that the fluid layer has a uniform mean depth, and that the fluid flow is inviscid, incompressible and irrotational. This theory was first published, in correct form, by George Biddell Airy in the 19th century.Airy wave theory is often applied in ocean engineering and coastal engineering for the modelling of random sea states – giving a description of the wave kinematics and dynamics of high-enough accuracy for many purposes. Further, several second-order nonlinear properties of surface gravity waves, and their propagation, can be estimated from its results. Airy wave theory is also a good approximation for tsunami waves in the ocean, before they steepen near the coast.This linear theory is often used to get a quick and rough estimate of wave characteristics and their effects. This approximation is accurate for small ratios of the wave height to water depth (for waves in shallow water), and wave height to wavelength (for waves in deep water).