Calculating the Number of Genes
... Duplication in Evolution …essential genes do not tolerate mutation, …duplications of essential genes, followed by mutations, confers adaptive potential to the organism, …new gene family members are ‘recruited’ to perform new functions. ...
... Duplication in Evolution …essential genes do not tolerate mutation, …duplications of essential genes, followed by mutations, confers adaptive potential to the organism, …new gene family members are ‘recruited’ to perform new functions. ...
Prof. Kamakaka`s Lecture 12 Notes
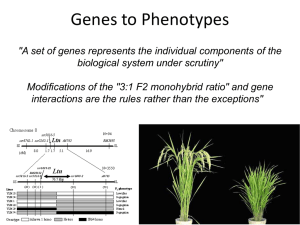
... A gene with one wild-type allele is monomorphic; a gene with two or more wild-type alleles is polymorphic. The vast majority of traits are determined by alleles of more than one gene. This means that most traits are multifactorial. A Heterogeneous Trait is One That May be caused by mutations in more ...
... A gene with one wild-type allele is monomorphic; a gene with two or more wild-type alleles is polymorphic. The vast majority of traits are determined by alleles of more than one gene. This means that most traits are multifactorial. A Heterogeneous Trait is One That May be caused by mutations in more ...
no isthmus and pax2.1 in zebrafish tubulogenesis
... with podocytes and surrounding parietal epithelium (Bowman’s capsule), suggesting glomerular differentiation and morphogenesis does not require pax2.1. Unlike the mouse or human pax2 mutations, which behave haploinsufficiently, noi heterozygotes do not display edema or show a histological pronephric ...
... with podocytes and surrounding parietal epithelium (Bowman’s capsule), suggesting glomerular differentiation and morphogenesis does not require pax2.1. Unlike the mouse or human pax2 mutations, which behave haploinsufficiently, noi heterozygotes do not display edema or show a histological pronephric ...
Exploratory data analysis for microarray data
... ❍ Sammon mapping: S(D, D ) = (dij − d0ij )2/dij . Puts more emphasis on the smaller distances being preserved. In R: sammon in package MASS. ...
... ❍ Sammon mapping: S(D, D ) = (dij − d0ij )2/dij . Puts more emphasis on the smaller distances being preserved. In R: sammon in package MASS. ...
Identifying Common Genetic Variants by High
... detected variants (7, 8, 11, 13 ). Indeed, heteroduplex scanning methods as a rule detect sequence variants but do not identify or genotype those variants. Common sequence variants that do not cause disease occur at a frequency much greater than that of disease-causing variants. These common variant ...
... detected variants (7, 8, 11, 13 ). Indeed, heteroduplex scanning methods as a rule detect sequence variants but do not identify or genotype those variants. Common sequence variants that do not cause disease occur at a frequency much greater than that of disease-causing variants. These common variant ...
Entering the second century of maize quantitative genetics
... Heredity (2014) 112, 30–38; doi:10.1038/hdy.2013.6; published online 6 March 2013 Keywords: maize; nested association mapping; quantitative traits; genome-wide association; heterosis ...
... Heredity (2014) 112, 30–38; doi:10.1038/hdy.2013.6; published online 6 March 2013 Keywords: maize; nested association mapping; quantitative traits; genome-wide association; heterosis ...
Functional Interactions of Genes Mediating Convergent Extension
... Members of the hedgehog (hh) gene family, consisting of at least four members in the mouse, chick, and zebrafish, encode secreted signaling proteins that function in multiple patterning processes during animal embryogenesis (for review, see Hammerschmidt et al., 1997). Among the above family members ...
... Members of the hedgehog (hh) gene family, consisting of at least four members in the mouse, chick, and zebrafish, encode secreted signaling proteins that function in multiple patterning processes during animal embryogenesis (for review, see Hammerschmidt et al., 1997). Among the above family members ...
1q21 microdeletions
... million base pairs, or one so-called megabase (Mb) of DNA. Base pairs are the chemicals in DNA that form the ends of the ‘rungs’ of its ladder-like structure. Chromosome 1 has around 247 Mb in total and band 1q21.1 alone contains around 5.4 Mb. In a class 1 deletion, DNA is typically missing between ...
... million base pairs, or one so-called megabase (Mb) of DNA. Base pairs are the chemicals in DNA that form the ends of the ‘rungs’ of its ladder-like structure. Chromosome 1 has around 247 Mb in total and band 1q21.1 alone contains around 5.4 Mb. In a class 1 deletion, DNA is typically missing between ...
Joachim Denner, Ralf R. Tönjes. Infection Barriers to Successful
... The major problem of xenotransplantation is the rejection of porcine cells, tissues, and organs, which occurs in several stages: (i) hyperacute rejection (HAR), (ii) acute vascular rejection (AVR), (iii) cellular rejection, and (iv) chronic rejection. HAR and AVR are mediated mainly by antibodies ag ...
... The major problem of xenotransplantation is the rejection of porcine cells, tissues, and organs, which occurs in several stages: (i) hyperacute rejection (HAR), (ii) acute vascular rejection (AVR), (iii) cellular rejection, and (iv) chronic rejection. HAR and AVR are mediated mainly by antibodies ag ...
Role of sexlinked genes in quantitative inheritance
... gene is a physical entity which (i) is duplicated and passed intact from generation to generations^!!) has a specific function in the production of the phenotype and (iii) can mutate to another entity satisfying (i) and (ii). It should be noted that there may exist also in the cytoplasm particulate ...
... gene is a physical entity which (i) is duplicated and passed intact from generation to generations^!!) has a specific function in the production of the phenotype and (iii) can mutate to another entity satisfying (i) and (ii). It should be noted that there may exist also in the cytoplasm particulate ...
MyGene.info Documentation
... “refseq” and “accession” fields now contain accession number including version. Data can be search with and without version. Version is available for “genomic”, “rna” and “protein” accession number keys. Note: “genomic” field is returned but is not searchable v2: http://mygene.info/v2/query?q=NM_052 ...
... “refseq” and “accession” fields now contain accession number including version. Data can be search with and without version. Version is available for “genomic”, “rna” and “protein” accession number keys. Note: “genomic” field is returned but is not searchable v2: http://mygene.info/v2/query?q=NM_052 ...
X-Chromosome dosage compensation
... In C. elegans, the processes of dosage compensation and sex determination are coordinately regulated by a group of genes that respond to the primary sex-determination signal. Following this common step of regulation, sex determination and dosage compensation are separately controlled by distinct gen ...
... In C. elegans, the processes of dosage compensation and sex determination are coordinately regulated by a group of genes that respond to the primary sex-determination signal. Following this common step of regulation, sex determination and dosage compensation are separately controlled by distinct gen ...
1q21 microdeletions
... after fertilisation. This is part of a natural process and as a parent there is nothing you can do to change or control it. At one point, all the chromosomes including the two chromosome 1s pair up and swap segments. To pair up precisely, each chromosome ‘recognises’ matching or nearmatching DNA seq ...
... after fertilisation. This is part of a natural process and as a parent there is nothing you can do to change or control it. At one point, all the chromosomes including the two chromosome 1s pair up and swap segments. To pair up precisely, each chromosome ‘recognises’ matching or nearmatching DNA seq ...
MRSA - Infectious Diseases
... mec gene complex (mecI, mecR1, mecA) + ccr gene complex (ccrA, ccrB) (responsible for mobility and insertion of the gene complex) + other transposons, plasmids ...
... mec gene complex (mecI, mecR1, mecA) + ccr gene complex (ccrA, ccrB) (responsible for mobility and insertion of the gene complex) + other transposons, plasmids ...
C 2: A A -
... PSEUDOMONAS AERUGINOSA – NOVEL DEVELOPMENTS AND CLINICAL IMPACT. [This section is prepared to conform to the print style set out by the American Society of Microbiology. Published in: Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, 2003; 47(8): 2385 – 2392.] ...
... PSEUDOMONAS AERUGINOSA – NOVEL DEVELOPMENTS AND CLINICAL IMPACT. [This section is prepared to conform to the print style set out by the American Society of Microbiology. Published in: Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, 2003; 47(8): 2385 – 2392.] ...
Developmental buffering: how many genes?
... Although most studies of Hsp90 and phenotypic variability have been conducted in Drosophila, similar patterns appear also to hold for other organisms. In zebrafish, pharmacological inhibition and knockdown of Hsp90 induced a range of specific abnormalities depending on the genotype (Yeyati et al. 2007 ...
... Although most studies of Hsp90 and phenotypic variability have been conducted in Drosophila, similar patterns appear also to hold for other organisms. In zebrafish, pharmacological inhibition and knockdown of Hsp90 induced a range of specific abnormalities depending on the genotype (Yeyati et al. 2007 ...
PDF
... and polarized light sensors (Hardie, 1985). According to their differentiated function, R1-6 innervate the first OL neuropil, which is the lamina, whereas R7 and R8 axons run across the lamina to innervate the neuropil beneath, which is the medulla. Next, the lobula and lobula plate (together called ...
... and polarized light sensors (Hardie, 1985). According to their differentiated function, R1-6 innervate the first OL neuropil, which is the lamina, whereas R7 and R8 axons run across the lamina to innervate the neuropil beneath, which is the medulla. Next, the lobula and lobula plate (together called ...
Building Individualized Medicine: Prevention of Adverse Reactions
... requirements. This approach uses genetic markers rather than functional polymorphisms and therefore does not provide information about possible mechanisms behind alterations in drug response. Instead, it relies on the assumption that a mutant allele is to be correlated with an allele of an assayed S ...
... requirements. This approach uses genetic markers rather than functional polymorphisms and therefore does not provide information about possible mechanisms behind alterations in drug response. Instead, it relies on the assumption that a mutant allele is to be correlated with an allele of an assayed S ...
Commentary: A century of Mendelism: on Johannsen`s genotype
... could claim that ‘Galtonian law of regression and its corollaries elaborated by Pearson pretended to have established the laws of “ancestral influences” in mathematical terms’ were an artefact. They were nothing but ‘interesting products of mathematical genius. . .but they have nothing at all to do ...
... could claim that ‘Galtonian law of regression and its corollaries elaborated by Pearson pretended to have established the laws of “ancestral influences” in mathematical terms’ were an artefact. They were nothing but ‘interesting products of mathematical genius. . .but they have nothing at all to do ...
View - Rai University
... on the genome, and transmitted by the standard laws of inheritance from one generation to the next. These sequences may be associated with a certain trait of an organism and help to trace out gene for a particular trait. Further use of molecular marker has helped research groups to dissect heterosis ...
... on the genome, and transmitted by the standard laws of inheritance from one generation to the next. These sequences may be associated with a certain trait of an organism and help to trace out gene for a particular trait. Further use of molecular marker has helped research groups to dissect heterosis ...
Processing the RefSeq and CCDS Annotation Datasets Using the SAS System: Creation of Gene Reference
... 50000 (and the first base of transcript would be 50001 since it is zero-indexed). This would mean that __POINT cycles from 50001-50000=1 to 50000. Note that the difference between 50000 and 1 is 49,999 but the number of bases is 50000 (50000-1+1). The variable P (Line 42) is the absolute position of ...
... 50000 (and the first base of transcript would be 50001 since it is zero-indexed). This would mean that __POINT cycles from 50001-50000=1 to 50000. Note that the difference between 50000 and 1 is 49,999 but the number of bases is 50000 (50000-1+1). The variable P (Line 42) is the absolute position of ...
Human RIF1 and protein phosphatase 1 stimulate DNA replication
... generally a few hundred kb in length, but the precise end-to-end length of each fiber being analysed is not a number easily obtained in such fiber methods. While the fiber size will indeed affect measurements (since you obviously can’t detect an IOD greater than the fibre size), there’s no reason to ...
... generally a few hundred kb in length, but the precise end-to-end length of each fiber being analysed is not a number easily obtained in such fiber methods. While the fiber size will indeed affect measurements (since you obviously can’t detect an IOD greater than the fibre size), there’s no reason to ...
Genetic and biochemical analysis of the adenylyl cyclase of
... (H), Sph I (Sp), Sal I (S), Xba I (X), Sma I (Sm), Kpn I (K), and Sac I (Sc) are indicated. The sequence encoding the carboxylterminal catalytic region of the protein is represented by the cross-hatched region, whereas the remainder of the coding sequence is represented by the open box. 5' and 3' un ...
... (H), Sph I (Sp), Sal I (S), Xba I (X), Sma I (Sm), Kpn I (K), and Sac I (Sc) are indicated. The sequence encoding the carboxylterminal catalytic region of the protein is represented by the cross-hatched region, whereas the remainder of the coding sequence is represented by the open box. 5' and 3' un ...
Site-specific recombinase technology

Nearly every human gene has a counterpart in the mouse (regardless of the fact that a minor set of orthologues had to follow species specific selection routes). This made the mouse the major model for elucidating the ways in which our genetic material encodes information. In the late 1980s gene targeting in murine embryonic stem (ES-)cells enabled the transmission of mutations into the mouse germ line and emerged as a novel option to study the genetic basis of regulatory networks as they exist in the genome. Still, classical gene targeting proved to be limited in several ways as gene functions became irreversibly destroyed by the marker gene that had to be introduced for selecting recombinant ES cells. These early steps led to animals in which the mutation was present in all cells of the body from the beginning leading to complex phenotypes and/or early lethality. There was a clear need for methods to restrict these mutations to specific points in development and specific cell types. This dream became reality when groups in the USA were able to introduce bacteriophage and yeast-derived site-specific recombination (SSR-) systems into mammalian cells as well as into the mouse