* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download When a net force acts on a body, the body accelerates. Newton`s
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
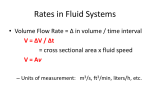
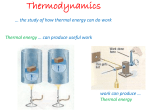
When a net force acts on a body, the body accelerates. Newton’s second law of motion describes the relationship between the net force, the body’s mass, and the body’s acceleration (F = ma). Whenever there is motion, there is opposition or resistance to the motion. Mechanical resistance is opposition to motion of a solid object when it is in contact with another solid object. This opposition is called friction. A linear model of friction describes the forces adequately in many situations. According to this model, the force of friction is proportional to the normal force between the objects (Fstatic ≤ μsN, and Fkinetic = μkN). Fluid resistance is opposition to fluid flow. Drag is the force that resists motion of an object moving through a fluid (or a fluid moving past a stationary object). Drag increases as speed increases. Resistance causes fluid • pressure to drop as fluid flows through a pipe, tube, or duct ( Rfluid = – ΔP /V ). The resistance depends on the radius of the pipe, the length of the pipe, and the viscosity of the fluid. Electrical resistance is opposition to charge flow. Resistance causes a potential difference, or voltage drop, as current flows through a conductor (R = ΔV/I). The resistance of a wire depends on the length of the wire, its cross-sectional area, and the resistivity of its material composition. Thermal resistance is opposition to heat flow. Heat flows through a wall from a region of high temperature to a region of low temperature. The thermal resistance of the wall is the ratio of the temperature drop to the heat • flow rate ( Rthermal = – ΔT / Q). Thermal resistance depends on the thickness of the wall, its cross-sectional area, and the thermal conductivity of its material composition. C HAPTER 4 SUMMARY 227