Lecture 24
... They reduce the E field to zero at the surface. This is equivalent to a field of point sources at the surface with opposite polarity. These sources re-radiate the signal at the reflection angle. ...
... They reduce the E field to zero at the surface. This is equivalent to a field of point sources at the surface with opposite polarity. These sources re-radiate the signal at the reflection angle. ...
Waves - Morgan Science
... Upright – image is right side up compared to object Inverted – image is upside down as compared to object ...
... Upright – image is right side up compared to object Inverted – image is upside down as compared to object ...
Optics-Light Lab - University of Michigan SharePoint Portal
... 7. Blue light (short wavelength) is refracted (bent toward the normal) more than red light (long wavelength). This is how a prism separates white light into its component colors. 8. The dispersion of the glass or plastic material used to construct a converging (convex) lens causes the different col ...
... 7. Blue light (short wavelength) is refracted (bent toward the normal) more than red light (long wavelength). This is how a prism separates white light into its component colors. 8. The dispersion of the glass or plastic material used to construct a converging (convex) lens causes the different col ...
Physics 234 Exam # 2 Review
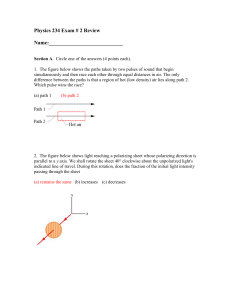
... 2. The figure below shows light reaching a polarizing sheet whose polarizing direction is parallel to a y axis. We shall rotate the sheet 40° clockwise about the unpolarized light's indicated line of travel. During this rotation, does the fraction of the initial light intensity passing through the s ...
... 2. The figure below shows light reaching a polarizing sheet whose polarizing direction is parallel to a y axis. We shall rotate the sheet 40° clockwise about the unpolarized light's indicated line of travel. During this rotation, does the fraction of the initial light intensity passing through the s ...
Slide - Journal of Vision
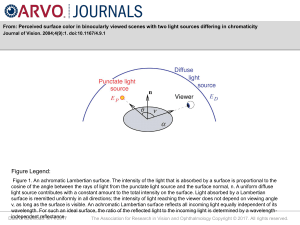
... Figure 1. An achromatic Lambertian surface. The intensity of the light that is absorbed by a surface is proportional to the cosine of the angle between the rays of light from the punctate light source and the surface normal, n. A uniform diffuse light source contributes with a constant amount to the ...
... Figure 1. An achromatic Lambertian surface. The intensity of the light that is absorbed by a surface is proportional to the cosine of the angle between the rays of light from the punctate light source and the surface normal, n. A uniform diffuse light source contributes with a constant amount to the ...
Ray Tracing
... Each ray interacts at the center of the lens. This approximation is why the lens is described as “thin”. With a thick lens one would have to apply Snell’s law in order to determine how that ray bends through the glass. However, in this case that is not a problem since the lens is thin and the light ...
... Each ray interacts at the center of the lens. This approximation is why the lens is described as “thin”. With a thick lens one would have to apply Snell’s law in order to determine how that ray bends through the glass. However, in this case that is not a problem since the lens is thin and the light ...
Chapt23_VG0
... wavelength is known as dispersion. Shown is the dispersion curves of two common glasses. Notice that n is larger when the wavelength is shorter, thus violet light refracts more than red light. ...
... wavelength is known as dispersion. Shown is the dispersion curves of two common glasses. Notice that n is larger when the wavelength is shorter, thus violet light refracts more than red light. ...
Waves & Oscillations Physics 42200 Spring 2015 Semester Lecture 28 – Geometric Optics
... to describe propagation of rays through any compound system Note: any ray passing through the first principal plane will emerge at the same height at the second principal plane For 2 lenses (above): Example: page 246 ...
... to describe propagation of rays through any compound system Note: any ray passing through the first principal plane will emerge at the same height at the second principal plane For 2 lenses (above): Example: page 246 ...
1. Visual perception
... compute the cosine of the angle of refraction in terms of the incident angle and the ratio of the indices of refraction. On page 24 of Watt, he develops a formula for computing this cosine. Notationally, he uses m instead of for the index of refraction in the text, but uses in Figure 1.16(!?), a ...
... compute the cosine of the angle of refraction in terms of the incident angle and the ratio of the indices of refraction. On page 24 of Watt, he develops a formula for computing this cosine. Notationally, he uses m instead of for the index of refraction in the text, but uses in Figure 1.16(!?), a ...
Chapter1 Fundamental law of geometrical optics 第一章 几何光学的
... The path along which light travels are known as rays in a homogeneous medium, they are straight lines. ﹡The location and brightness of an image can be determined by ray ...
... The path along which light travels are known as rays in a homogeneous medium, they are straight lines. ﹡The location and brightness of an image can be determined by ray ...
Unit 7 Lab Review - Harrison High School
... speed of sound? 2. In this lab what factor did we have to use to find the theoretical value for the speed of sound? ...
... speed of sound? 2. In this lab what factor did we have to use to find the theoretical value for the speed of sound? ...
11.1 law of reflection and curved mirrors
... An image can be larger or smaller or the same as your object A = attitude. An image can be upright or inverted compared to the original object or can be laterally inverted (left and right switch) L = location. The distance between the image and mirror and whether the image is made in front or behind ...
... An image can be larger or smaller or the same as your object A = attitude. An image can be upright or inverted compared to the original object or can be laterally inverted (left and right switch) L = location. The distance between the image and mirror and whether the image is made in front or behind ...
File
... • A light source radiates millions of light rays in all directions, but you are only concerned with the rays that actually strike the mirror and are reflected into your eyes, with the angle of incidence being equal to the angle of reflection. • In an image, the distance from the object to the mirror ...
... • A light source radiates millions of light rays in all directions, but you are only concerned with the rays that actually strike the mirror and are reflected into your eyes, with the angle of incidence being equal to the angle of reflection. • In an image, the distance from the object to the mirror ...
reflection, refraction, lense and optical instruments
... Now sinθrefl can never be greater than 1, and is maximal for θrefl = 90o the angle θinc (this is now on the inside of the glass, not the angle the outside of the glass is hit at) where this happens is given the name critical angle since for any θinc > θcritical, the sine would have to greater than 1 ...
... Now sinθrefl can never be greater than 1, and is maximal for θrefl = 90o the angle θinc (this is now on the inside of the glass, not the angle the outside of the glass is hit at) where this happens is given the name critical angle since for any θinc > θcritical, the sine would have to greater than 1 ...
124-07_Reflection_and_Refraction
... is now on the inside of the glass, not the angle the outside of the glass is hit at) where this happens is given the name critical angle since for any θinc > θcritical, the sine would have to greater than 1. Since this can not be, light must be trapped inside the glass, it must be totally reflected. ...
... is now on the inside of the glass, not the angle the outside of the glass is hit at) where this happens is given the name critical angle since for any θinc > θcritical, the sine would have to greater than 1. Since this can not be, light must be trapped inside the glass, it must be totally reflected. ...
Chapter #35 Light and Optics Wave Fronts Electromagnetic Wave
... • Electromagnetic Wave moves outwards from a small source in three dimensions. It forms spherical wave. At far distance from the source front becomes flat and rays become parallel. ...
... • Electromagnetic Wave moves outwards from a small source in three dimensions. It forms spherical wave. At far distance from the source front becomes flat and rays become parallel. ...
4.Bending Light PhET
... Google the phrase, “Bending Light PhET” and click on the first link. Click the “Download Now!” button. In the last unit, you learned that reflection occurs when light bounces off of a surface. Refraction occurs when light changes direction (bends) when entering a new medium. The laser is pointing to ...
... Google the phrase, “Bending Light PhET” and click on the first link. Click the “Download Now!” button. In the last unit, you learned that reflection occurs when light bounces off of a surface. Refraction occurs when light changes direction (bends) when entering a new medium. The laser is pointing to ...
2 Reflection
... I is located at the point where the line OA’ and the mirror intersect. Draw a solid line (representing the reflected ray of light) over the portion IO of the line. No real ray travels between A’ and I. ...
... I is located at the point where the line OA’ and the mirror intersect. Draw a solid line (representing the reflected ray of light) over the portion IO of the line. No real ray travels between A’ and I. ...
Reflecting And Refracting Light
... • We describe the path of light as straight-line rays • Reflection off a flat surface follows a simple rule: – angle in (incidence) equals angle out (reflection) – angles measured from surface “normal” (perpendicular) ...
... • We describe the path of light as straight-line rays • Reflection off a flat surface follows a simple rule: – angle in (incidence) equals angle out (reflection) – angles measured from surface “normal” (perpendicular) ...
Ray tracing (graphics)

In computer graphics, ray tracing is a technique for generating an image by tracing the path of light through pixels in an image plane and simulating the effects of its encounters with virtual objects. The technique is capable of producing a very high degree of visual realism, usually higher than that of typical scanline rendering methods, but at a greater computational cost. This makes ray tracing best suited for applications where the image can be rendered slowly ahead of time, such as in still images and film and television visual effects, and more poorly suited for real-time applications like video games where speed is critical. Ray tracing is capable of simulating a wide variety of optical effects, such as reflection and refraction, scattering, and dispersion phenomena (such as chromatic aberration).