* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Optics supplemental notess
Nonlinear optics wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Optical coherence tomography wikipedia , lookup
Image intensifier wikipedia , lookup
Thomas Young (scientist) wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
Ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Ray tracing (graphics) wikipedia , lookup
Nonimaging optics wikipedia , lookup
Johan Sebastiaan Ploem wikipedia , lookup
Anti-reflective coating wikipedia , lookup
Night vision device wikipedia , lookup
Retroreflector wikipedia , lookup
Photographic film wikipedia , lookup
Optical aberration wikipedia , lookup
Atmospheric optics wikipedia , lookup
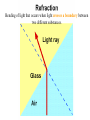
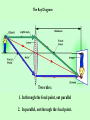
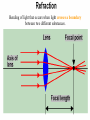
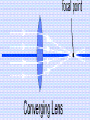
Optics What is Optics? – the study of how light behaves, or – the collection and use of light to create images. • Optical system: Collects light and uses refraction and reflection to form an image – lenses-which refract (bend) light – mirrors - which reflect (bounce) light How can it bend? • Light always travels in a straight line, but if it encounters another object or medium, it can change directions. – when light is bent so that it comes together it is called converging – when light is bent so that it spreads apart it is called diverging Light Rays • an imaginary arrow that follows a single beam of light Bending of light that occurs when light crosses a boundary between two different substances. Objects or waves “bounce” off a surface Images • A place where many light rays from the same point on an object meet together again in a point called the focus, or focal point. – They are “pictures” of objects Two types of images: – virtual - "not real" - the image only seems to be where it is; cannot be projected onto a screen – real -can be projected onto a screen, because the light actually passes through the point where the image appears Optical Devices • Most optical devices have two functions: 1. They collect light rays 2. They bend the collected rays to form an image. • To illustrate how an optical device works, we draw ray diagrams to trace several light rays through a system The Ray Diagram Two rules: 1. In through the focal point, out parallel 2. In parallel, out through the focal point. Ray diagrams • Help answer questions like: – – – – Where is the focal point (or is there one)? Will the image be magnified or reduced in size? Will the image be upside down or right side up? Will the image be inverted left or right? Law of Reflection Light rays bounce off a mirror at the same angle at which they arrive. Three Types of Mirrors –plane - flat – image is right-side-up, the same size and virtual –concave - curved inward; creates a focal point –if the object is placed at the focal point, the image is inverted, smaller, and real –if the object is placed closer to the mirror the image is larger and virtual –convex - curved outward –the image is right-side-up, smaller, and virtual Lenses a transparent material that refracts light usually made of glass or plastic with one or two curved surfaces Bending of light that occurs when light crosses a boundary between two different substances. Two types of lenses: –convex converging –- thicker in the center than at the edges –converges the light rays (forms a focal point) –forms a real image (magnifies objects) –corrects farsightedness –concave diverging –thicker at the edges and thinner in the center –diverges the light rays –images are smaller and right-side-up –forms virtual images –corrects nearsightedness