Unfolding ray trace for plates and wedges - E
... sometimes is easier to construct because it has only one inclined plane. The stack of virtual wedges is shown in Fig. 7. The analysis is similar to those carried out above for the symmetric wedge. Then we follow the same procedure: a ray is traced through the stack, producing several crossings of th ...
... sometimes is easier to construct because it has only one inclined plane. The stack of virtual wedges is shown in Fig. 7. The analysis is similar to those carried out above for the symmetric wedge. Then we follow the same procedure: a ray is traced through the stack, producing several crossings of th ...
The Laws of Reflection
... ray, the reflected ray, and the normal all lie on the same plane.) Do the light rays in Figure 5 obey the laws of reflection? How do you know? (Yes. The angle of incidence and the angle of reflection are equal, and the incident ray, the reflected ray, and the normal all lie on the same plane.) • Dif ...
... ray, the reflected ray, and the normal all lie on the same plane.) Do the light rays in Figure 5 obey the laws of reflection? How do you know? (Yes. The angle of incidence and the angle of reflection are equal, and the incident ray, the reflected ray, and the normal all lie on the same plane.) • Dif ...
Image formation with broad bundles of rays
... The change in phase along different rays between points of intersection with two given wave surfaces is the same. The total change in phase between the points O and O’ is the same for the different rays. The optical path length y is the same for all these rays. ...
... The change in phase along different rays between points of intersection with two given wave surfaces is the same. The total change in phase between the points O and O’ is the same for the different rays. The optical path length y is the same for all these rays. ...
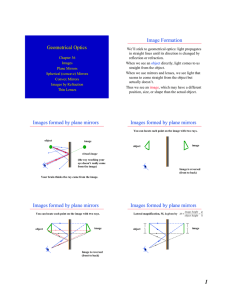
Geometrical Optics Image Formation Images formed by plane
... in straight lines until its direction is changed by reflection or refraction. When we see an object directly, light comes to us straight from the object. When we use mirrors and lenses, we see light that seems to come straight from the object but actually doesn’t. Thus we see an image, which may hav ...
... in straight lines until its direction is changed by reflection or refraction. When we see an object directly, light comes to us straight from the object. When we use mirrors and lenses, we see light that seems to come straight from the object but actually doesn’t. Thus we see an image, which may hav ...
Light T
... rays never meet when reflected so objects in this mirror are always __virtual_____ and __smaller________ than the object. Example: ...
... rays never meet when reflected so objects in this mirror are always __virtual_____ and __smaller________ than the object. Example: ...
HP unit 12 - wave optics student handout
... Essentially, part of an incident wave is reflected off the top surface of film while the other part is transmitted into the thin film where it reflects off bottom surface (of film). Waves are NEARLY parallel. ...
... Essentially, part of an incident wave is reflected off the top surface of film while the other part is transmitted into the thin film where it reflects off bottom surface (of film). Waves are NEARLY parallel. ...
The angle of refraction
... When light travels from a vacuum of space into our atmosphere there is a very slight refraction. This is normally not noticed, except when there is a total eclipse of the moon. During the total eclipse stage, the moon is not visible, but will appear very slightly. This is because it has been lit up ...
... When light travels from a vacuum of space into our atmosphere there is a very slight refraction. This is normally not noticed, except when there is a total eclipse of the moon. During the total eclipse stage, the moon is not visible, but will appear very slightly. This is because it has been lit up ...
Chapter 20-Light The Nature of Light Visible Light Is a Form of
... c. Light is a unit for measuring great distances (distance in the solar system) 3. Transport, Translucent, and Opaque Materials a. Light can pass through certain material not is stopped by others i. Transparent=air, plastic wrap, water and clear glass ii. Translucent=frosted glass, some plastics iii ...
... c. Light is a unit for measuring great distances (distance in the solar system) 3. Transport, Translucent, and Opaque Materials a. Light can pass through certain material not is stopped by others i. Transparent=air, plastic wrap, water and clear glass ii. Translucent=frosted glass, some plastics iii ...
Optics-Light Lab - University of Michigan SharePoint Portal
... Reflected waves are redirected according to the law of reflection: the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. The angles of incidence and reflection are defined with respect to the direction normal (perpendicular) to the mirror surface as shown below. The law of reflection holds for ...
... Reflected waves are redirected according to the law of reflection: the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. The angles of incidence and reflection are defined with respect to the direction normal (perpendicular) to the mirror surface as shown below. The law of reflection holds for ...
Chapter 25 The Reflection of Light: Mirrors
... If the inside surface of the spherical mirror is polished, it is a concave mirror. If the outside surface is polished, is it a convex mirror. R is the radius of curvature of the mirror. The law of reflection applies, just as it does for a plane mirror, i.e. the angles of incidence and reflection are ...
... If the inside surface of the spherical mirror is polished, it is a concave mirror. If the outside surface is polished, is it a convex mirror. R is the radius of curvature of the mirror. The law of reflection applies, just as it does for a plane mirror, i.e. the angles of incidence and reflection are ...
Physics - No Brain Too Small
... The rays from the bottom of the pencil refract away from the normal because it is travelling faster in air compared to water / water is more optically dense than air. The human eye projects the image in a straight line and “sees” the end of the pencil where it is not and the pencil looks bent. (Avoi ...
... The rays from the bottom of the pencil refract away from the normal because it is travelling faster in air compared to water / water is more optically dense than air. The human eye projects the image in a straight line and “sees” the end of the pencil where it is not and the pencil looks bent. (Avoi ...
PHYSICS 504 OPTICS REVIEW: Important things to remember: 1
... the surface!!! Your angles are formed by the light ray and the normal line!!! ...
... the surface!!! Your angles are formed by the light ray and the normal line!!! ...
PHYSICS 504 OPTICS REVIEW: Important things to remember
... the surface!!! Your angles are formed by the light ray and the normal line!!! ...
... the surface!!! Your angles are formed by the light ray and the normal line!!! ...
19_InstructorGuideMac
... As emphasized in Chapter 18, students’ ability to successfully use the thin-lens equation does not mean that they have an understanding of image formation. Thus it is important that, especially at first, examples and problems on the thin-lens equation are first preceded by graphical ray tracing. It ...
... As emphasized in Chapter 18, students’ ability to successfully use the thin-lens equation does not mean that they have an understanding of image formation. Thus it is important that, especially at first, examples and problems on the thin-lens equation are first preceded by graphical ray tracing. It ...
physics
... formed at the least distance of distinct vision. 7. State and prove Prism Formula. 8. A ray of light falls normally on a refracting face of a prism of refractive index (1.5) . Find the angle of the prism if the ray just fails to emerge from the prism. 9. A diver looks into the external worlds from a ...
... formed at the least distance of distinct vision. 7. State and prove Prism Formula. 8. A ray of light falls normally on a refracting face of a prism of refractive index (1.5) . Find the angle of the prism if the ray just fails to emerge from the prism. 9. A diver looks into the external worlds from a ...
PhysicsTutor
... from the top surface of the film with light reflected from the film-glass interface. • The number of phase jumps is the same for recombining beams (air to soap and soap to glass). • Find the optical path length difference between the two beams, phase shift of 2. ...
... from the top surface of the film with light reflected from the film-glass interface. • The number of phase jumps is the same for recombining beams (air to soap and soap to glass). • Find the optical path length difference between the two beams, phase shift of 2. ...
An introduction to Optics
... In optics, refraction is a phenomenon that often occurs when waves travel from a medium with a given refractive index to a medium with another at an oblique angle. At the boundary between the media, the wave's phase velocity is altered, usually causing a change in direction. Its wavelength increases ...
... In optics, refraction is a phenomenon that often occurs when waves travel from a medium with a given refractive index to a medium with another at an oblique angle. At the boundary between the media, the wave's phase velocity is altered, usually causing a change in direction. Its wavelength increases ...
Light Waves
... a.It bends light inward and can create either a virtual or a real image. b.It bends light inward and can only create a real image. c.It bends light outward and can create either a virtual or a real image. d.It bends light outward and can only create a virtual image. ...
... a.It bends light inward and can create either a virtual or a real image. b.It bends light inward and can only create a real image. c.It bends light outward and can create either a virtual or a real image. d.It bends light outward and can only create a virtual image. ...
Light waves Review
... The color that an object appears to be depends on the angle at which visible light is reflected off the object. b) use of additive rather than subtractive colors. c) wavelengths of visible light that reaches your eyes. d) speed with which visible light reaches it. a) ...
... The color that an object appears to be depends on the angle at which visible light is reflected off the object. b) use of additive rather than subtractive colors. c) wavelengths of visible light that reaches your eyes. d) speed with which visible light reaches it. a) ...
Theory - BrainMass
... Ni is the refractive index of the medium the light is leaving, Ai is the incident angle between the light ray and the normal to the meduim to medium interface, Nr is the refractive index of the medium the light is entering, Ar is the refractive angle between the light ray and the normal to the medui ...
... Ni is the refractive index of the medium the light is leaving, Ai is the incident angle between the light ray and the normal to the meduim to medium interface, Nr is the refractive index of the medium the light is entering, Ar is the refractive angle between the light ray and the normal to the medui ...
From a flat mirror, designer light — Harvard School of Engineering
... CONTACT: Caroline Perry, 617-496-1351 Cambridge, Mass. - September 1, 2011 - Exploiting a novel technique called phase discontinuity, researchers at the Harvard School of Engineering and Applied Sciences (SEAS) have induced light rays to behave in a way that defies the centuries-old laws of reflecti ...
... CONTACT: Caroline Perry, 617-496-1351 Cambridge, Mass. - September 1, 2011 - Exploiting a novel technique called phase discontinuity, researchers at the Harvard School of Engineering and Applied Sciences (SEAS) have induced light rays to behave in a way that defies the centuries-old laws of reflecti ...
Snell`s Law
... The rays (directions of propagation) are straight lines perpendicular to the wave fronts The above assumption is valid only when the size of the barrier (or the size of the media) is much larger than the wavelength of light ...
... The rays (directions of propagation) are straight lines perpendicular to the wave fronts The above assumption is valid only when the size of the barrier (or the size of the media) is much larger than the wavelength of light ...
Science Olympiad 2011 Practice Optics C
... 19. List the 7 regions of the electromagnetic spectrum in order from lowest frequency to highest frequency. Label which end of the spectrum has the highest energy, and which has the longest wavelength. 20. What are the two types of photoreceptor cells in the human eye? What is the specific function ...
... 19. List the 7 regions of the electromagnetic spectrum in order from lowest frequency to highest frequency. Label which end of the spectrum has the highest energy, and which has the longest wavelength. 20. What are the two types of photoreceptor cells in the human eye? What is the specific function ...
optimizing combined volume and surface data ray casting
... However, this technique produces two separate images, one for the volumetric part and the other for the geometric objects, and so it does not correctly combine color and opacity data for non-opaque objects. Our approach has not been tested in realtime visualization but a parallel ray casting impleme ...
... However, this technique produces two separate images, one for the volumetric part and the other for the geometric objects, and so it does not correctly combine color and opacity data for non-opaque objects. Our approach has not been tested in realtime visualization but a parallel ray casting impleme ...
Ray tracing (graphics)

In computer graphics, ray tracing is a technique for generating an image by tracing the path of light through pixels in an image plane and simulating the effects of its encounters with virtual objects. The technique is capable of producing a very high degree of visual realism, usually higher than that of typical scanline rendering methods, but at a greater computational cost. This makes ray tracing best suited for applications where the image can be rendered slowly ahead of time, such as in still images and film and television visual effects, and more poorly suited for real-time applications like video games where speed is critical. Ray tracing is capable of simulating a wide variety of optical effects, such as reflection and refraction, scattering, and dispersion phenomena (such as chromatic aberration).