* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Principles of Technology
Mechanical filter wikipedia , lookup
Mechanical-electrical analogies wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
Lumped element model wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
Newton's laws of motion wikipedia , lookup
Centripetal force wikipedia , lookup
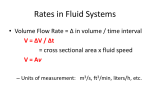
Unit 1: FORCE Unit Objectives: ◦ Describe in your own words, what force is. ◦ Give examples of complex technological devices where force must be controlled, measured, or applied ◦ Describe what force, pressure, voltage and temperature difference have in common ◦ Describe or predict what happens to an object when forces on it are balanced and when forces on it are unbalanced. ◦ Measure force in mechanical, fluid, electrical and thermal systems. ◦ List occupations that require technicians to measure, control, or otherwise deal with force in complex devices. Forces are a part of our everyday activities Mechanical, fluid, electrical and thermal energy systems involve forces. A prime mover, such as an unbalanced force, pressure difference, voltage difference, or temperature difference, causes whatever it “acts” on to move. Mathematics is essential for technicians working in advanced-technology occupations. Force is a push or a pull. A force can ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Cause an object to start moving or to move faster Cause a moving object to change direction Cause an object to slow down or to stop moving Change the shape of an object Force is what makes things move in a mechanical system. In a mechanical system, force is called the “prime mover.” Each system has a prime mover that acts very much like force. Energy Systems Prime Movers Mechanical Force Fluid Pressure Electrical Voltage Thermal Temperature Difference Automobile ◦ Mechanical – Pistons, connecting rods, crankshaft ◦ Fluid Systems – Hydraulic system transfers motion from the brake pedal to the brake shoes ◦ Electrical system – battery, alternator, spark plugs ◦ Thermal – or cooling system – radiator, fan and thermostat, water pump, liquid coolant,