Lipids
... Glucose is an abundant and very important monosaccharide. It contains six carbon atoms, so it is a hexose sugar. Its general formula is C6H12O6. Glucose is the major energy source for most cells. It is highly soluble and is the main form in which carbohydrates are transported around the body of anim ...
... Glucose is an abundant and very important monosaccharide. It contains six carbon atoms, so it is a hexose sugar. Its general formula is C6H12O6. Glucose is the major energy source for most cells. It is highly soluble and is the main form in which carbohydrates are transported around the body of anim ...
Review Keystone Biology Multiple choice
... What would the opposite reaction from the one in the diagram show? a. how enzymes are need to build maltose b. how water is added to break apart maltose c. how water is lost in order to make maltose d. how water is only needed to build molecules and not to break molecules down ...
... What would the opposite reaction from the one in the diagram show? a. how enzymes are need to build maltose b. how water is added to break apart maltose c. how water is lost in order to make maltose d. how water is only needed to build molecules and not to break molecules down ...
Biology Standard 1 (BiologyStandard1)
... 69. If transpiration stopped completely, how would a plant's homeostasis first be affected? A. More carbon dioxide molecules would be taken in by leaves. B. Fewer sugars stored in roots and stems would diffuse into the soil. C. Carbohydrates would no longer be formed. D. Water molecules would not be ...
... 69. If transpiration stopped completely, how would a plant's homeostasis first be affected? A. More carbon dioxide molecules would be taken in by leaves. B. Fewer sugars stored in roots and stems would diffuse into the soil. C. Carbohydrates would no longer be formed. D. Water molecules would not be ...
Advances in affinity purification mass spectrometry of
... (RNP) complexes and their maturation pathways. Analysis of RNA can be performed by hybridization or sequencing-based methods; however, in the cellular environment RNA is associated, often transiently, with RNA-binding proteins (RBPs) forming functional RNP complexes. Technological advances permittin ...
... (RNP) complexes and their maturation pathways. Analysis of RNA can be performed by hybridization or sequencing-based methods; however, in the cellular environment RNA is associated, often transiently, with RNA-binding proteins (RBPs) forming functional RNP complexes. Technological advances permittin ...
Function of Biomolecules Worksheet
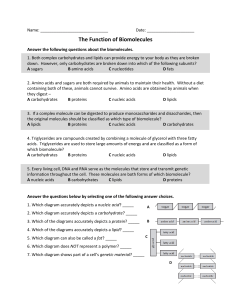
... Answer the following questions about the biomolecules. 1. Both complex carbohydrates and lipids can provide energy to your body as they are broken down. However, only carbohydrates are broken down into ...
... Answer the following questions about the biomolecules. 1. Both complex carbohydrates and lipids can provide energy to your body as they are broken down. However, only carbohydrates are broken down into ...
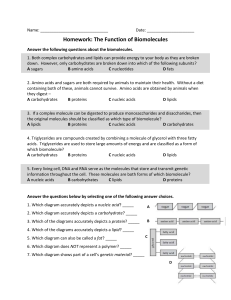
Name: __ Date: Homework: The Function of Biomolecules Answer
... Answer the following questions about the biomolecules. 1. Both complex carbohydrates and lipids can provide energy to your body as they are broken down. However, only carbohydrates are broken down into which of the following subunits? A sugars B amino acids C nucleotides D fats 2. Amino acids and su ...
... Answer the following questions about the biomolecules. 1. Both complex carbohydrates and lipids can provide energy to your body as they are broken down. However, only carbohydrates are broken down into which of the following subunits? A sugars B amino acids C nucleotides D fats 2. Amino acids and su ...
Graph 1: Rabbits Over Time
... To provide energy for all cell processes that require energy – active transport for example. ...
... To provide energy for all cell processes that require energy – active transport for example. ...
Biology Common Syllabus
... Nucleic acids are composed of very long chains of subunits called nucleotides, which contain carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen and phosphorus. The two chief types of nucleic acids are DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) which contains the hereditary information in all living organisms and RNA (ribonucleic ...
... Nucleic acids are composed of very long chains of subunits called nucleotides, which contain carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen and phosphorus. The two chief types of nucleic acids are DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) which contains the hereditary information in all living organisms and RNA (ribonucleic ...
Nutrition/Digestion/Excretion PPT
... water and gases in for photosynthesis; other times the stomata must be closed as protection This is called a feedback mechanism -If it is really hot and dry outside, the stomata will be closed to lower water loss -If it is cooler and humid outside, the stomata will be open to increase water content ...
... water and gases in for photosynthesis; other times the stomata must be closed as protection This is called a feedback mechanism -If it is really hot and dry outside, the stomata will be closed to lower water loss -If it is cooler and humid outside, the stomata will be open to increase water content ...
Enzymes: “Helper” Protein molecules
... Enzymes are not changed by the reaction used only temporarily re-used again for the same reaction with other molecules very little enzyme needed to help in many reactions ...
... Enzymes are not changed by the reaction used only temporarily re-used again for the same reaction with other molecules very little enzyme needed to help in many reactions ...
Chemistry, Bonds, Phospholipids, triglycerides, proteins, ATP
... • Matter exists as either SOLID, LIQUID or GAS. • Solids maintain their volume and their shape at ordinary temperature and pressure. • Liquids have a constant volume but no fixed ...
... • Matter exists as either SOLID, LIQUID or GAS. • Solids maintain their volume and their shape at ordinary temperature and pressure. • Liquids have a constant volume but no fixed ...
Biology Review
... Extremes in pH or temperature can alter the secondary and tertiary bonds of a protein; altered shape means altered function. Explain the lock-and-key model of enzymes and substrates. The substrate fits the enzyme like a lock fits a key; there is an active site where the substrate fits into the enzym ...
... Extremes in pH or temperature can alter the secondary and tertiary bonds of a protein; altered shape means altered function. Explain the lock-and-key model of enzymes and substrates. The substrate fits the enzyme like a lock fits a key; there is an active site where the substrate fits into the enzym ...
1 Chapter 3: Chemistry of Water Polar covalent bonds within water
... living things and often H and O as well. Before, chemists couldn’t synthesize the complex molecules found in living organisms, so they believed that life did not involve physical and chemical laws, a belief called vitalism. Mechanism, which organic chemistry is based on, holds that physical and chem ...
... living things and often H and O as well. Before, chemists couldn’t synthesize the complex molecules found in living organisms, so they believed that life did not involve physical and chemical laws, a belief called vitalism. Mechanism, which organic chemistry is based on, holds that physical and chem ...
Biology 118, Oct. 13, 2016 Exam 1, Version C Name
... 20. Blood pressure is regulated by _____ feedback, so over time (on X-axis) blood pressure (Y-axis) will be closest to line ___ in Fig. A. a. negative – V b. positive - M c. negative – Z d. positive – Z 21. To synthesize insulin, _____ is copied to form a template of ______ that is “translated” into ...
... 20. Blood pressure is regulated by _____ feedback, so over time (on X-axis) blood pressure (Y-axis) will be closest to line ___ in Fig. A. a. negative – V b. positive - M c. negative – Z d. positive – Z 21. To synthesize insulin, _____ is copied to form a template of ______ that is “translated” into ...
biosensori
... A sensor that uses light to detect the effect of a chemical on a biological system. [Kopelman et al.] The small size of the optical fibers allow sensing intracelular intercelular physiological and biological parameter in microenvironment. Two kind of fabrication methods for optical fiber tips; 1) He ...
... A sensor that uses light to detect the effect of a chemical on a biological system. [Kopelman et al.] The small size of the optical fibers allow sensing intracelular intercelular physiological and biological parameter in microenvironment. Two kind of fabrication methods for optical fiber tips; 1) He ...
Key - UCSB CLAS
... secondary ⇒ regular conformations assumed by segments of the protein’s backbone when it folds (in order to maximize H-bonds in the backbone) tertiary ⇒ the 3D structure of the entire protein quaternary ⇒ if a protein has more than one polypeptide chain (aka subunit) the quaternary structure is the w ...
... secondary ⇒ regular conformations assumed by segments of the protein’s backbone when it folds (in order to maximize H-bonds in the backbone) tertiary ⇒ the 3D structure of the entire protein quaternary ⇒ if a protein has more than one polypeptide chain (aka subunit) the quaternary structure is the w ...
Estimating Mineral Weathering Rates in Catskills
... ◘ Basic Cations: Ca, Mg, K, Na ◘ Silica: H4SiO4 ◘ Aluminum: potentially toxic to aquatic biota ...
... ◘ Basic Cations: Ca, Mg, K, Na ◘ Silica: H4SiO4 ◘ Aluminum: potentially toxic to aquatic biota ...
Atomic Structure (Bohr or Planetary Model)
... – lipids (fats) • uncharged (neutral) molecules • Polar molecules include those containing a moderate number of polar covalent bonds (moderate amounts of O and/or N) ...
... – lipids (fats) • uncharged (neutral) molecules • Polar molecules include those containing a moderate number of polar covalent bonds (moderate amounts of O and/or N) ...
Atomic Structure (Bohr or Planetary Model)
... – lipids (fats) • uncharged (neutral) molecules • Polar molecules include those containing a moderate number of polar covalent bonds (moderate amounts of O and/or N) ...
... – lipids (fats) • uncharged (neutral) molecules • Polar molecules include those containing a moderate number of polar covalent bonds (moderate amounts of O and/or N) ...
Chemical Bonding, Carbon style
... If you remember that water is made up of the elements hydrogen and oxygen, then you should be able to remember the three elements in carbohydrates. ...
... If you remember that water is made up of the elements hydrogen and oxygen, then you should be able to remember the three elements in carbohydrates. ...
Glossary - Hodder Education
... clade the branch of a phylogenetic tree containing the set of all organisms descended from a particular common ancestor which is not an ancestor of any non-member of the group cladistics method of classifying living organisms that makes use of lines of descent only (rather than phenotypic similariti ...
... clade the branch of a phylogenetic tree containing the set of all organisms descended from a particular common ancestor which is not an ancestor of any non-member of the group cladistics method of classifying living organisms that makes use of lines of descent only (rather than phenotypic similariti ...
ppt
... Types of Chemical Reactions • Atoms and molecules react to create chemical reactions. • There are thousands of different chemical reactions, where atoms are never lost, just rearranged. ...
... Types of Chemical Reactions • Atoms and molecules react to create chemical reactions. • There are thousands of different chemical reactions, where atoms are never lost, just rearranged. ...
Document
... Answer ALL 43 questions by marking your answers on your scantron. Take your time and understand each question before you answer. Good Luck! Please keep this document when finished. Just return your scantron to me and the page with the bonus question. As you leave I will check to see that you are enr ...
... Answer ALL 43 questions by marking your answers on your scantron. Take your time and understand each question before you answer. Good Luck! Please keep this document when finished. Just return your scantron to me and the page with the bonus question. As you leave I will check to see that you are enr ...
High-throughput screens for fluorescent dye discovery
... for most proteins. If enough is known about a biological pathway, an investigator can readily create antibodies to proteins known to be expressed differently in the cellular compartment, state or cell type of interest. For instance, an antibody to a well-known marker of mitosis, phosphorylated histo ...
... for most proteins. If enough is known about a biological pathway, an investigator can readily create antibodies to proteins known to be expressed differently in the cellular compartment, state or cell type of interest. For instance, an antibody to a well-known marker of mitosis, phosphorylated histo ...