Light and Optics - Mayfield City Schools
... at which the light will not enter the air but reflect back into the water! • This effect is called total internal reflection. ...
... at which the light will not enter the air but reflect back into the water! • This effect is called total internal reflection. ...
refl and refr, mirrors
... we see images where light appears to come from Consider how light from your eye reflects from a mirror to get to ...
... we see images where light appears to come from Consider how light from your eye reflects from a mirror to get to ...
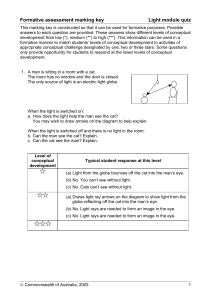
Formative assessment marking key: Light Module Quiz
... (optically dense) media such as glass and water (ie different colours have a different refractive index). As different colours travel at different speeds in glass, when white light strikes the surface of glass, the light disperses into its colours, red light bends (refracts) least and violet the mos ...
... (optically dense) media such as glass and water (ie different colours have a different refractive index). As different colours travel at different speeds in glass, when white light strikes the surface of glass, the light disperses into its colours, red light bends (refracts) least and violet the mos ...
Chapter 36 Summary – Magnetism
... Directions: #1-6, are true/false. Write the sentence and explain why it’s true, or how to make it true. #7-23 are multiple choice. Write the question and correct answer and explain why. 1) Diffuse reflection occurs when light is refracted in many directions from a rough surface. 2) Reflection occurs ...
... Directions: #1-6, are true/false. Write the sentence and explain why it’s true, or how to make it true. #7-23 are multiple choice. Write the question and correct answer and explain why. 1) Diffuse reflection occurs when light is refracted in many directions from a rough surface. 2) Reflection occurs ...
Light II - Galileo and Einstein
... equations reveals that where the beam is totally internally reflected, in fact there is an electromagnetic wave in the air, but it dies away in a distance of order the wavelength on going from the surface. However, if another substance is brought close, this wave can be absorbed and/or scattered bac ...
... equations reveals that where the beam is totally internally reflected, in fact there is an electromagnetic wave in the air, but it dies away in a distance of order the wavelength on going from the surface. However, if another substance is brought close, this wave can be absorbed and/or scattered bac ...
Sign convention
... •Design of ideal imaging systems with geometrical optics –Paraxial, thin lenses and graphical ray tracing ...
... •Design of ideal imaging systems with geometrical optics –Paraxial, thin lenses and graphical ray tracing ...
No Slide Title
... Each wavelength is 360o, so DN=496.41 means Df=DNx360o=0.41x360o=148o •How thick should the glass be so that the beams are exactly out of phase at the exit (destructive interference!) DN=D/ ls- D/ lg= (D/ l)(n2-n1)=0.31 (D/ l)=m+1/2 A thickness D=(m+0.5) 2.02 mm would make the waves OUT of phase. Fo ...
... Each wavelength is 360o, so DN=496.41 means Df=DNx360o=0.41x360o=148o •How thick should the glass be so that the beams are exactly out of phase at the exit (destructive interference!) DN=D/ ls- D/ lg= (D/ l)(n2-n1)=0.31 (D/ l)=m+1/2 A thickness D=(m+0.5) 2.02 mm would make the waves OUT of phase. Fo ...
chapter35
... Refraction: When light enters from one medium to the second, it changes its direction in the second medium. The angle the refracted light makes with the normal ( 2 in the diagram) is called the angle of refraction. The incident ray, the reflected ray, the refracted ray, and the normal all lie in t ...
... Refraction: When light enters from one medium to the second, it changes its direction in the second medium. The angle the refracted light makes with the normal ( 2 in the diagram) is called the angle of refraction. The incident ray, the reflected ray, the refracted ray, and the normal all lie in t ...
Total Reflection
... face will hit the curved surface at a right angle; this will prevent refraction at the air/glass boundary of the curved surface. At the glass/air boundary of the flat surface, what happens will depend on the angle. Where θc is the critical angle measurement which is caused by the sun or a light so ...
... face will hit the curved surface at a right angle; this will prevent refraction at the air/glass boundary of the curved surface. At the glass/air boundary of the flat surface, what happens will depend on the angle. Where θc is the critical angle measurement which is caused by the sun or a light so ...
Lecture 28 - LSU Physics
... In glass, λg=0.625µm/1.46= 0.428 µm and Ng=D/ λg=2336.45 In sapphire, λs=0.625µm/1.77= 0.353 µm (UV!) and Ns=D/ λs=2832.86 •What is the phase difference in the beams when they come out? The difference in wavelengths is Ns-Ng=496.41. Each wavelength is 360o, so ΔN=496.41 means Δφ=ΔNx360o=0.41x360o=14 ...
... In glass, λg=0.625µm/1.46= 0.428 µm and Ng=D/ λg=2336.45 In sapphire, λs=0.625µm/1.77= 0.353 µm (UV!) and Ns=D/ λs=2832.86 •What is the phase difference in the beams when they come out? The difference in wavelengths is Ns-Ng=496.41. Each wavelength is 360o, so ΔN=496.41 means Δφ=ΔNx360o=0.41x360o=14 ...
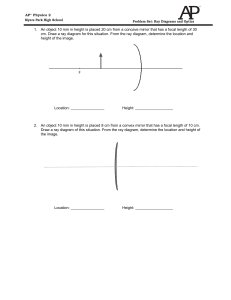
AP® Physics 2 Myers Park High School Problem Set: Ray Diagrams
... 4. A beam of light emerges from water into air at an angle. The beam is bent _____. a. toward the normal b. away from the normal c. at an angle of 49° d. only if it is polarized 5. When a light beam emerges from water into air, the light speed _____. a. increases b. remains the same c. decreases 6. ...
... 4. A beam of light emerges from water into air at an angle. The beam is bent _____. a. toward the normal b. away from the normal c. at an angle of 49° d. only if it is polarized 5. When a light beam emerges from water into air, the light speed _____. a. increases b. remains the same c. decreases 6. ...
Principles of light guidance
... Different rays propagate along step profile fibres at different rates - this is known as multimode dispersion. Pulse distortion is greater for fibres with many modes, and gets worse as the fibre length increases. ...
... Different rays propagate along step profile fibres at different rates - this is known as multimode dispersion. Pulse distortion is greater for fibres with many modes, and gets worse as the fibre length increases. ...
Extra Credit
... where n1 and n2 are the indices of refraction of the media which form the boundary on which the light is incident. Light is incident in medium 1 and for total internal reflection we must have n1 n2 (light is trying to pass from a “slow” to a “fast” medium). Polarization by Reflection. Know that a ...
... where n1 and n2 are the indices of refraction of the media which form the boundary on which the light is incident. Light is incident in medium 1 and for total internal reflection we must have n1 n2 (light is trying to pass from a “slow” to a “fast” medium). Polarization by Reflection. Know that a ...
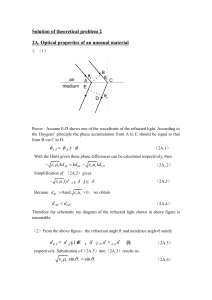
Solution of theoretical problem 2
... On the right side of above equation the first term shows the phase difference of the light wave accumulated during its propagation in air, the second term shows the phase difference of the light wave accumulated during its propagation in the unusual medium, while the third term accounts for the phas ...
... On the right side of above equation the first term shows the phase difference of the light wave accumulated during its propagation in air, the second term shows the phase difference of the light wave accumulated during its propagation in the unusual medium, while the third term accounts for the phas ...
Ray Tracing
... • Ray contribution color += colortrans * – Stop if reflected / trace transmitted ray ...
... • Ray contribution color += colortrans * – Stop if reflected / trace transmitted ray ...
PowerPoint - cs.Virginia
... Snell’s law applies to perfect mirror-like surfaces, but aside from mirrors (and chrome) few surfaces exhibit perfect specularity How can we capture the “softer” reflections of surface that are glossy rather than mirror-like? One option: model the microgeometry of the surface and explicitly bounce r ...
... Snell’s law applies to perfect mirror-like surfaces, but aside from mirrors (and chrome) few surfaces exhibit perfect specularity How can we capture the “softer” reflections of surface that are glossy rather than mirror-like? One option: model the microgeometry of the surface and explicitly bounce r ...
PHYS 1111 Mechanics, Waves, & Thermodynamics
... Chapter 36 Image Formation (Lens and Mirrors) Using the ray approximation of geometric optics, we can now study how images are formed with mirrors and lens Then we can apply these principles to practical optical devices: the eye, telescopes, … First consider the common flat mirror to make some defin ...
... Chapter 36 Image Formation (Lens and Mirrors) Using the ray approximation of geometric optics, we can now study how images are formed with mirrors and lens Then we can apply these principles to practical optical devices: the eye, telescopes, … First consider the common flat mirror to make some defin ...
Plane Mirror Worksheet - Solutions
... Copy this distance (dOtop) to the other side of the mirror. It becomes (dItop). ...
... Copy this distance (dOtop) to the other side of the mirror. It becomes (dItop). ...
Lecture Series: Building the Future of Optical Modeling and Design
... increasing number of us has experienced that in practice already. Ray tracing suffers from serious limitations in advanced optical modeling. Maybe some of you has already tried to solve that problem by applying a Maxwell’s solver like Finite-Difference Time-Domain Technique (FDTD). Then you found ou ...
... increasing number of us has experienced that in practice already. Ray tracing suffers from serious limitations in advanced optical modeling. Maybe some of you has already tried to solve that problem by applying a Maxwell’s solver like Finite-Difference Time-Domain Technique (FDTD). Then you found ou ...
Document
... being reflected. These curved mirrors are silvered on the concave side and are known as concave mirrors. Other curved mirrors are silvered on the convex side. They are commonly used too give a wider field view. These mirrors cause the parallel rays incident on their surface to be reflected as throug ...
... being reflected. These curved mirrors are silvered on the concave side and are known as concave mirrors. Other curved mirrors are silvered on the convex side. They are commonly used too give a wider field view. These mirrors cause the parallel rays incident on their surface to be reflected as throug ...
F1 The ray approximation in optics assumes that light travels from
... The ray approximation in optics assumes that light travels from one point to another along a narrow path called a ray that may be represented by a directed line (i.e. a line with an arrow on it). In a uniform medium (where the refractive index is the same everywhere) the rays are straight lines, tho ...
... The ray approximation in optics assumes that light travels from one point to another along a narrow path called a ray that may be represented by a directed line (i.e. a line with an arrow on it). In a uniform medium (where the refractive index is the same everywhere) the rays are straight lines, tho ...
GRADE 10 SA2 PHYSICS revision worksheet-2
... (b) The lens prescribed by the doctor has a power equal to +2.0 D. What does it mean? (c) What would be the approximate focal length of a spherical lens preferred to use while reading small letters found in a dictionary? 6. (a) A convex lens of focal length 20 cm can produce a magnified virtual as w ...
... (b) The lens prescribed by the doctor has a power equal to +2.0 D. What does it mean? (c) What would be the approximate focal length of a spherical lens preferred to use while reading small letters found in a dictionary? 6. (a) A convex lens of focal length 20 cm can produce a magnified virtual as w ...
optics(conceptuals)
... What changes in interference pattern in Young’s double slit experiment will be observed when: (i) distance between slits is reduced? (ii) the apparatus is immersed in water? (iii) monochromatic source is replaced by a source of white light? (iv) the screen is moved away from the slits? Justify your ...
... What changes in interference pattern in Young’s double slit experiment will be observed when: (i) distance between slits is reduced? (ii) the apparatus is immersed in water? (iii) monochromatic source is replaced by a source of white light? (iv) the screen is moved away from the slits? Justify your ...
Guided Discovery and Lesson Notes on Mirrors and Applications
... 1. Parallel rays far from the axis do converge at a point slightly closed to the mirror than the focal point: thus, the image formed by parallel rays is a disk instead of a point. 2. This deviation from an ideal point is called spherical aberration. 3. Spherical aberration can be eliminated using pa ...
... 1. Parallel rays far from the axis do converge at a point slightly closed to the mirror than the focal point: thus, the image formed by parallel rays is a disk instead of a point. 2. This deviation from an ideal point is called spherical aberration. 3. Spherical aberration can be eliminated using pa ...
Plane mirrors
... B. Concave Mirrors: 1. Concave mirror- a mirror with a surface that curves inward like the inside of a bowl. 2. Optical Axis- imaginary line that divides a mirror in half. 3. Focal Point-The point at which rays parallel to the optical axis meet. 4. The more curved the mirror the closer the focal poi ...
... B. Concave Mirrors: 1. Concave mirror- a mirror with a surface that curves inward like the inside of a bowl. 2. Optical Axis- imaginary line that divides a mirror in half. 3. Focal Point-The point at which rays parallel to the optical axis meet. 4. The more curved the mirror the closer the focal poi ...
Ray tracing (graphics)

In computer graphics, ray tracing is a technique for generating an image by tracing the path of light through pixels in an image plane and simulating the effects of its encounters with virtual objects. The technique is capable of producing a very high degree of visual realism, usually higher than that of typical scanline rendering methods, but at a greater computational cost. This makes ray tracing best suited for applications where the image can be rendered slowly ahead of time, such as in still images and film and television visual effects, and more poorly suited for real-time applications like video games where speed is critical. Ray tracing is capable of simulating a wide variety of optical effects, such as reflection and refraction, scattering, and dispersion phenomena (such as chromatic aberration).