The Bernoulli equation
... KE is 0.5mv22 and PE is mgh2. Now mgh1 = 0.5mv22 + mgh2 so v2 = ( 2g(h1- h2))0.5 This gives an expression for the velocity of the water as it flows from of a pipe nozzle at a height (h1- h2) below the surface of the reservoir.(Ignoring friction losses in the pipe and the nozzle). Volume of flow. The ...
... KE is 0.5mv22 and PE is mgh2. Now mgh1 = 0.5mv22 + mgh2 so v2 = ( 2g(h1- h2))0.5 This gives an expression for the velocity of the water as it flows from of a pipe nozzle at a height (h1- h2) below the surface of the reservoir.(Ignoring friction losses in the pipe and the nozzle). Volume of flow. The ...
Week_2
... example by evaporation, by pumping it out or by using some for a chemical reaction such as photosynthesis) or add some (for example by rain). Mass is related to volume and density: density=Mass/volume. When the fluid density changes (for example, due to changes in temperature), its volume changes. I ...
... example by evaporation, by pumping it out or by using some for a chemical reaction such as photosynthesis) or add some (for example by rain). Mass is related to volume and density: density=Mass/volume. When the fluid density changes (for example, due to changes in temperature), its volume changes. I ...
Halliday-ch14
... A change in the pressure applied to an enclosed incompressible fluid is transmitted undiminished to every portion of the fluid and to the walls of its container. ...
... A change in the pressure applied to an enclosed incompressible fluid is transmitted undiminished to every portion of the fluid and to the walls of its container. ...
Bernoulli’s, Pascal’s, & Archimedes’ Principles
... Fluid exerted on an object. • What is the downward Force exerted on an object? Gravity ...
... Fluid exerted on an object. • What is the downward Force exerted on an object? Gravity ...
Bernoulli`s Principle
... • Why are we learning about it? – To understand pressure systems and apply them to real life examples ...
... • Why are we learning about it? – To understand pressure systems and apply them to real life examples ...
b. Positive-Displacement Pumps. - Universal College of Engineering
... In a vane-type pump, a slotted rotor splined to a drive shaft rotates between closely fitted side plates that are inside of an elliptical- or circular-shaped ring. Polished, hardened vanes slide in and out of the rotor slots and follow the ring contour by centrifugal force. Pumping chambers are ...
... In a vane-type pump, a slotted rotor splined to a drive shaft rotates between closely fitted side plates that are inside of an elliptical- or circular-shaped ring. Polished, hardened vanes slide in and out of the rotor slots and follow the ring contour by centrifugal force. Pumping chambers are ...
Control volume analysis (Part 2) Linear Momentum Equations
... Water flows through a horizontal, pipe bend as illustrated in the figure below. The flow cross-sectional area is constant at a value A through the bend. The magnitude of the flow velocity everywhere in the bend is axial and equal to V. The absolute pressures at the entrance and exit of the bend are ...
... Water flows through a horizontal, pipe bend as illustrated in the figure below. The flow cross-sectional area is constant at a value A through the bend. The magnitude of the flow velocity everywhere in the bend is axial and equal to V. The absolute pressures at the entrance and exit of the bend are ...
Xie-EGM-RPI-2011 - Rensselaer Hartford Campus
... • COMSOL Multi-physics has been used to model the steady laminar flow and convective heat transfer of an electrically conducting fluid subjected to an applied electromagnetic field in two simple flow configurations, namely, flow between parallel plates (Hartmann flow) and flow around a backward faci ...
... • COMSOL Multi-physics has been used to model the steady laminar flow and convective heat transfer of an electrically conducting fluid subjected to an applied electromagnetic field in two simple flow configurations, namely, flow between parallel plates (Hartmann flow) and flow around a backward faci ...
Xie-EGM-RPI-2011.pdf
... • The obtained results are encouraging and suggest that COMSOL Multi-physics could be used to investigate more complex magnetohydrodynamic flows. ...
... • The obtained results are encouraging and suggest that COMSOL Multi-physics could be used to investigate more complex magnetohydrodynamic flows. ...
fluid - GEOCITIES.ws
... Jets and nozzles Bernoulli’s equation suggests that for fluid flow where the potential energy change hg is very small or zero, as in a horizontal pipe, the pressure falls when the velocity rises The velocity increases at a constriction and this creates a pressure drop. The following devices make us ...
... Jets and nozzles Bernoulli’s equation suggests that for fluid flow where the potential energy change hg is very small or zero, as in a horizontal pipe, the pressure falls when the velocity rises The velocity increases at a constriction and this creates a pressure drop. The following devices make us ...
Types of sediment load
... • saltation (hopping)--grains are temporarily suspended by fluid vortices or by ballistic impact and then released • Grain movement may be continuous or intermittent depending on the flow regime (strength of flow as defined by Froude Number). ...
... • saltation (hopping)--grains are temporarily suspended by fluid vortices or by ballistic impact and then released • Grain movement may be continuous or intermittent depending on the flow regime (strength of flow as defined by Froude Number). ...
Vortex Shedding
... Repeating pattern of swirling vortices caused by the unsteady separation of flow of a fluid over bluff bodies ...
... Repeating pattern of swirling vortices caused by the unsteady separation of flow of a fluid over bluff bodies ...
Physics--Chapter 9: Fluid Mechanics
... through a pipe 1A1ν1t = 2A2ν2t, but density (1 and 2) and time interval (t) would be the same so they are canceled out leaving A1ν1 = A2ν2 3. This equation, A1ν1 = A2ν2, is referred to as the continuity equation where A1 and A2 represent the two different cross-sectional areas of the pipe, an ...
... through a pipe 1A1ν1t = 2A2ν2t, but density (1 and 2) and time interval (t) would be the same so they are canceled out leaving A1ν1 = A2ν2 3. This equation, A1ν1 = A2ν2, is referred to as the continuity equation where A1 and A2 represent the two different cross-sectional areas of the pipe, an ...
When a net force acts on a body, the body accelerates. Newton`s
... of motion describes the relationship between the net force, the body’s mass, and the body’s acceleration (F = ma). Whenever there is motion, there is opposition or resistance to the motion. Mechanical resistance is opposition to motion of a solid object when it is in contact with another solid objec ...
... of motion describes the relationship between the net force, the body’s mass, and the body’s acceleration (F = ma). Whenever there is motion, there is opposition or resistance to the motion. Mechanical resistance is opposition to motion of a solid object when it is in contact with another solid objec ...
Low Noise, increased reliability, digital control
... During one revolution of the pump each piston chamber is connected over an angle of 180° to the low pressure and to the high pressure side. During the transition process the pressure in the piston chamber is alternating between this two levels. The transition process is very rapid and is finished af ...
... During one revolution of the pump each piston chamber is connected over an angle of 180° to the low pressure and to the high pressure side. During the transition process the pressure in the piston chamber is alternating between this two levels. The transition process is very rapid and is finished af ...
10-6 - Physics
... Shows fluid flowing through a horizontal constricted pipe Speed changes as diameter changes Can be used to measure the speed of the fluid flow Swiftly moving fluids exert less pressure than do slowly moving fluids ...
... Shows fluid flowing through a horizontal constricted pipe Speed changes as diameter changes Can be used to measure the speed of the fluid flow Swiftly moving fluids exert less pressure than do slowly moving fluids ...
ch4
... A conical tube of 4 m length is fixed at an inclined angle of 30° with the horizontal-line and its small diameter upwards. The velocity at smaller end is (u1 = 5 m/s), while (u2 = 2 m/s) at other end. The head losses in the tub is [0.35 (u1-u2)2/2g]. Determine the pressure head at lower end if the f ...
... A conical tube of 4 m length is fixed at an inclined angle of 30° with the horizontal-line and its small diameter upwards. The velocity at smaller end is (u1 = 5 m/s), while (u2 = 2 m/s) at other end. The head losses in the tub is [0.35 (u1-u2)2/2g]. Determine the pressure head at lower end if the f ...
Fluid Mechanics
... • From the table in your book, the density of gold is 19.3 x 103 kg/m3. • Because 8.0 x 103 kg/m3 < 19.3 x 103 kg/m3, the crown cannot be pure gold. ...
... • From the table in your book, the density of gold is 19.3 x 103 kg/m3. • Because 8.0 x 103 kg/m3 < 19.3 x 103 kg/m3, the crown cannot be pure gold. ...
ch14
... A change in the pressure applied to an enclosed incompressible fluid is transmitted undiminished to every portion of the fluid and to the walls of its container. ...
... A change in the pressure applied to an enclosed incompressible fluid is transmitted undiminished to every portion of the fluid and to the walls of its container. ...
Physics 123 Fluid Mechanics Review
... the bottom, as illustrated. The height of the water level above the ground is h + H = 2.00 m. In order to increase the flow rate through the hole, you could: A. Increase H, leaving H + h constant. B. Increase H, leaving h constant. C. Increase the size of hole to allow more water to flow through the ...
... the bottom, as illustrated. The height of the water level above the ground is h + H = 2.00 m. In order to increase the flow rate through the hole, you could: A. Increase H, leaving H + h constant. B. Increase H, leaving h constant. C. Increase the size of hole to allow more water to flow through the ...
1P1, 2013-14, Thermofluid Mechanics: examples paper 2
... A gas turbine is being tested under steady flow conditions in the rig shown in the figure above. The engine thrust is balanced by the tension force F in the diagonal strut, which makes an angle α = 45o with the vertical. The mass flow rate of air from the ambient atmosphere into the engine is m˙ a = ...
... A gas turbine is being tested under steady flow conditions in the rig shown in the figure above. The engine thrust is balanced by the tension force F in the diagonal strut, which makes an angle α = 45o with the vertical. The mass flow rate of air from the ambient atmosphere into the engine is m˙ a = ...
Document
... accounting for losses due to friction in pipes and other components of pipe systems; calculate the performance of a pump needed in a simple pipe flow system. An Introduction to Mechanical Engineering: Part One ...
... accounting for losses due to friction in pipes and other components of pipe systems; calculate the performance of a pump needed in a simple pipe flow system. An Introduction to Mechanical Engineering: Part One ...
Lecture24
... • Mass flow rate (kg/s) on the left must be equal to the mass flow rate on the right. • Imaginary tubes bound the flow of the fluid. ...
... • Mass flow rate (kg/s) on the left must be equal to the mass flow rate on the right. • Imaginary tubes bound the flow of the fluid. ...
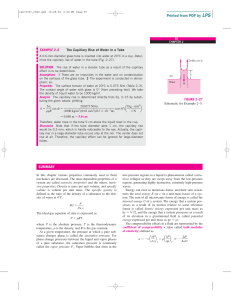
summary - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... where f is the contact angle. The capillary rise is inversely proportional to the radius of the tube and is negligible for tubes whose diameter is larger than about 1 cm. Density and viscosity are two of the most fundamental properties of fluids, and they are used extensively in the chapters that fo ...
... where f is the contact angle. The capillary rise is inversely proportional to the radius of the tube and is negligible for tubes whose diameter is larger than about 1 cm. Density and viscosity are two of the most fundamental properties of fluids, and they are used extensively in the chapters that fo ...
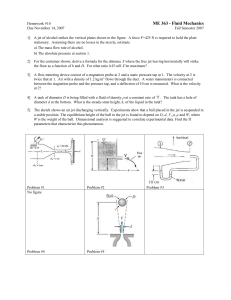
Department of Mechanical Engineering
... 1] A jet of alcohol strikes the vertical plates shown in the figure. A force F=425 N is required to hold the plate stationary. Assuming there are no losses in the nozzle, estimate a) The mass flow rate of alcohol. b) The absolute pressure at section 1. 2] For the container shown, derive a formula fo ...
... 1] A jet of alcohol strikes the vertical plates shown in the figure. A force F=425 N is required to hold the plate stationary. Assuming there are no losses in the nozzle, estimate a) The mass flow rate of alcohol. b) The absolute pressure at section 1. 2] For the container shown, derive a formula fo ...
Hydraulic machinery

Hydraulic machines are machinery and tools that use liquid fluid power to do simple work. Heavy equipment is a common example.In this type of machine, hydraulic fluid is transmitted throughout the machine to various hydraulic motors and hydraulic cylinders and which becomes pressurised according to the resistance present. The fluid is controlled directly or automatically by control valves and distributed through hoses and tubes.The popularity of hydraulic machinery is due to the very large amount of power that can be transferred through small tubes and flexible hoses, and the high power density and wide array of actuators that can make use of this power.Hydraulic machinery is operated by the use of hydraulics, where a liquid is the powering medium.